Abstract
In today's world, the internet has become a hub for communication and information exchange. People from all over the world can connect and share their ideas, opinions, and experiences. However, with the abundance of information, it can be difficult for individuals to find a platform where they can connect with like-minded individuals and engage in meaningful discussions. For instance, a passionate environmentalist might struggle to find a space where they can connect with others who share their concerns about climate change and renewable
To address this issue, the following report outlines the design and implementation of a platform that aims to connect people with similar interests, allowing them to carry out relevant discussions. The platform provides a space for users to form communities around common topics or themes, building a sense of community among them and fostering engagement and participation on the platform. This could lead to more informed and thoughtful conversations about important topics, such as mental health, political activism, or scientific
Project Specification
Authentication and Account Management
The system has several key user authentication and account management features designed to ensure that users have a seamless and secure experience:
- Users can sign up using email and password
- Users can sign up using third-party authentication providers such as Google and GitHub
- Users can log in using email and password
- Users can log out
- Users can reset their password
- Users can modify their profiles (profile image and username)
Community
The system has several key community management features designed to promote engagement and collaboration among users:
- Users can create communities (different types)
- Users can subscribe and unsubscribe to and from a community
- Admins can change or delete the community logo
- Admins can change community visibility
- Users can view and navigate to all public and restricted communities
Posts
The system has several key features designed to make it easy for users to create and view posts within communities:
- Users can create a post in a specific community with an optional image
- Users can view all posts from a community
- Users can open post to interact with them
- Users can view posts from subscribed communities
- Users can delete a post they have created
- Users can vote on a post
- Users can share a post
Comments
The web application has several key features designed to make it easy for users to engage with others by creating and viewing comments:
- Users can create a comment to reply to a post
- Users can view comments in a post
- Users can delete a comment they created
General
The system has several general features to make the site user-friendly and accessible:
- Logged-in users can view posts from various communities they are subscribed to in the home feed
- Logged-out users can view posts from all communities in order of likes
- System UI is responsive, hence it can be used on smartphones, tablets, or computers
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Problems & Objectives
One of the core values of the platform is to facilitate the sharing of knowledge and information [1][2]. Users can ask for help and receive assistance in solving issues, as others who have already experienced it can provide answers and share their expertise on various topics [1]. These discussions can be neatly collected in their respective communities, making it easier for users to find the information they need. For example, someone who needs help with a maths problem can ask in a Maths community, where mathematicians can provide help
Another key aspect of the platform is learning. Users can learn about different topics or subjects they are interested in from others, or inform others about their expertise [1][3]. The platform provides a way for users to learn from one another, collecting learning material and discussions in its own community [1][3]. For example, someone who needs help with development can ask for help in a development-related
The platform also facilitates the sharing of knowledge, resources, and ideas with other users, providing a way for users to gain new insights and perspectives on various topics [1][3]. Additionally, the platform allows for discussions to take place regardless of a user's background, helping everyone to get involved and learn from the discussions they take part in [4]. Participating in discussions is far more engaging than just reading about
In today's society, it is not uncommon for individuals to face personal attacks for their opinions. To mitigate this, the platform allows users to express their opinions without fear of being attacked, as personal information is not allowed on the platform [4]. People should not be personally attacked or even worse, physically attacked for their views. For example, if someone has strong political views which other people do not agree with, the user should not be attacked on the platform or be tracked
The platform allows users to create groups of private communities where only specific trusted people can join. This allows users to discuss certain topics only with people they trust, providing a secure space for private discussions
Finally, the platform's open-source nature promotes transparency between the users and the platform [5]. This means that users can be assured that the platform operates ethically and that there are no hidden agendas or unethical practices [5]. Unlike many social media platforms that prioritize maximizing screen time at the expense of the user or invade users' privacy [6], this platform is designed to foster a sense of community and facilitate meaningful discussions. The open-source nature of the platform also enables users to provide feedback and contribute to the platform's development themselves [5]. This reflects the overall purpose of the platform, as the discussions are meant to be open, and the platform promotes collaboration. Open-source projects are inherently collaborative, and the platform aims to bring people together to learn from one another and work on projects together
1.2 Aims & Goals of the Project
The project aims to create a platform that facilitates discussions and knowledge sharing between like-minded people via communities that encapsulate specific topics [1]. The importance of this goal lies in enabling users to find relevant and focused information, fostering productive exchanges and helping users learn from each other [1]. By providing a space where users can ask for help and solutions from other users in specific communities, the platform makes it easier to connect with people who share similar interests and expertise
The platform also aims to make learning more accessible by allowing people to join communities of like-minded individuals to learn about topics they are interested in but have minimal background knowledge about [4]. This goal is important because it encourages lifelong learning, personal development, and skill-building [2]. For instance, someone who is trying to learn about programming can join a programming community to gain a better understanding of the field
Another aim of the platform is to create a safe environment for users to express their opinions without fear of being personally attacked or harassed [4]. This goal is crucial as it promotes a healthy and respectful online community, enabling users to offer controversial opinions in debate-heavy communities without fear of personal attacks [4]. By not allowing personal information, such as names, dates of birth, and addresses on the platform, users can confidently share their ideas and participate in intense discussions
Additionally, the platform allows groups of friends to join small private communities where they can carry out discussions [3]. This feature is important as it creates a secure space for private conversations, catering to users' needs for privacy and trust [4]. These private communities can serve various purposes, such as revision groups, hanging out places, or more organized group chats, and further enhance the platform's value as a versatile tool for different types of interactions
For instance, a platform user interested in gardening could join a gardening community, where they could ask questions about plant care, share tips on growing specific plants, and discuss sustainable gardening practices. Users could also join communities related to career fields they aspire to enter, such as data science, to network with professionals and learn from their
1.3 Rationale
and discover information [1]. This project is built around the idea of community and encourages users to participate in meaningful conversations and discussions [3]. The platform allows users to post content and vote on it, allowing the community to decide what content is most valuable [3]. This helps create an environment where people can learn from one another, share their opinions, and get feedback from other users [3].
Communities help to organize content and make it easier for users to find the topics they are interested in [3]. Communities also help foster a sense of belonging and allow users to connect with others who share similar interests [3]. Communities are also designed to provide a safe, welcoming environment for users to engage in meaningful conversations and discussions [3]. By having a variety of communities, the project creates a platform where users can explore new topics and interests, find like-minded people, and have meaningful conversations [3]. Without communities, topics would be very messy and hard to find, as more people are in a bigger pool, it would be harder to find like-minded people, there would also be much more irrelevant content, and it would overall provide a worse user/social experience [2].
manner [4]. It should encourage people to learn about different topics and share opinions with other people who are passionate about their interests [4]. This platform can also be used by friends and colleagues as a useful tool, for example as study groups which would allow for seamless collaboration, learning, and growth [4]. People must feel safe on this platform [4].
manner. This is crucial for ensuring that users feel comfortable and confident when using the platform. A safe and organized environment will encourage users to engage in discussions, share their opinions, and learn about different topics. This, in turn, will lead to a thriving community
someone to be identified individually [4]. This facilitates controversial discussions as people can discuss topics without the fear of being abused [4]. Without having access to personal information such as names, date of birth, home address, etc, it is almost impossible to determine who the user is. This makes the platform more private.
eliminates the fear of having irrelevant discussions with outsiders [2]. Additionally, it also allows for participating in more private or more controversial discussions which should not be known by outsiders [2]. Furthermore, it can also facilitate learning as users can potentially create revision groups that are organized by posts [1]; for example, each post can be a question from a revision
transparently [5]. This allows users to contribute to the development of the platform and offer feedback, ensuring that the platform evolves to meet the needs of the community it serves [5]. This collaborative approach to platform development reflects the overall purpose of the platform, which is to bring people together to learn from one another and work on projects together [5].
a community dedicated to discussing literature [2]. In this community, users can discuss specific books, authors, and genres, as well as share their favourite quotes, analyses, and interpretations [2]. By having a dedicated space for literature enthusiasts, it would be easier for users to find relevant content and engage with others who share their passion .
Potential challenges and limitations of the platform could include managing the influx of information and ensuring the quality of content shared by users. As the platform grows, it may become difficult to maintain a sense of community, and users may feel overwhelmed by the sheer volume of content. Additionally, moderation and community management would be crucial to prevent the spread of misinformation and maintain a respectful environment. This could require significant resources and collaboration between users and platform
Another potential limitation could be related to the privacy of users. While the platform aims to protect user privacy by not storing personal information, ensuring complete anonymity may be challenging. Users may inadvertently reveal personal details through their posts or interactions, which could lead to privacy
Moreover, the open-source nature of the platform may present challenges in terms of security and maintenance [7]. Ensuring that the platform remains secure while being open to contributions from the community may require continuous monitoring and evaluation of the codebase to prevent vulnerabilities or malicious activities
By considering these potential challenges and limitations, the platform can be better equipped to address and overcome these issues, ensuring a more successful implementation and user
1.4 Survey of Related Systems
This section is an analysis of existing online platforms that are similar in nature to the proposed project. In this section, the similarities and differences between the proposed project and other popular online platforms such as Quora and Discord are compared and evaluated. The aim is to understand the strengths and weaknesses of these existing platforms and to identify areas where the proposed project can improve or differentiate itself. By conducting a thorough analysis of related systems, the proposed project can learn from the successes and failures of existing platforms and create a unique and effective solution that meets the needs of its target
1.4.1 Quora
Quora is a platform where people can ask and answer questions on a variety of topics [8]. It aims to provide high-quality and relevant answers from experts and enthusiasts [8]. Users can follow topics, people, or questions that interest them and see personalised content on their feeds [8]. Quora also allows users to upvote, comment, share, and edit answers
Quora and this project are both online forum sites that allow users to discuss related topics, ask and answer questions, and interact with other users. However, there are several differences between the two websites that set them apart from each
Differences
One of the main differences between the two websites is the user interface. Quora has a more cluttered user interface with several unnecessary features such as 3D avatars and stickers, which can create distractions for users [9]. In contrast, this project has a simpler user interface that is more focused and user-friendly, making it easier for users to navigate and find relevant content. This project also has a more specific target audience, as it is designed for a specific niche or community, while Quora is more general and open to a wider range of topics and discussions
Another difference between the two websites is the privacy settings. Quora provides more information about users such as their full name, when they joined the service, what spaces they are subscribed to, site usage, etc [10]. On the other hand, this project does not include personally identifiable information, and users can only view the username and profile picture of the user, making it harder to track users. This project also allows for greater customization of communities, with the ability to create private or restricted communities, while Quora does not have this feature
Another difference between Quora and this project is the ability to modify posts or comments [8]. Unlike Quora, this project does not allow users to edit their posts or comments after they have been published. This is because there are ethical considerations around editing content after it has been published, as it can lead to a lack of transparency and accountability for what has been said or written [11]. Allowing users to modify their posts or comments can also create confusion for other users who may have read the original content and may not be aware of any changes that have been made
This project does not have moderation yet, while Quora has a moderation system where moderators can review and remove content that violates community guidelines. Additionally, this project will be open source, allowing for more transparency between users and the platform and allowing the community to improve and collaborate on it, while Quora is not open
Similarities
Both Quora and this project have a voting system where users can upvote or downvote posts, which can help determine the relevance and popularity of a post
In terms of functionality, both Quora and this project allow users to post multimedia content such as images and have a search function where users can search for specific topics or posts [8]. However, this project does not allow messaging other users directly as it is not a messaging platform, while Quora allows users to follow other
Overall, while Quora and this project are both online forum sites for discussion and question-and-answer platforms, they have several differences in terms of the user interface, privacy settings, functionality, and target audience. This project is more focused, user-friendly, and customizable, while Quora is more general, cluttered, and has a wider range of topics and
1.4.2 Discord
Discord is a platform that allows users to communicate with each other through text, voice and video chat [12]. Users can create or join servers that are dedicated to specific topics, interests or communities [12]. Discord also offers various features such as bots, emojis, stickers and integrations with other applications [12]. Discord is popular among gamers, streamers, content creators and online learners
Discord and this project are very different types of platforms. Discord is a communication platform that allows users to communicate with each other through text, voice, and video chat, while this project is a forum site that allows users to discuss related topics, ask and answer questions, and interact with other
Similarities
One similarity between the two platforms is the communities feature in this project, which is very similar to servers in Discord. Both allow users to create or join communities that are dedicated to specific topics, interests, or communities [12]. This allows users to connect with others who share similar interests and engage in discussions and interactions
Another similarity between the two platforms is the comments within posts in this project, which are similar to chats within channels in Discord. Both allow users to participate in discussions and exchange information with others [12]. However, this project does not have nested comments, similar to how there are no nested messages in Discord
Differences
Despite these similarities, there are several differences between Discord and this project. Discord includes chat features such as emojis, stickers, and integrations with other applications, while this project does not include chat features as it is not a chatting platform [12]. Discord also includes calling features, allowing users to make voice and video calls with each other [12], while this project does not include calling features as it is not a calling platform. Additionally, Discord includes automated bots, which can perform various tasks, while this project does not include
Another difference between the two platforms is the categorization of content. Discord has subcategories for channels, which are groups of channels, while this project does not have subcategories for tags
1.5 User Stories
User stories are short descriptions of a feature or a functionality from the perspective of an end user. User stories are important because they help to define the value and scope of a product, communicate the needs and expectations of the users, and prioritize the development tasks based on their relevance and
These user stories describe the functionalities of the end system. Almost all the functionalities described here have been implemented (see Features of the End System section). They are each assigned a priority which helps develop the most important functionality first:
- Most Important
- Medium Importance
- Least Important /Optional
General
- As a user, I want to be able to participate in discussions without being distracted by side features (2)
- As a user, I want to be able to participate in discussions openly without being attacked (1)
- As a user, I want to be able to use the system in any platform (1)
- As a user, I want to be able to modify my account to create a personalised profile.(3)
Authentication
- As a user, I want to be able to create an account and log into the site to interact with my favourite communities (1)
- As a user, I want to be able to create an account quickly and easily to participate in discussions with minimal friction
Communities
- As a user, I want to be able to create a community to be able to discuss about topics I am interested in with other people given a community does not already exist (1)
- As a user, I want to be able to find a community to be able to join in discussions I am interested in (1)
- As a user, I want to be able to subscribe to a community to be able to discuss about topics I am interested in with other people given a community already exists (1)
- As a user, I would like to be able to unsubscribe to a community if I am no longer interested in taking part in discussions (1)
- As a user, I want to be able to create private communities where only people I decide can join (2)
- As a creator of a community, I want to be able to change the logo of the community to make it more appropriate a convey the purpose of the community (3)
- As a creator of a community, I want to be able to change the visibility of the community if I no longer want the discussion to be available for everyone or if I want a public community discussion to become public.(3)
Posts
- As a user, I want to be able to create a post to discuss a topic with other people in the community (1)
- As a user, I want to be able to add images to posts to convey information that would be difficult to convey with just text.(1)
- As a user, I want to be able to delete a post if I think this discussion should not longer take place (2)
- As a user, I want to be able to delete a post if I feel like it is irrelevant (2)
- As a user, I would like to be able to like or dislike a post based on the relevance or usefulness of a post (1)
- As a user, I would like to be able to save certain posts in case I need to refer back in the future (3)
- As a user, I would like to tag posts so that they can be found more easily.(3)
- As a user, I would like to share a post to invite other people into the discussion.(1)
Comments
- As a user, I want to be able to reply to posts to offer my views on a specific post and start a discussion (1)
- As a user, I want to be able to reply to other comments to offer views on a comment made for a post (2)
- As a user, I want to be able to delete a post if I no longer want to be part of the discussion (2)
Profile Management
- As a user, I would like to edit some of my profile information such as username or password in order to keep my account secure or if I no longer like the current username (3)
Chapter 2: Technologies (Web Frameworks)
2.1 Back-End Technologies
The backend of a web app is the part that runs on a server and handles the logic, data storage and communication of the app [13]. The backend is responsible for processing user requests, interacting with databases and APIs, and sending responses to the frontend (the part that runs on a browser and displays the user interface)[13]. The backend is important because it enables complex functionality, security and scalability of a web app [13]. Without a backend, a web app would be limited to static content and simple interactions that do not require any data manipulation or verification
2.1.1 Current System based on Firebase
Introduction to Firebase
Firebase is a Backend-as-a-Service (BaaS) platform that provides developers with a suite of tools for building and managing web and mobile applications [14][23]. Firebase offers a range of services including real-time databases, authentication, hosting, storage, and more [15]. These services can be integrated into web or mobile applications with just a few lines of code, allowing developers to focus on building the core functionality of their applications rather than worrying about managing the backend and making sure it is secure and reliable [15]. Firebase is known for its ease of use, scalability, and real-time capabilities, making it a popular choice among developers for building and deploying dynamic and fast-paced applications
Services and Tools Offered by Firebase
Firebase offers a suite of services that can be used to build, manage and scale applications. Some of the key features of Firebase include real-time database, authentication, hosting, cloud functions, storage, and machine learning [16]. The real-time database provides a way to store and retrieve data in real time, which is ideal for real-time applications such as chat apps and multiplayer games [16]. The authentication service provides a way to authenticate users using email, phone number or social media logins [16]. The hosting service provides a way to host and serve web content [16]. The cloud functions service provides a way to run backend code in response to events triggered by Firebase features and HTTPS requests [16]. The storage service provides a way to store and serve files such as images, videos and audio. The machine learning service provides a way to build and train machine learning models [16]. With these services and tools, Firebase provides a complete solution for building and deploying web and mobile applications
Use in the Project
The current system uses Firebase for its back-end services. Firebase is easy to start with as it provides many tools such as authentication, database, cloud functions, etc. as mentioned before [16][23]. This allows for faster development and is well-tested and proven, as many developers use it [15][23]. Additionally, these tools also for faster development as less functionality has to be implemented as less rigorous testing is required [17][23]. Furthermore, as this is a service, there is less maintenance as this is handled by the provider in this case Google
However, it is a paid service for large applications and the costs add up rapidly [18]. Additionally, the database (Firestore) is non-relational, which may not be suitable for all applications, especially for highly relational data which was the case for this application [18][19]. Firebase may also be less flexible as it is not custom-built for the exact specifications of the system [18]. Despite these limitations, Firebase is widely used, and there is a large community of developers with many
resources and tools available, such as "react-firebase-hooks," that can make development faster and to a higher standard
2.1.2 Previous System based on Flask (Python)
Introduction to Flask
Flask is a micro web framework written in Python that provides a simple and easy-to-use platform for web development [20]. It is a minimalistic framework that provides only the essential tools required to build a web application, making it a great choice for small to medium-sized projects [20]. Flask is designed to be flexible, allowing developers to easily extend its functionality by adding additional packages or plugins as needed [20]. Additionally, Flask is lightweight and fast, making it a great choice for building high-performance web applications [20]. Due to its ease of use and versatility, Flask has become a popular choice for building web applications in Python, and is widely used in the web development community
Services and Tools Offered by Flask
There are several tools and services that Flask provides to assist with development. One of these tools is routing, which allows you to define and manage the URLs of your application in a simple and flexible way [20]. Another tool is templating, which enables you to create and render dynamic HTML pages using various templating engines, such as Jinja2[20]. Flask also supports database integration, which lets you connect to and interact with different types of databases, such as SQL databases and NoSQL databases [20]. Moreover, Flask has a middleware architecture that allows you to add custom logic to your application at different stages of the request-response cycle [20]. Flask also has a built-in debugging mechanism that helps you troubleshoot issues with your application during development [20]. Furthermore, Flask has a large and active community of developers who have created many extensions that add additional functionality to the framework [20]. These extensions can be easily installed and integrated into your application to provide additional features and tools
However, it does not provide certain built-in tools and services that are commonly found in full-stack frameworks. These include an ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) to interact with databases, and an administration panel for managing the backend [21]. Flask relies on third-party libraries for these features, which can make it more flexible but also more complex to set up [21]. Additionally, Flask does not have built-in security features, such as protection against cross-site scripting (XSS) or cross-site request forgery (CSRF) attacks, so these must be implemented manually or with additional libraries [21]. Furthermore, Flask is not designed to handle large amounts of traffic or complex deployment scenarios, so it may not be the best choice for large-scale applications
Use in the Project
The previous system used Flask, which allowed for using the same back-end for multiple interfaces [22]. Flask supports the use of a relational databases, which is more suitable for modelling the application. It offers more options for deployment and scalability as it is possible to choose different platforms depending on price and availability, or even build custom servers [22]. Flask also allows for more flexibility and can be designed to the exact specification of the system
However, everything would have to be built manually, such as authentication, managing data in the database, and managing security [22][24]. This could also lead to a less stable system that requires more rigorous testing to ensure quality, reliability and security
2.1.3 Supabase as an Alternative to Firebase
Introduction to Supabase
Supabase is a relatively new backend as a service that provides developers with an alternative to Firebase [25][26]. Like Firebase, Supabase offers a set of tools and services that make it easy for developers to build and deploy web applications without having to worry about setting up and maintaining a custom backend [25][26]. Supabase provides a number of features and benefits that are similar to Firebase, but with a focus on open-source and fully customizable options [25][26]. This allows developers to have more control over their backend while still taking advantage of the benefits of using a backend as a service
Services and Tools Offered by Supabase
Supabase offers a range of services and tools (similar to Firebase) that are designed to simplify and streamline the backend development process [25][26]. Some of the key services it offers include a real-time database, authentication, file storage, and APIs. The real-time database provides a cloud-based solution for storing and managing data, making it easy to build and scale applications with real-time data syncing and updates [25][26]. The authentication service offers a secure and flexible solution for managing user authentication, with support for passwordless authentication and multi-factor authentication (which are paid in Firebase), it also offers more third-party providers compared to Firebase [25][26]. The file storage service provides a secure and scalable solution for storing and managing files, while the APIs allow developers to easily create and manage APIs for their applications [25][26]. In addition to these services, Supabase also offers a range of tools for managing and deploying applications, including a CLI, an API playground, and a dashboard for managing and monitoring applications [25][26]. With its range of services and tools, Supabase provides a comprehensive and flexible solution for building, deploying, and managing applications in the cloud
Comparison to Firebase
Supabase offers a number of services that are not available on Firebase, making it a more comprehensive backend as a service solution [25][26]. One of the key features is the advanced SQL interface, which allows developers to query and manipulate data stored in its PostgreSQL databases using SQL [25][26]. This is a major difference from Firebase, which only provides a NoSQL interface. Supabase also offers built-in user authentication, allowing users to log in with email and password or social logins like Google and GitHub [25][26]. This is more extensive than the authentication provided by Firebase [25][26]. Additionally, Supabase provides a way to dynamically create APIs using SQL, making it easier for developers to expose data stored in their databases to other systems [25][26]. This is not available on Firebase. Supabase also allows developers to use custom domains for their APIs, making it easier to use their APIs in production. This feature is not offered by Firebase [25][26]. Lastly, Supabase provides a collaborative SQL editor that allows multiple users to work on the same query at the same time, making it easier to work with team members [25][26]. This feature is not available on Firebase
Firebase offers a number of services that are not available on Supabase, providing a wider range of tools for developers. Some of these services include Remote Config, which allows developers to change the behavior and appearance of their app without having to release a new version, Dynamic Links, which create deep links that work across multiple platforms, and App Indexing, which makes it easier for users to find and launch an app from Google Search results [25][26]. Additionally, Firebase provides Cloud Messaging, a free service that allows developers to send notifications and messages to their users, and In-App Messaging, which allows developers to send targeted messages to users while they are actively using the app [25][26]. Finally, Firebase also provides a built-in integration with Google Analytics, providing valuable insights into user interactions with the app
How it Could be Used in this Project
Supabase has many of the advantages of Firebase and Flask, such as being a backend as a service with tools such as authentication, database, and edge functions included. It is widely used and proven, ensuring a certain level of stability, security, and quality [23]. Unlike Firebase, it uses a relational database based on Postgres, which is more suitable for modelling the application
[25][26]. Supabase is a newer service and has only recently become viable for large production applications. The community is not as large as Firebase, so there are fewer resources and tools available, such as hooks for React [25][26]. Supabase offers more flexible deployment and scalability options as it provides a Docker image, allowing for choosing any cloud provider and not being locked into a specific provider like Firebase [25][26]. This could also allow for packaging the entire application in a Docker image
2.2 Front-End Technologies
The front end of a website is the part that users can see and interact with on their browsers [27]. It includes elements such as text, images, buttons, menus, forms, and animations [27]. The front end is also called the client-side because it runs on the user's device [27]. It is important to make the front-end well designed, engaging and accessible as it is what users directly interact with
2.2.1 React Library
React is a popular JavaScript library for building user interfaces and has been widely adopted by developers for building web and mobile applications [28]. React allows developers to create reusable UI components and manage the state of their applications, making it easier to build complex and dynamic user interfaces [29]. React uses a virtual DOM (Document Object Model) to efficiently update the UI and optimize performance [29]. This makes React a fast and reliable option for building high-performance applications
For this project, both the first prototype and the current system use React. Both also use React component libraries for faster and more agile
2.2.2 Component Libraries for Both Systems
React component libraries are pre-built and pre-styled UI components that can be easily imported and used in React projects [30]. These libraries provide a set of components with consistent design, behavior, and functionality, making it easier for developers to build user interfaces and ensure consistency across their applications [30]. React component libraries are a great way to speed up development and reduce the amount of time spent on creating and styling individual components. They also help to maintain a consistent design and user experience, making it easier for users to navigate and understand the application
As mentioned before, both the current system and the first prototype use React and components libraries for faster development and well-tested styling that adheres to accessibility guidelines [30]. This means that high-level components do not have to be created from scratch and custom CSS does not have to be developed and thoroughly tested [31]. However, the use of component libraries makes it less flexible, making it harder to implement more complex UI designs that were not added to the library
Chakra UI
Chakra UI has proven to be easier to use compared to Material UI. It has a smaller library of components, but this has not been a problem in the current system. Chakra UI is also more flexible in terms of using custom designs, as it does not follow a set design standard like Material UI but rather allows the developer to build from what is provided. Additionally, Chakra UI provides a theme object that changes the theme of the entire app at once, making it easier to manage the overall design and reducing the risk of
Material UI
Material UI, on the other hand, has a larger library of components but this has not been an issue as the components provided by Chakra UI were adequate [32]. Material UI is also much older meaning that there are more resources online but this has not been a major advantage as Chakra UI is also well documented and despite its short existence, it has managed to gain a lot of users contributing to its resources online [32]. However, it is harder to learn and less flexible in terms of using custom designs [32]. Material UI follows a set design standard inspired by Google, which may not be suitable for every project making it less flexible than Chakra UI [32]. Material UI also provides a theme object, but it is not as simple to use and requires more configuration to work with different styling solutions
Alternative Component Libraries
The developer considered several other less popular or less flexible component libraries for React, including Ulkit and Blueprint [33]. Ulkit was found to be very simple and fast, but it only had 30 components, making it less viable for complex applications like this project [33]. Blueprint, on the other hand, was mainly used in data visualization, which was not the main focus of this application
2.2.3 Next.JS Compared to Regular React
React has many weaknesses which make it unsuitable for large complex projects such as this one. One of the main weaknesses of React is its lack of structure, as it allows developers to write code in any way they want, which can lead to a cluttered codebase and make it harder to maintain and scale the project in the future [34]. React is also not a full-fledged framework and requires additional libraries and tools to handle tasks such as routing, state management, and server-side rendering [34]. These additional tools can lead to a steep learning curve for new developers and can make the development process more complex [34]. Furthermore, React does not have a built-in solution for SEO optimization, which can make it difficult for search engines to crawl and index the content of a React-based website. This makes using React very difficult for the first prototype
Next.JS on the other hand, eliminates all the issues and adds missing functionalities to React [34]. It is a popular and widely used JavaScript framework for building server-side rendered (SSR) and static web applications [34]. It is built on top of React and provides a seamless and simple way to build and deploy fast, reliable and scalable web applications [34]. Next.JS provides a set of built-in features such as automatic code splitting, optimized performance, and easy-to-use APIs for server-side rendering and data fetching, making it a popular choice for web developers [34]. Additionally, Next.JS also supports static exporting, allowing developers to generate static HTML files that can be served directly from a CDN, resulting in faster page load times and improved performance
For these reasons, Next.JS was chosen to be used for the final system after running into roadblocks using regular React for the first project. It has provided a set standard forcing consistency which would allow developers to collaborate and contribute to this project in the future [34]. On the first prototype, the use of regular React was a hindrance and slowed down development as a lot of time was taken up by configurations and adding missing functionalities to the library by adding other libraries [34]. The lack of a standard in the project structure would also make it more difficult for developers to contribute to the project in the future
2.2.4 State Management
State
In React, state is an updatable structure (observable object) that is used to contain data or information about the component [35]. State is used by React to control how a component behaves depending on its current state [35]. This state changes when certain events take place or by specific user interactions [35]. Once the state changes due to the event, the component would observe this and re-render
Because state is dynamic, a component can keep track of changing information between renders, thereby keeping it dynamic and interactive [35]. This is what allows the site to be interactive. For example, a counter component can use state to store and update the current count value in the user interface without refreshing the
State Management
State management is the process of handling state changes in a React application [36]. State management involves creating, updating, and accessing the state object in a component [36]. State management also involves passing state data to other components as props [36]. For example, a parent component can pass its state data to a child component as a prop. This allows the state of one component to change the behaviour of children if necessary
The purpose of state management is to make the application consistent, predictable, and easy to debug [37]. State management helps to avoid unnecessary re-rendering of components and ensures that the UI reflects the latest state data [37]. State management also helps to organize and modularize the code by separating concerns and responsibilities among components [37]. Furthermore, using state a manager helps avoid fetching data from the backend caching the data locally and reusing it across components
React has a built-in tool for managing the state called React Context API [36]. This is not suitable for large projects for various reasons [38]. One of the reasons is that it is cumbersome to use when there are multiple pieces of state that need to be shared across different components [38]. Multiple context providers and consumers need to be created, which can result in a lot of boilerplate code and nested components, and makes it difficult to manage the state [38]. Another reason is that it does not support derived or computed state that can depend on other state or external sources requiring additional libraries or custom logic to achieve this functionality [38]. Finally, it can cause unnecessary re-rendering of components that consume the context, even if they don't use the part of the state that changed
State Management Tools
A state manager is a tool or library that helps with state management in a React application [37]. A state manager provides features such as global state, actions, reducers, selectors, middleware, etc. that simplify and optimize state management [37]. For example, Redux is a popular state manager for React that implements the Flux architecture [37]. The main reason to use a state manager is to handle complex and large-scale applications that have many components that share and manipulate state data [37]. A state manager can help with performance optimization by avoiding unnecessary re-rendering of components [37]. A state manager can also help with code readability and maintainability by enforcing best practices and patterns for state management
Comparing Recoil to the Built-In React Context API
For this project, Recoil is the state management tool that was used. It provides many advantages over the Context API built into React [40]. Recoil uses atoms and selectors, which are fine-grained units of state that can be subscribed to individually, this prevents unnecessary re-rendering from components that may be related to a state [40]. Recoil provides one context provider (atom or selector) which can be accessed from any component, this eliminates the need to create multiple context providers [40]. Finally, Recoil supports derived state with selectors, which can also handle asynchronous operations and error handling unlike the Context API
Alternative State Management Tools
There are several state management solutions available, each with its own unique features and
Redux is one of the most popular state management solutions for React [41]. It provides a predictable and centralized state management system that allows developers to manage the state of their applications in a structured way [41]. However, Redux can be difficult to understand and implement, especially for new React developers [41]. Additionally, it can lead to verbose and complex code, making it harder to maintain and debug
Jotai is a relatively new state management solution that provides a simpler and more intuitive approach to state management [41]. Unlike Redux, Jotai does not require developers to write a lot of boilerplate code, making it easier to implement and maintain [41]. However, it does not provide the same level of control and flexibility as other state management solutions
Rematch is another popular state management solution for React [41]. It is based on Redux and provides a more elegant and developer-friendly API for state management [41]. Rematch also provides a simpler and more intuitive approach to state management, making it easier to use and maintain than Redux [41]. However, it may not be suitable for complex state management scenarios
Zustand is another minimalistic state management solution that is easy to use and implement [41]. It provides a simple and intuitive API for state management, making it a good choice for small-scale React applications [41]. However, it may not be suitable for large-scale and complex applications
Recoil was chosen for this project because it provides a unique approach to state management that combines the best features of other state management solutions [41]. Recoil provides a simple and intuitive API, like Jotai and Zustand, while also providing the control and flexibility of Redux and Rematch [41]. Additionally, Recoil is built and maintained by Facebook, ensuring that it is a robust and well-supported state management solution
In conclusion, the choice of state management solution depends on the specific requirements of the project. Recoil was chosen for this project because it provided a balanced approach to state management, combining the best features of other popular state management
2.2.5 Alternative JavaScript UI Libraries and Frameworks
When it comes to alternative UI libraries and frameworks to React, there are several options to
One such alternative is Svelte [42]. Although it is relatively newer and less used compared to React, Svelte is a full-stack framework that includes features such as routing and client-side functionality, making it instantly usable with minimal configurations [42][43]. Full-stack frameworks like Next.JS help to build these features on top of React [42][43]. Svelte is easier to learn as it is better designed and uses a structure similar to HTML instead of JSX [42]. The use of component libraries also makes React very easy to use [42][43]. Additionally, Svelte is faster than React as it compiles to JavaScript without a virtual DOM or runtime libraries
Another framework that could have been used is Solid [44]. It is faster than React and includes features such as client-side functionality, for example, handling data storage [44]. Additionally, Solid is more beginner-friendly as it uses regular JavaScript or TypeScript instead of JSX [44]. However, most of these issues
Vue is another alternative that is simpler to use compared to JSX, but it uses its own less standardized structure [45]. However, it is not suitable for large projects as 2-way data binding makes data management harder
Angular is an MVC framework designed for efficient design of the UI [46]. It is more structured and stricter compared to React, enforcing a consistent structure and coding style, making it easier for collaboration with larger teams [46]. Angular has built-in features such as routing, proper state management, and form validation, as it is a full-stack framework [46]. However, it also has a steeper learning curve and is more complex compared to other libraries and frameworks due to its strict syntax, dependency injection, and directives
2.3 Database
A database is a tool for collecting and organizing information that can be stored electronically in a computer system [47]. A database is usually controlled by a database management system (DBMS) that allows users to create, update, delete, and query data [47]. A database can store information about people, products, orders, or anything else related to a web application [47]. A web application uses a database to store and retrieve data that is needed for its functionality [47]. For example, a web application can use a database to store user accounts, preferences, orders, inventory, etc.[47]. A web application can also use a database to perform calculations, generate reports, and display dynamic content on web pages. A web application connects to a database using various methods such as connection strings, drivers, APIs, or frameworks
2.3.1 Relational Database used on First Prototype
A relational database (SQL) is a type of database that stores data in tables, which consist of rows and columns [48]. Each row represents a record of data, and each column represents a field or attribute of data [48]. A relational database uses a programming language called SQL (Structured Query Language) to create, manipulate, and query the data in the tables [48]. SQL is widely used for web application development and data analysis
A relational database is used because it allows users to easily access and manipulate data based on logical relationships between tables [48]. For example, a user can join two tables that share a common column (such as customer ID) and retrieve information from both tables at once. A relational database also ensures data integrity and consistency by enforcing rules such as primary keys, foreign keys, and constraints
Advantages
There are many benefits of using a relational database given they are normalised. Relational databases are more robust as they have higher data integrity (overall completeness, accuracy and consistency of data) insuring the data is valid and consistent improving its reliability [48][49][50]. It also reduces data redundancies by eliminating all data repetitions improving consistency [48][49][50]. This consistency reduces errors where data does not match up or it is not found [48][49][50]. Relational databases are extremely efficient at modelling relationships between objects making them ideal for this type of project
Disadvantages
However, there are many disadvantages that must be considered when using a relational database. The initial cost is higher as they must be normalised to insure the benefits discussed above [49][50]. relational databases are also less flexible as modifying the schema would require normalising the database again [49][50]. Furthermore, fetching data from multiple tables requires joining the table which has a negative effect on performance [49][50]. Finally, they are more difficult to scale horizontally as the database cannot easily be split into multiple smaller databases and stored in separate servers
Use in the Project
As mentioned before, the first prototype of the project used a relational database based on MySQL. This is because relational databases are highly efficient at modelling the highly relational data in this project [50]. However, designing the database schema was time consuming as it required normalising the database as shown in the Relational Database (SQL) section [50]. Additionally, as this was an agile project, the database schema changed often requiring normalisation to be carried out multiple times. This rigid schema made it difficult to change the functionality of the project. Refer to Relational Database (SQL) to view the database
2.3.2 Non-Relational Database using on Final System
A non-relational database is a database that does not use the tabular schema of rows and columns found in most traditional database systems [51]. Instead, non-relational databases use a storage model that is optimized for the specific requirements of the type of data being stored [51]. Non-relational databases are sometimes referred to as "NoSQL" [51]. Non-relational databases are often used when large quantities of complex and diverse data need to be organized, or when data is frequently changed or updated [51]. The data is normally stored in a structure similar to a file system
Advantages
Non-relational databases have many advantages. One advantage is that they are are easier to scale vertically, due to the way the data is stored [52]; as mentioned before, the data is stored in a similar way to files in a file-system (folders and documents) which makes it much easier to split into multiple smaller databases and store them in different servers [52]. Because of its minimal use of relations between objects, there is no joining making them much faster than relational databases for large amounts of data [52]. The lack of normalisation also makes them more flexible allowing for the schema to change [52]. Sometimes, non relational databases are used as cache for relational databases when the data is highly relational but there is a lot of data to process
Disadvantages
There are some disadvantages to using non relational databases. The lack of ACID (atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) transactions across multiple documents or collections make it harder to update related data and can lead to failures due to the lack of integrity and consistency [52]. Due to the lack of the properties mentioned above, querying non relational databases is also more difficult, especially in the case of complex queries [52]. Unlike relational database which all work in a similar way, different non relational databases work in different ways making the ecosystem more fragmented [52], for example, Firestore and MongoDB do not function the same way even if the base concept is the
Use in the Project
As mentioned before, the current system uses a non relational database provided by Firebase. Due to the object modelled in the project being highly relational, querying data was difficult, however, these complex queries were not carried out often [50]. However, the schema was much more flexible which was vital for this project as the requirements were chaining constantly as the project went on meaning that the database was also being extended often, this would have required multiple normalisations procedures if using a relational database [50]. This flexibility also decreased development time facilitating Agile development as discussed in the Methodology section [53]. As mentioned before, this type of database is also more scalable meaning that it would be much easier to reach a wider audience at lower costs
Chapter 3: Software Engineering
3.1 Methodology
Project management methodologies are approaches used to plan, organize, and execute projects efficiently [54]. The chosen methodology depends on the project's specific requirements, including scope, timeline, budget, and stakeholders
There are several different project management methodologies, each with its own strengths and weaknesses [54]. Some are focused on linear, sequential approaches, while others prioritize flexibility and adaptability [54]. Some methodologies are more suited to larger, more complex projects, while others are better suited to smaller, more straightforward projects
The key to selecting the appropriate methodology for a given project is to understand the project's specific requirements and constraints [54]. Factors to consider when selecting a methodology include the level of clarity of project requirements, the degree of stakeholder involvement, the level of complexity, and the project timeline and budget
3.1.1 Agile
Agile is a project management approach that values flexibility and collaboration [55]. It emphasizes adaptation to change and delivering small, incremental improvements to a project, rather than trying to deliver a perfect final product all at once [55]. The Agile approach encourages regular communication and feedback between team members, allowing for continuous improvement and adaptation to changing requirements [55]. This approach has become popular in software development and is now widely used in other industries as well
Advantages
The Agile methodology used in this project proved advantageous in many ways. By setting short-term deadlines, it encouraged the developer to be productive and efficient in their work [56]. The approach also allowed for flexibility in changing project direction and experimenting with new features or functionalities [56]. The methodology was client-facing, which meant that developers constantly delivered some version of the product for the client's feedback [56]. This constant feedback helped ensure that the final product met the client's expectations and needs
One of the key benefits of the Agile methodology is its ability to adapt to changing requirements [56]. As the project went along, requirements were discovered, and the developer was able to adjust their approach accordingly [56]. The initial plan was not rigid but rather a list of features that needed to be implemented [56]. This allowed for more flexibility in adapting to changing requirements and implementing new features as they were discovered
In addition, mockups were used before development to evaluate what the site would look like as a simple prototype or proof of concept. This allowed for early feedback and changes to be made before development, reducing the likelihood of costly changes later on. The feedback from mockups helped ensure that the final product met the client's expectations and
Disadvantages
While the Agile approach has many advantages, it also has some potential downsides. For instance, there is a potential for overlap or unnecessary effort spent on later stages if an early phase needs to be modified [56]. Additionally, the project timeline can be difficult to determine from the start [56]. However, in the case of this project, these potential downsides were not an issue since there was only one
How it Affected the Development
The project followed an Agile approach, as the requirements were discovered during the project's progression. The initial plan was a list of features that needed to be implemented, which allowed for more flexibility in adapting to changing requirements and implementing new
Mockups were used to evaluate what the site would look like as a simple prototype or proof of concept, which allowed for early feedback and changes to be made before development. This hybrid approach allowed for constant feedback and experimentation, making it easier to adapt to changing requirements while also providing a structured plan for the
The Agile approach also allowed for ample experimentation, by allowing the developer to try different technologies at a small scale and evaluate what worked without deciding on a technology too early on. The initial prototype of the system used Flask for the back-end and React (Material UI) for the front
The use of a non-relational database also facilitated this Agile workflow, as its flexibility allowed the system to be changed quickly if there were changes in requirements, while the requirements were still being discovered and during the experimentation phase. On the other hand, the use of a relational database, as used in the first prototype of the project, was a hindrance to the development as each time there was a change, the database required restructuring and redoing the calculations necessary to normalize the database, which is something that would have to be done often as the requirements were not
The use of React component libraries also contributed to this project's Agile development. This is because using component libraries made development faster as components did not have to be created from scratch and less testing was required as Chakra UI and Material UI already carried out their own testing to verify that the components meet accessibility standards
3.1.2 Waterfall
The Waterfall methodology is a sequential approach to project management that follows a strict, linear process from start to finish [57]. The process is divided into distinct phases, with each phase needing to be completed before progressing to the next one [57]. The project requirements are established early on, and a concrete plan for the project is created from start to finish
Advantages
One of the benefits of the Waterfall methodology is its structured approach, where each phase of the project requires a deliverable to progress to the next phase [57]. This makes the workflow more structured, and it is easier to determine when each phase of the project is complete [57]. Additionally, the team establishes project requirements early on, which can save time in the long run
Disadvantages
However, the rigidity of the plan can also make it difficult to make changes once the plan has been made [57]. If an issue with a phase is realized after progressing to the next one, the process can take longer as the team would have to go back and check where the mistake or error occurred [57]. Furthermore, the plan is too rigid, meaning that it can be hard to make changes once the plan has been made [57]. This makes the Waterfall methodology less suitable for projects with constantly evolving requirements
Reason Why it was Not Used
As mentioned before, the Waterfall methodology was not used due to the evolving nature of the project requirements. The initial plan was not rigid but rather a list of features that needed to be implemented. The requirements of the project were being discovered as the project went along, which would have made it difficult to create a concrete plan from start to finish. Additionally, the project was being developed by only one developer who could adapt the project requirements as needed. In this context, the Agile methodology was more suitable since it allowed for more flexibility in adapting to changing requirements and implementing new features as they were discovered.
3.2 Testing
Testing ensures that the system meets a certain quality keeping faults to a minimum and verifying that the system meets requirements that were defined [58]. Additionally, tests also document the functionality and expected behaviour of the code [58]. Furthermore, it facilitates refactoring code, this is because passing code can be refactored and tested again to verify if the code still functions the same way
3.2.1 Unit Testing
Unit testing is a software development practice that involves writing and running small pieces of code to verify the functionality and quality of individual units or components of a larger system [59]. A unit can be a function, a class, a module, or any other logical part of the code [59]. Unit testing is important for several reasons: it helps developers find and fix bugs early in the development process, it improves the design and maintainability of the code by encouraging modularity and separation of concerns, it facilitates code reuse and refactoring by ensuring that changes do not break existing functionality, and it enhances the confidence and reliability of the software by providing evidence that it meets its specifications and requirements
Python
The first prototype of the project was based on Python, hence appropriate libraries were used for testing. One such library was PyTest, which was used for testing the code due to its easier and more flexible
On the other hand, UnitTest is a built-in testing library for Python, however, it was not used in the project due to it being more complex to use and not as powerful or flexible as PyTest [60]. PyTest offers a more comprehensive and flexible approach to testing, making it easier to test different parts of the code and ensuring that the code is functioning as expected
There are other Python testing libraries available, however, PyTest was selected as the preferred option due to its ease of use and flexibility
TypeScript
As mentioned before, the current system uses TypeScript meaning that testing libraries appropriate for this language must be chosen to carry out testing. The two main choices that have been considered are Jest and
Jest and Vitest are both popular JavaScript testing frameworks that are used to write and run tests for JavaScript applications [61]. Jest is a fast and flexible testing framework that provides a simple and easy-to-use interface for testing applications [61].. It is highly configurable and comes with a wide range of features and functionalities that make it a popular choice for many developers
On the other hand, Vitest is a relatively new testing framework that has been designed specifically for testing large-scale JavaScript applications [61]. It is built on top of the popular and well-established Jest framework, and it provides a more robust and scalable approach to testing [61]. Vitest is designed to handle complex testing scenarios and it provides a number of advanced features that make it well suited for testing large and complex applications
In terms of advantages, Jest has a lot of community support, making it easier to find resources and solutions to common problems [61]. Jest also has a large number of plugins and extensions that can be used to extend its functionality [61]. On the other hand, Vitest provides a more robust and scalable approach to testing, making it well suited for testing large and complex applications
Vitest also provides a number of advanced features that make it well suited for testing complex testing scenarios
In terms of disadvantages, Jest can be a bit slow for large applications, and its simplicity can sometimes lead to a lack of customization options [61]. Vitest, on the other hand, may have a steeper learning curve for new users, as it provides a more complex and feature-rich approach to testing
In conclusion, Vitest has been chosen as it provides benefits that are more appropriate for this project. Due to the scale of this project, its performance its critical and being a newer library there are not as many old complexities that are not longer needed
3.2.2 User Testing
User testing refers to the process of evaluating a product, application or website by having real users interact with it [62]. The aim is to collect feedback from users about the product's usability, functionality, and overall satisfaction [62]. User testing is an important step in the development process as it allows developers to identify any problems or pain points in the product that may affect the user experience [62]. This information can then be used to make improvements and optimize the product for the end-user [62]. By conducting user testing, developers can ensure that the product meets the needs and expectations of the target audience and provides a positive user experience [62]. This helps to increase user satisfaction, loyalty, and the overall success of the product. In addition, user testing can also help to identify any potential security or privacy issues that may need to be addressed
For this project, user testing was a crucial aspect of the development process. The goal was to gather feedback from real users to understand their experience with the system and identify areas for improvement. To gather this feedback, participants were asked to fill in a questionnaire on Google Forms. The questionnaire was designed to gather information about the participant's experience with the system, their satisfaction with its features, and any suggestions for
To prevent abuse or the same person from voting multiple times, creating bias in the results, participants' emails were taken and used to keep track of who had filled out the questionnaire. This ensured that the results were accurate and representative of the actual user experience. The use of Google Forms also made it easy to collate and analyse the data, providing valuable insights into the user experience and the areas that needed improvement. The results of the user testing were then used to guide further development and ensure that the system was meeting the needs of its
Usability of the system
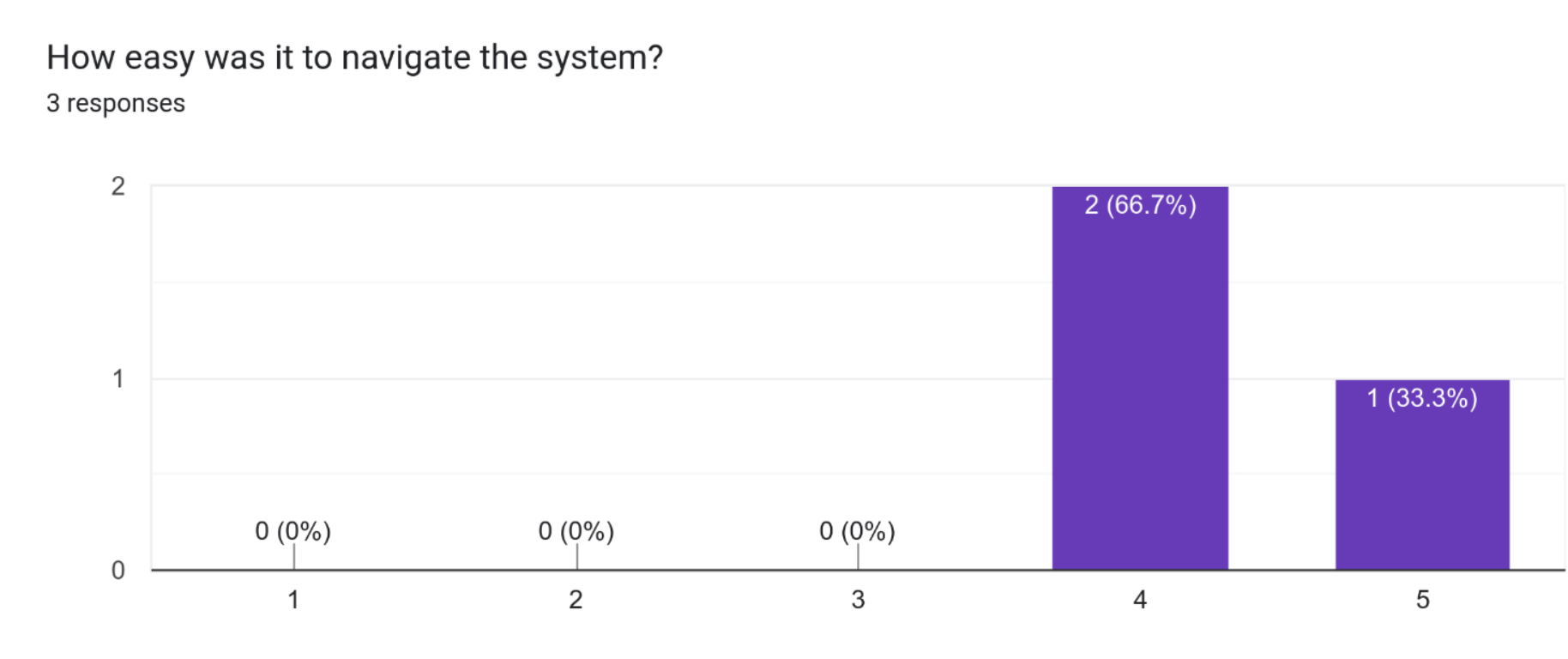
Based on the results, it can be seen that a majority of the participants found the system to be easy to navigate with 2 out of 3 participants rating it as "Easy" and 1 out of 3 participants rating it as "Very Easy". This suggests that the design and structure of the system was user-friendly and straightforward for the majority of the participants.
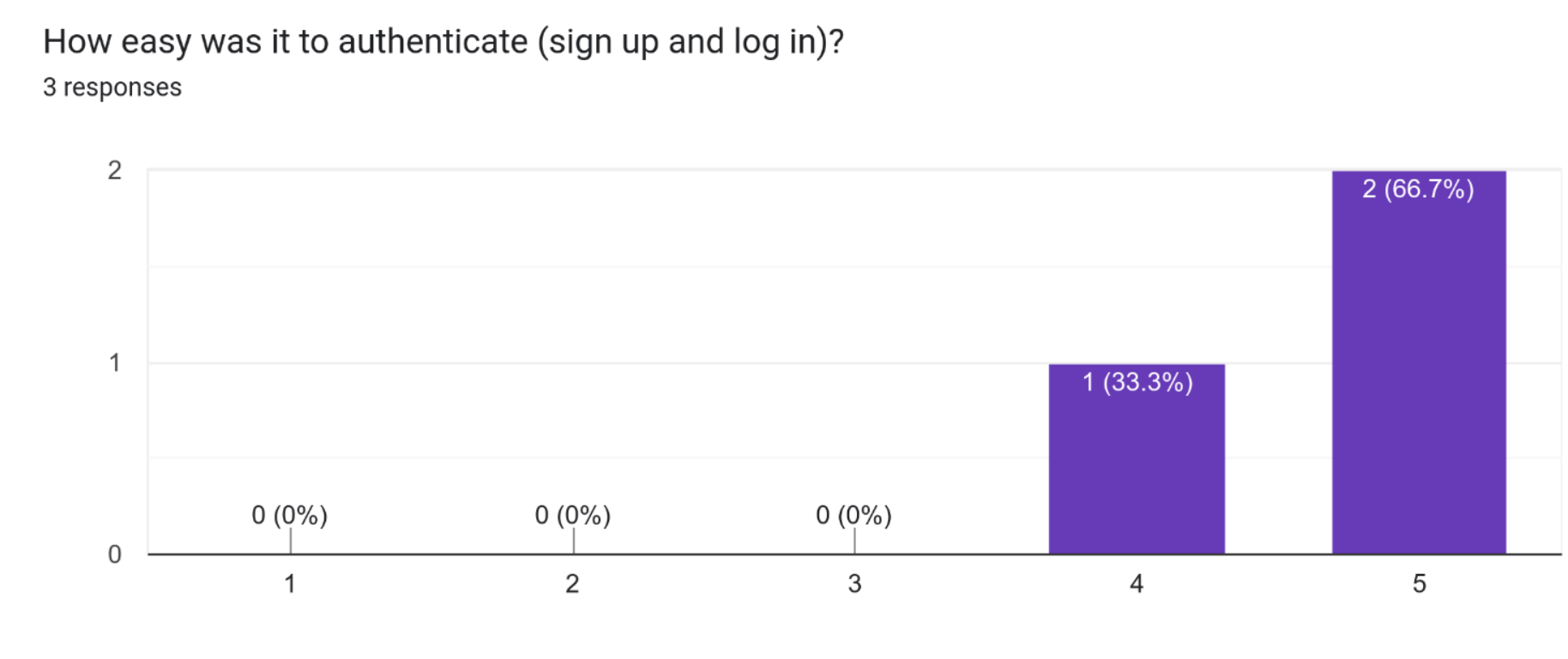
Based on the results of the user testing for the project, it appears that the majority of the participants found the authentication process to be very easy with 2 out of 3 participants rating it as such. This suggests that the sign up and login process was well designed and user-friendly. The remaining participant rated it as easy, indicating that there may have been some minor issues or areas for improvement.
The developer has given the flexible authentication methods for users making the site accessible; the standard email and password authentication is available along with third party providers such as Google and GitHub
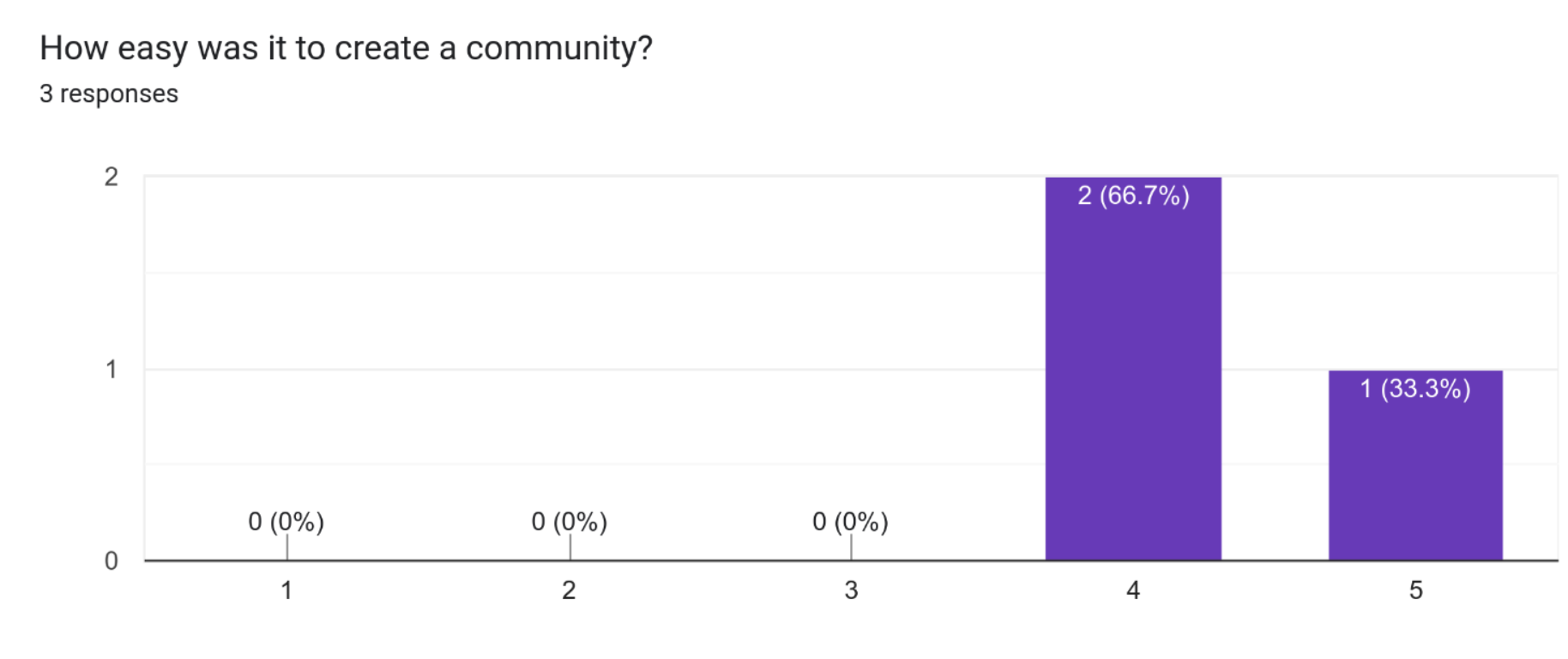
Based on the results of the user testing, 2 out of 3 participants found it easy to create a community on the system, while 1 participant found it very easy. This indicates that the majority of participants had a positive experience when it came to creating a community on the system. It could be due to the intuitive interface and clear instructions provided by the system, making it easy for users to understand how to create a community.
There are currently tow mechanisms for creating communities. However, when using the site on mobile, there is only one mechanism which does not give the user with multiple options.
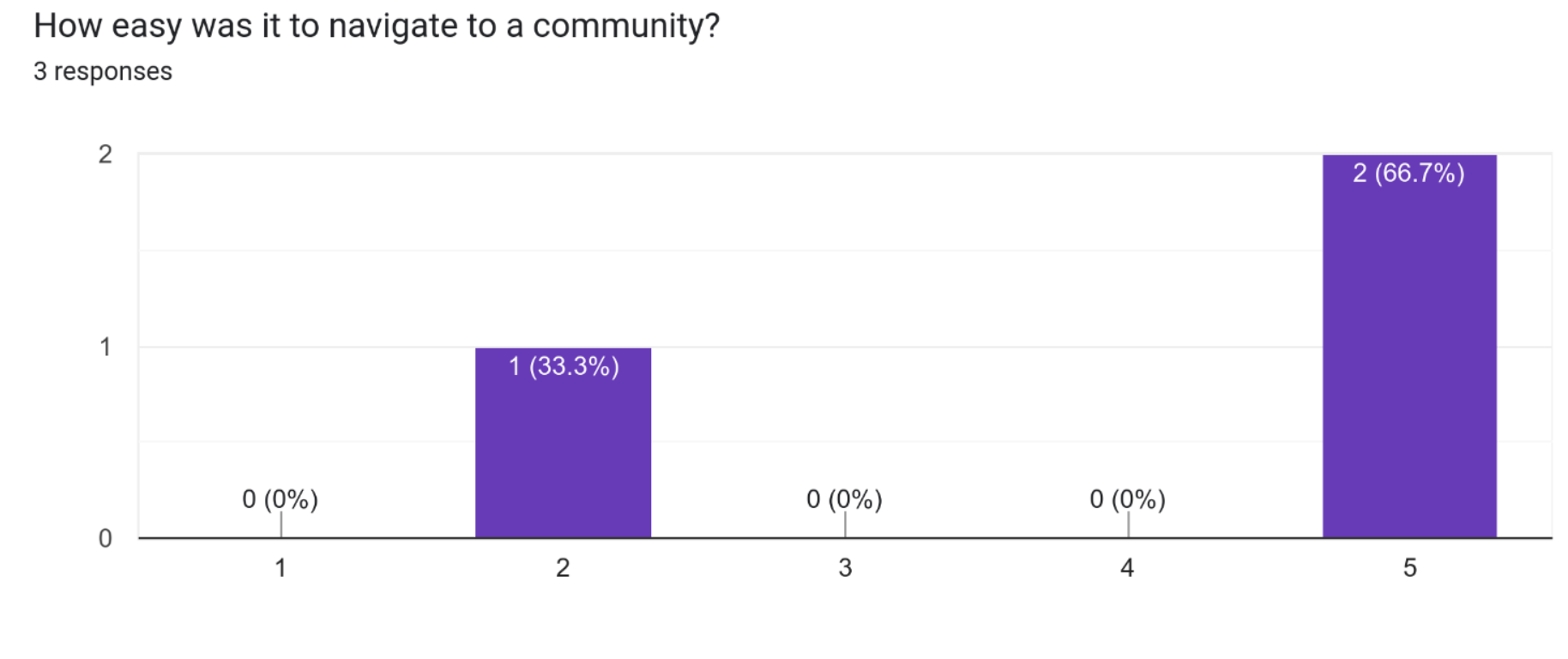
Based on the results, it seems that 2 out of 3 participants found it very easy to navigate to a community on the system. This indicates a high level of user-friendliness and ease of use for this particular aspect of the system. On the other hand, 1 participant found it hard to navigate to a community, which could indicate some room for improvement in terms of user experience.
Based on this feedback, a new page for accessing all the communities in the site has been created. Previously, only the top 5 communities could be viewed and this feature was only accessible on computers and not smartphones meaning they would have no way of finding communities. The new page which was implemented was accessible to both mobile and computer users: mobile users could use the community directory menu to navigate whereas computer users could the same method as mobile as well as using the recommended card on the side and click on a button to navigate to the same page.
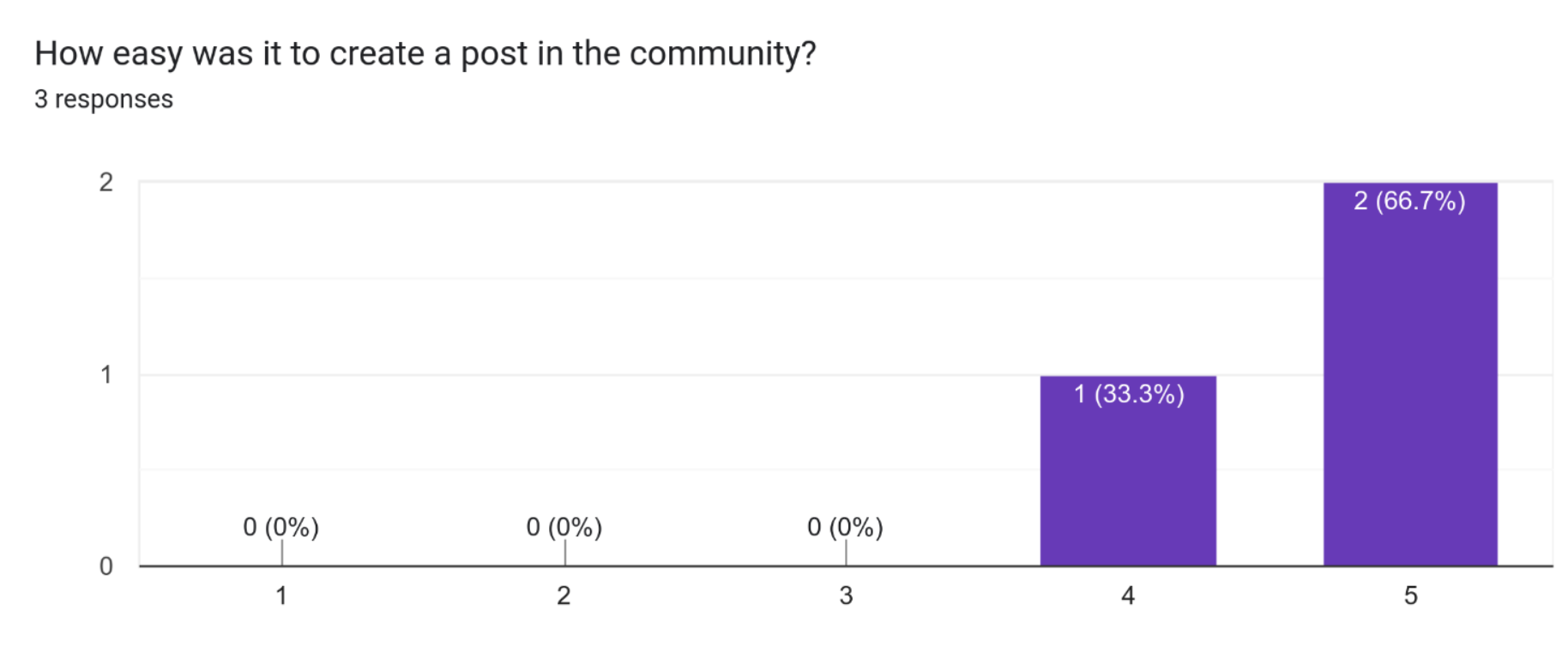
These results suggest that the majority of participants (2 out of 3) found it very easy to create a post in the community. Only 1 participant found it easy to create a post. This indicates that the process for creating a post in the community is user-friendly and easy to understand for the majority of users. This could be a result of clear and intuitive navigation, as well as a simple and straightforward user interface. The high level of ease in creating posts in the community could also indicate that users have a good understanding of how to use the site and that they are able to complete tasks with ease.
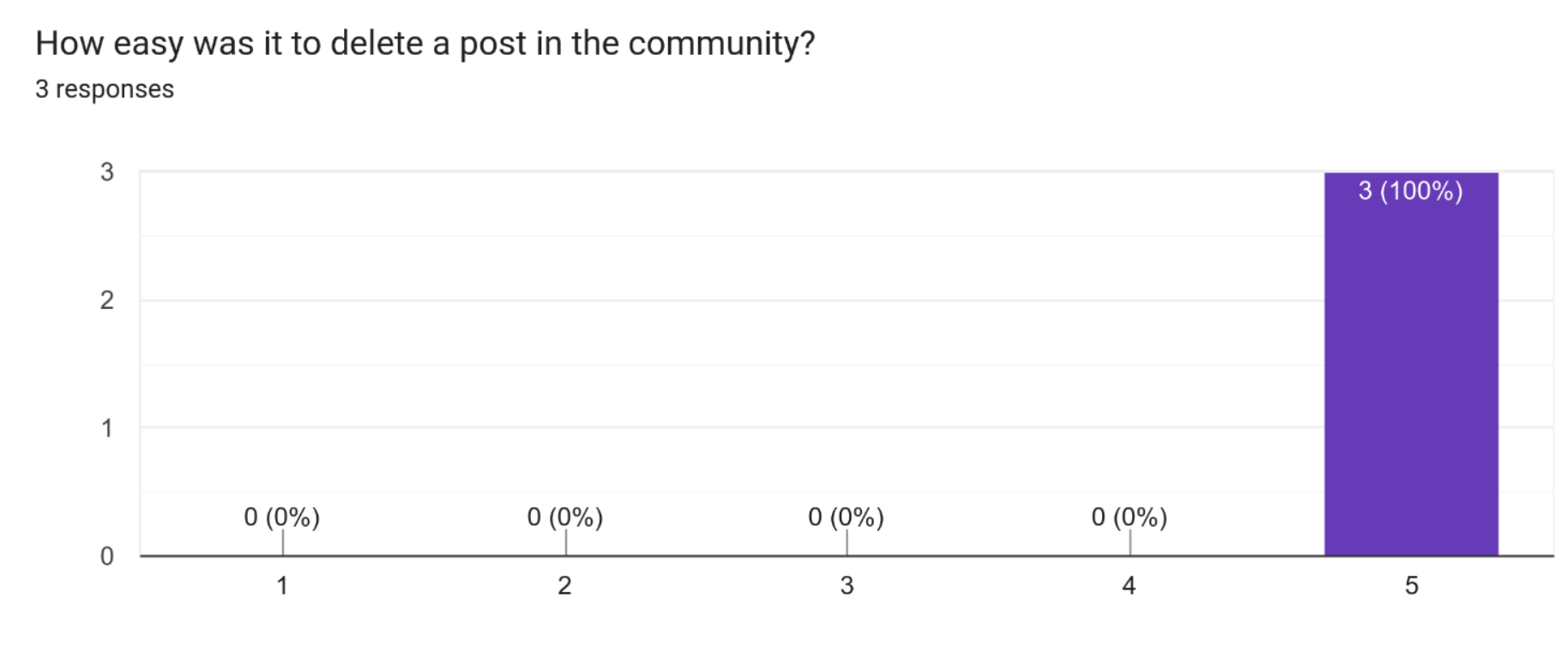
It appears that all three participants found it very easy to delete a post in the community. This suggests that the functionality for deleting posts in the community is well designed and user-friendly. Having an intuitive and easy-to-use interface for managing content within communities is important for fostering active and engaged communities. The button for deleting posts is only available to the users who created the post and it is accessible everywhere across the app.
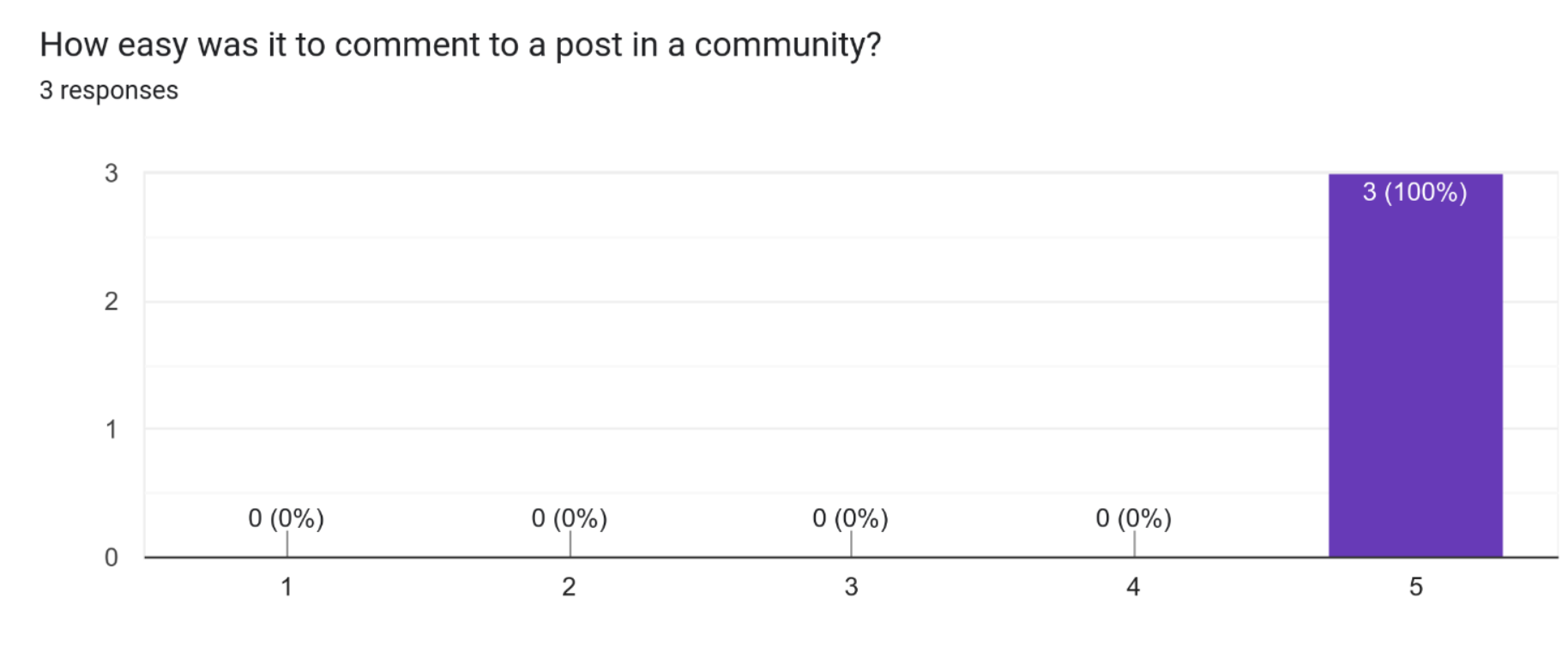
This suggests that all of the participants found it very easy to comment on a post within a community. This indicates a high level of user-friendliness and ease of use for this feature of the system. This is because opening a post gives the user a big text field (which is very visible) to create a post.
What were technical issues that you encountered if any while using the website? On phone sometimes when pressing the screen some of the boxes didn’t go away. nope
- I am not able to view my profile when "My profile" is clicked. - I cannot post to the main feed nor add images or links to the post.
These are examples of technical issues encountered by some users while using the website. It seems like some users faced difficulties with the interface on their phone and also encountered issues with their profile and the ability to post to the main feed or add images and links to the post. These technical issues may need to be addressed in order to improve the user experience on the website.
Trying to create a post from the main page opens the communty directory menu as posts can only be created within the community page. This probably means that it was not clear enough to the users that they were supposed to go to the approapriate community. This could potentially be improved by allowing the user to go the post creation page but giving them a drop down to select a community if the were directed from the home page.
What are some improvement you would like to see?
- More responsive
- Functionality.
- When the community is created, I need to refresh my page before I am able to see it in the drop down list.
- One may want want a modal that confirms whether they want the comment to be deleted. This can help prevent accidental deletion.
Some of the improvements that the participants would like to see are: better responsiveness of the website, improved functionality and an additional confirmation step before deleting a comment to prevent accidental deletion.
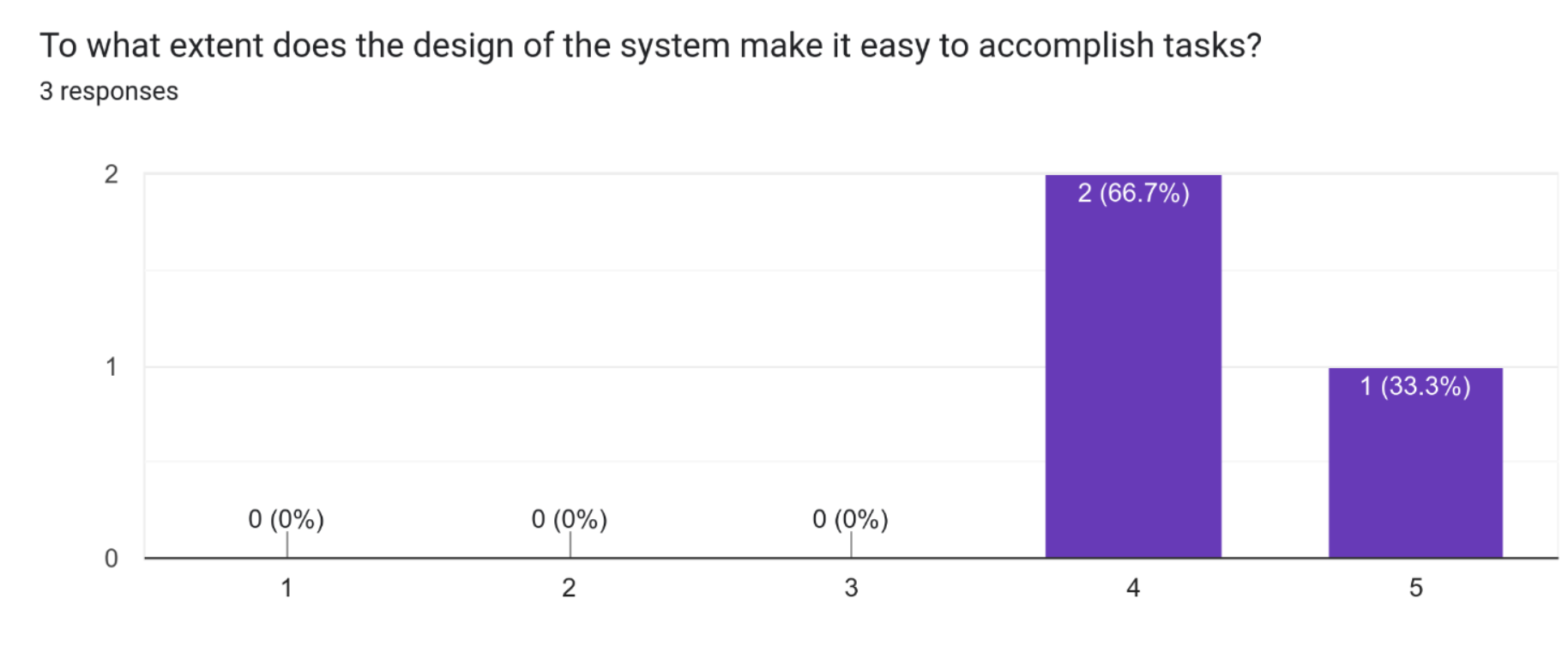
Based on the feedback, 2 out of 3 participants found the design of the system easy to accomplish tasks, while 1 out of 3 participants found it very easy. This suggests that the majority of the participants found the design to be user-friendly and straightforward. However, there is still room for improvement, and some participants may have faced difficulties while using the system.
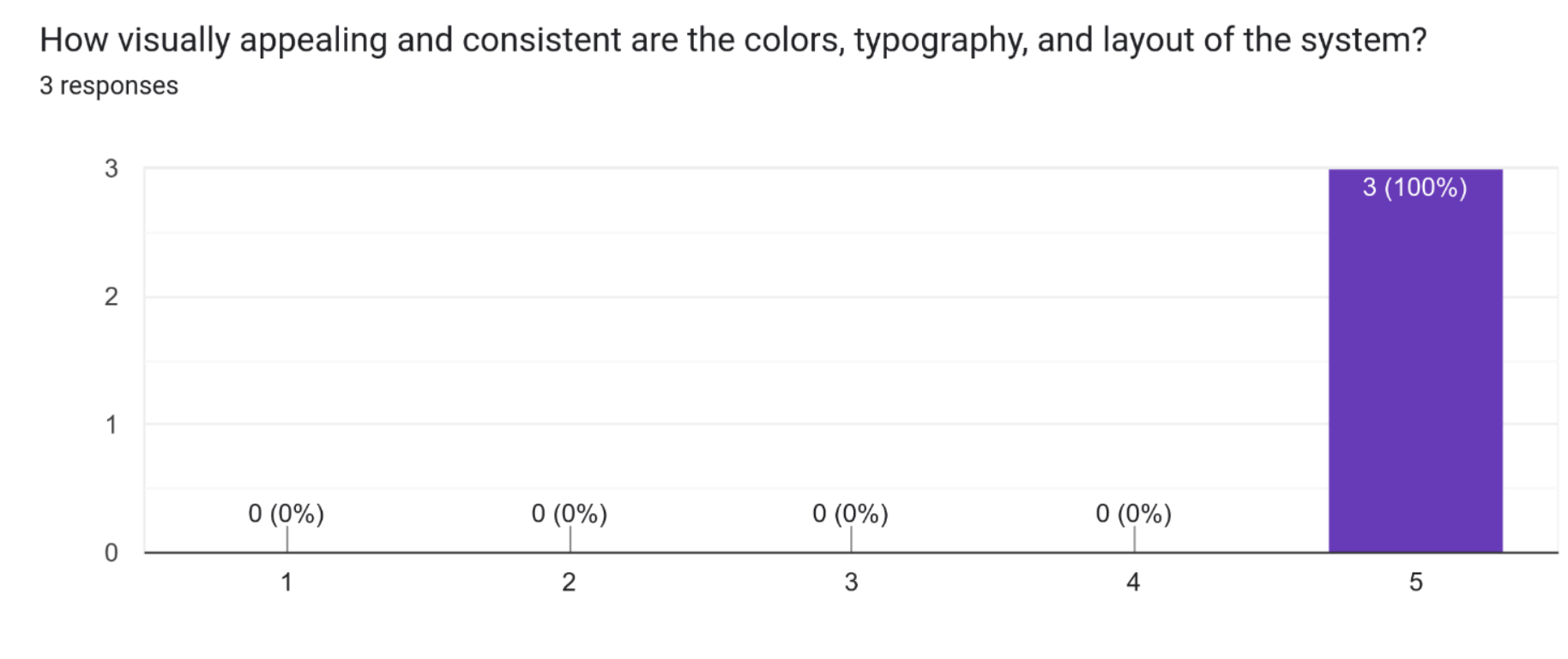
It appears that 3 out of 3 participants found the visual design of the system to be very appealing and consistent in terms of colours, typography, and layout. This suggests that the design elements of the system are well-coordinated and pleasing to the eye, which can enhance the overall user experience.
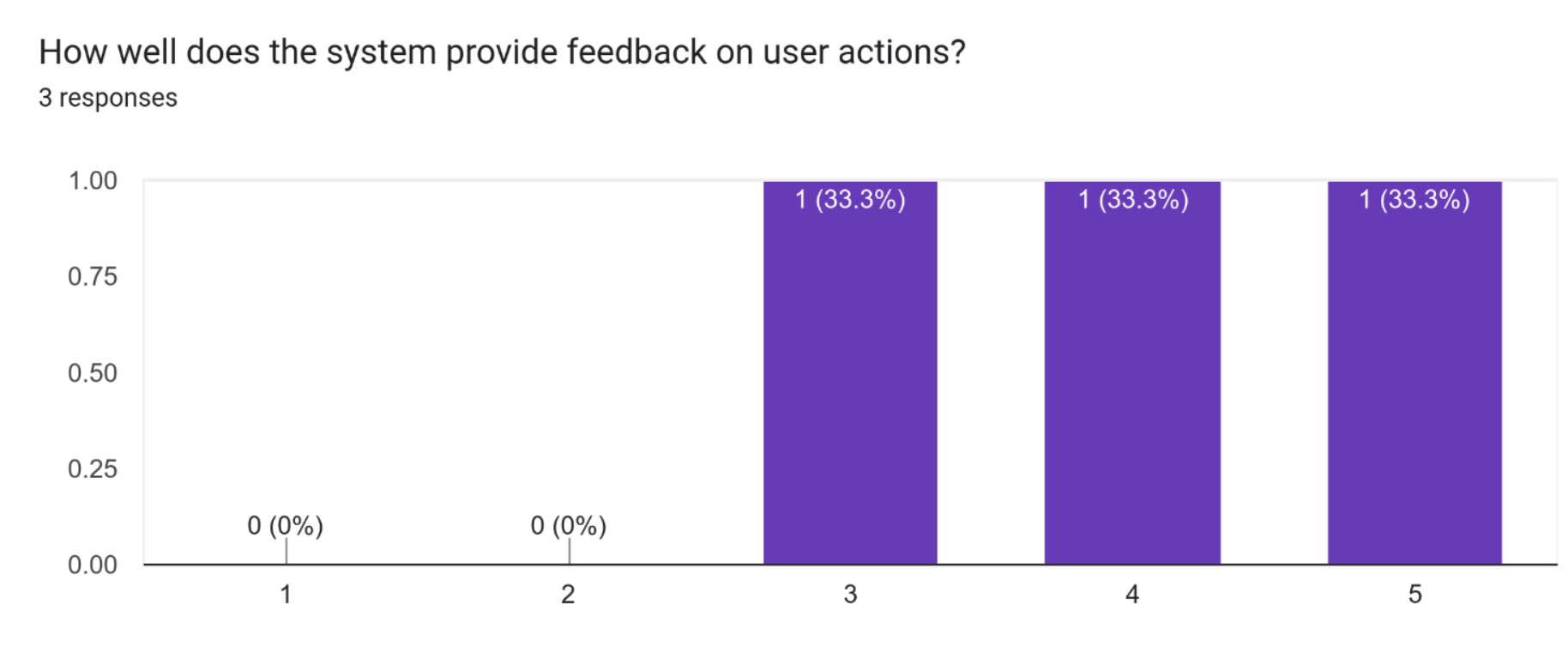
It can be seen from the feedback that the system provides adequate feedback on user actions, but it could be improved in certain areas to make it more intuitive and user-friendly. This can include providing more clear and immediate feedback after a user performs an action, or making the feedback more visually appealing and consistent with the overall design of the system.
This could potentially be improved by adding pop up messages confirming when an action was successfully completed for example when deleting an image or creating a post. Adding more confirmation dialogues (as mentioned in one of the previous questions) for deleting posts or other actions would further improve the user experience.
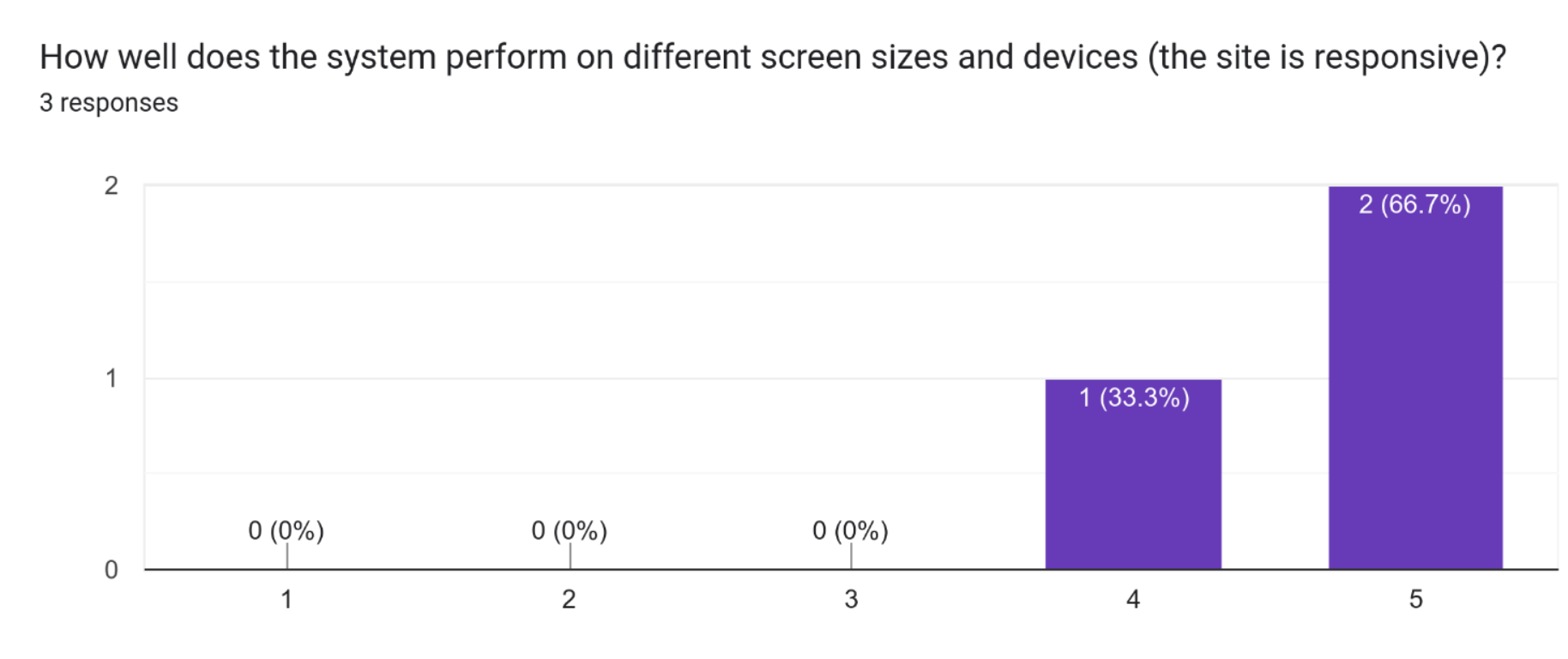
According to the feedback, 2 out of 3 participants found the system to perform very well on different screen sizes and devices, indicating that the site has a good level of responsiveness. This is an important aspect of modern web development, as users increasingly access websites from a variety of devices including desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. A responsive design ensures that the site can be easily used on all these devices, providing a consistent user experience regardless of the device being used.
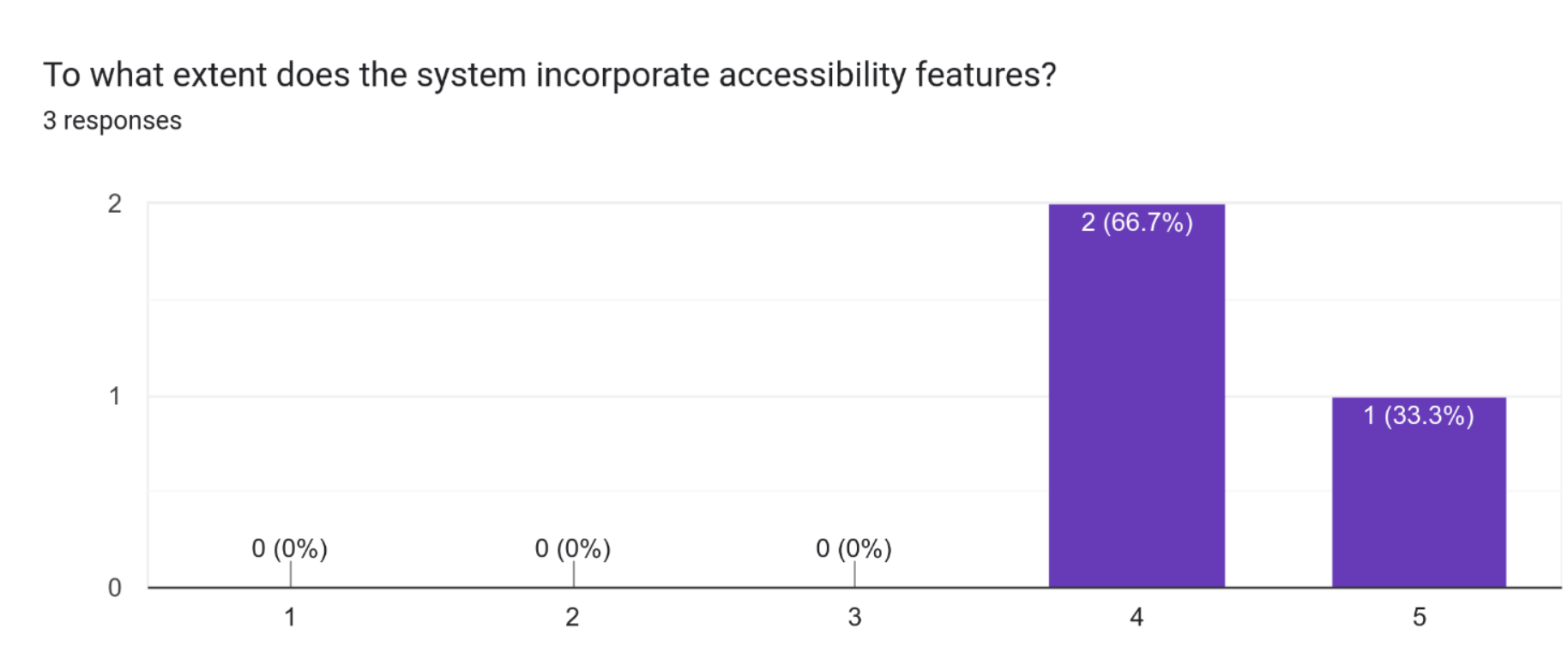
Based on the responses, it seems that the system is considered "accessible" by 2 out of the 3 participants and "very accessible" by 1 participant. This suggests that the system incorporates accessibility features to some extent, but there is still room for improvement in this area.
What are some improvements you would like to see?
- Add the ability to save posts
- A helper guide, or message showing usability would be nice
- It would be nice to have a homepage in the system. I was unsure of what I was looking at when I first opened the link so an indication that I am on my feed would also be appreciated. - I like the fact that you can sign in with Google and Github. - I would like to be able to view my profile.
These are great suggestions for improving the system. Having the ability to save posts can be useful for users who would like to come back to a post later. A helper guide or message indicating the usability of the system would also be helpful for new users. A homepage can provide a clear indication to the users of where they are in the system and what they are looking at. The ability to sign in with Google and Github is a great feature, but it would also be helpful to be able to view one's profile.
Conclusion
The results of the user testing of the project indicate that the system was generally well received by users. The majority of users found the system easy to navigate and perform tasks, with a few minor technical issues being reported. The design of the system was found to be visually appealing and consistent, and the system provided good feedback on user actions. The system performed well on different screen sizes and devices, with some users suggesting improvements in the area of accessibility. The results indicate that the system is user-friendly and well designed, but there is room for improvement in certain areas. The sample size of the user testing was small and only included a limited number of participants who completed the questionnaire. However, there were many more users who used the system and provided feedback in person, but were not included in the formal user testing results due to the small sample size.
3.3 Version Control System
A version control system is a tool that helps software engineers manage the changes and history of their code. It allows them to track, compare, merge and revert different versions of the same project [63]. Version control systems are commonly used because they enable collaboration, backup, documentation and quality assurance in software development [63].
3.3.1 Git
Git is a version control system (VCS) that is widely used in software development to manage and track changes to source code over time [64]. It allows developers to collaborate on a codebase by keeping track of changes made by different contributors and providing tools for managing conflicts and merging changes [64]. Git also enables developers to revert to previous versions of the codebase and provides a detailed history of changes (and revert to those changes), including who made the changes and when [64].
Branches
In this project, Git was used extensively to manage the codebase and facilitate collaboration between the developer and the supervisor [65]. Each feature was developed in its own branch, allowing for easy tracking of changes and reducing the risk of conflicts when merging changes back to the main branch [65]. Once a feature was implemented and its functionality was verified, it was merged into the main branch [65]. This approach allowed for a structured development process, with each feature being implemented and tested separately before being integrated into the main codebase [65]. This also allowed for the asynchronous development of features for parallel development [65].
This example highlights the existence of multiple Git branches as multiple tasks and features were being developed independently at the same time.
Tags
Tags were also created for marking milestones for each feature that was implemented [66]. This helped to keep track of the progress of the project and allowed for easy identification of important changes or additions to the codebase [66]. This was vital for tracking the complete history of the features that were implemented such as authentication, communities, posts, etc, without viewing the commits leading to these functionalities. It also made it easier to roll back to a previous version of the codebase if necessary [66].
This example demonstrates the different functionalities and sub-functionalities of the authentication system. Each tag shows the exact functionality that was implemented making it easier to locate.
Collaboration
Using Git in this way will be especially beneficial as the project is going to be open source and other developers interested in the project can participate. By having a clear and organized history of the codebase, it will be easier for other developers to understand the project and contribute to it [67]. They can easily identify the changes made to the codebase and track the progress of the project [67]. The use of tags will also make it easier for other developers to identify important milestones in the development process [67]. Additionally, the use of Git will allow for easy collaboration between developers, ensuring that the project can continue to evolve and improve over time [67].
3.3.2 Remotes
One major benefit of using a remote for Git, such as GitHub or GitLab, is the ability to collaborate with other developers [68]. With a remote repository, multiple developers can work on the same codebase simultaneously, and all changes can be tracked and merged seamlessly [68]. This allows for efficient collaboration, even when team members are working remotely or in different time zones [68].
Another advantage of using a remote for Git is the ability to share code with other developers and the broader open source community [68]. With a remote repository, developers can easily share their code with others, allowing them to contribute to the project and providing opportunities for peer review and feedback [68].
Using a remote also enables easy backups and disaster recovery [68]. By storing copies of the repository in the cloud, developers can ensure that their code is always backed up and available even in the event of hardware failure or other disasters
Finally, a remote Git repository allows for easy deployment of software [68]. By creating different branches of the codebase, developers can manage different environments such as development, testing, and production, making it easier to ensure that the correct version of the code is being used in each environment [68]. This can help to minimize errors and bugs in the deployed software
3.4 Code Quality
Code quality is a measure of how well-written, readable, maintainable and reliable a piece of code is [69]. Code quality can affect various aspects of software development, such as performance, security, usability and scalability [69]. Code quality is important because it can have a direct impact on the success and satisfaction of the end-users, as well as the efficiency and productivity of the developers [69][71]. Code quality can be improved by following coding standards and best practices, using code analysis tools and testing frameworks, conducting code reviews and refactoring regularly
3.4.1 Linting
A linter is a tool used in software development to analyse source code and flag programming errors, bugs, stylistic errors, and suspicious constructs [70][71]. It can detect potential bugs, syntax errors, uses of undeclared variables, calls to undefined or deprecated functions, and other programming issues [70][71] Linters perform static analysis, enforce configuration flags, check for compliance with style guides or security rules, and much more
Linters are used to improve code quality and reduce errors before execution [70]. They can improve readability, remove silly errors before execution and code review, create consistency, give visibility of codebase health, spread awareness and ownership over code quality, and control technical debt [70]. Linters help to standardize code and enforce best practices, ensuring that the code is more maintainable and efficient, and can save time by reducing the need for manual code reviews. This consistency makes it much easier for other developers to collaborate
First Prototype (Python)
The first prototype of this project was based on Python (Flask) hence the appropriate linter was selected. Flake8 was chosen as the preferred linter over PyLint due to its advantages [71]. Firstly, Flake8 is easier to use and is more configurable than PyLint [71]. Flake8 also has superior plug-in support, which means that it can be customized to meet the specific needs of the development team [71]. Additionally, Flake8 is faster than PyLint, which is an important factor when working on large codebases [71]. Although PyLint is more comprehensive than Flake8, its strictness can be a disadvantage, and it can be time-consuming to configure camel cases for some codebases [71]. On the other hand, Flake8 is not as strict as PyLint, but it can be configured to be more strict if needed
Current Project (Next.JS & TypeScript)
For the current project stack which is based on Next.JS. ESLint was chosen because it is the most flexible and extensible of the four JavaScript linters compared [72]. It comes with a large number of custom rules and is easy to install more in the form of plugins [72]. ESLint also includes many rules that are not available in other linters, making it more useful for detecting problems [72]. Additionally, it has the best support for ES6 and is the only tool that supports JSX. The output is easy to understand, and it supports custom reporters [72]. Although some configuration is required, the article does not mention this as a significant disadvantage [72]. The article also notes that JSCS only detects coding style violations and not potential bugs, while JSLint and JSHint are less flexible and less extensible than ESLint
The alternatives were not chosen for various reasons. JSLint lacks customization options and has limited configuration options [72]. JSHint is more difficult to configure compared to ESLint and does not support custom rules. JSCS only detects coding style violations and not potential bugs or errors, which may be important for some projects
3.4.2 Unit Testing
Unit testing is a software development practice that involves testing individual units of code in isolation to ensure that they function correctly [59]. By writing automated tests for individual functions, classes, or modules, developers can identify and correct errors early in the development process, leading to better code quality
These are some ways that unit testing leads to better code quality:
- Early detection of bugs: Unit testing allows developers to catch bugs early in the development process. By testing individual units of code in isolation, developers can identify and fix errors before they impact other parts of the system. This leads to better code quality and reduces the likelihood of bugs in the final product [59].
- Increased confidence in code changes: Unit tests provide a safety net for developers when making changes to the codebase. When a change is made, the relevant unit tests can be run to ensure that the change does not introduce any new bugs or regressions. This increases developers' confidence in their changes and reduces the likelihood of introducing bugs into the codebase [59].
- Facilitates refactoring: Unit tests also make it easier to refactor code by providing a way to ensure that the code still functions correctly after changes have been made. By running unit tests after each refactoring step, developers can ensure that the code still functions correctly and that any changes have not introduced new bugs [59].
- Better code structure: Writing unit tests requires developers to break down their code into smaller, more manageable units. This encourages developers to write code that is more modular and easier to maintain, leading to better code structure and organization [59].
- Better documentation: Unit tests can serve as a form of documentation for the codebase. By reading the tests, developers can understand how the code is intended to function and how it interacts with other parts of the system. This makes it easier for developers to work with the codebase and reduces the likelihood of errors
Overall, unit testing is a valuable tool for ensuring code quality. By catching bugs early in the development process, increasing developers' confidence in code changes, facilitating refactoring, encouraging better code structure, and serving as documentation, unit testing leads to better code quality and a more reliable final product. Testing methodologies are discussed in the Testing
3.4.3 Code Architecture
Code architecture is the practice of designing and organizing the structure of the codebase in a way that makes it easy to understand, maintain, and scale [73]. It is a critical practice that leads to better code quality by improving the readability, maintainability, and scalability of the codebase
These are some reasons why code architecture is important and leads to better code quality:
- Improved code organization: Code architecture makes it easier to organize the codebase in a way that makes it easy to understand and navigate. By grouping related code together and separating unrelated code, developers can quickly find the code they need, which reduces the likelihood of errors and bugs [73].
- Easier maintenance: Code architecture also makes it easier to maintain the codebase over time. By designing the codebase in a way that is modular and easy to understand, developers can quickly identify potential issues, debug the code, and fix bugs, which saves time and effort [73].
- Better scalability: Code architecture helps to facilitate scalability by making it easier to add new features and modify existing ones. By designing the codebase in a way that is flexible and easy to modify, developers can quickly make changes to the codebase, which reduces the time and effort required to scale the application
- Improved collaboration: Code architecture helps to facilitate collaboration among developers by making it easier for them to understand and work with each other's code. By designing the codebase in a way that is consistent and well-organized, developers can work together more efficiently, which leads to better code quality and faster development cycles [73].
- Better code quality: By improving the organization, maintenance, scalability, and collaboration of the codebase, code architecture leads to better code quality overall. This reduces the likelihood of errors and bugs, which improves the stability and reliability of the application
The architecture of this project has been designed to be as modular as possible decreasing coupling and allowing flexibility. This is discussed in more detail in the Diagram Detailing Architecture of the Whole System
Overall, code architecture is an important practice that leads to better code quality by improving the organization, maintenance, scalability, and collaboration of the codebase. By making it easier for developers to understand, maintain, and work with the code, code architecture reduces the likelihood of errors and bugs and improves the stability and reliability of the application. Therefore, developers should prioritize code architecture as a key practice in their development
3.4.4 Code Refactoring
Code refactoring is the process of restructuring existing code without changing its external behaviour [74]. It is a critical practice that leads to better code quality by improving the readability, maintainability, and scalability of the codebase
These are some reasons why code refactoring is important and leads to better code quality:
- Improved code structure: Code refactoring involves breaking down large and complex code structures into smaller, more manageable units. By doing so, code becomes more modular and easier to maintain, understand, and extend. This results in a cleaner codebase that is easier to work with and reduces the likelihood of bugs and errors [74].
- Better performance: Refactoring can also improve the performance of the codebase by optimizing algorithms and improving data structures. By identifying and addressing performance bottlenecks, developers can create a more responsive and efficient application [74].
- Code reuse: Refactoring also makes it easier to reuse code across the application. By creating more modular and reusable code, developers can save time and effort by not having to re-write code that has already been written [74].
- Increased maintainability: Code refactoring makes it easier to maintain the codebase over time. By improving the code structure, it becomes easier to identify and fix bugs, add new features, and modify existing functionality [74].
- Reduced technical debt: Technical debt is the cost of maintaining existing code that is hard to understand, modify or maintain. Refactoring can help to reduce technical debt by improving the code structure and making it easier to maintain, which leads to cost savings in the long run
In this project, the codebase has been refactored several times to achieve the points made above. React components have been split into sub-components (children) and common functionalities between components have been encapsulated into React hooks which can be called, more on hooks in the Design Patterns
Overall, code refactoring is an important practice that leads to better code quality by improving the structure, performance, maintainability, and scalability of the codebase. By making the codebase more modular, easier to understand and maintain, refactoring reduces the likelihood of bugs and
errors and increases developer productivity. Therefore, developers should prioritize code refactoring as a key practice in their development
3.4.5 Code Documentation
Code documentation refers to the process of providing descriptive and explanatory text about the codebase to help developers understand the code and how it works [75]. It is a critical practice that leads to better code quality by improving the readability, maintainability, and scalability of the codebase
These are some reasons why code documentation is important and leads to better code quality:
- Improved code understandability: Code documentation makes it easier for developers to understand how the code works and how it is intended to be used. By providing clear and concise explanations of code functionality, developers can quickly grasp the purpose of the code, which reduces the likelihood of errors and bugs [75].
- Easier maintenance: Code documentation also makes it easier to maintain the codebase over time. By providing documentation that explains the code structure, developers can quickly identify potential issues, debug the code, and fix bugs, which saves time and effort [75].
- Improved collaboration: Code documentation helps to facilitate collaboration among developers by making it easier for them to understand and work with each other's code. By providing documentation that explains how the code works and how it is intended to be used, developers can work together more efficiently, which leads to better code quality and faster development cycles [75].
- Easier onboarding: Code documentation helps new developers to quickly become familiar with the codebase, which reduces the learning curve and improves their productivity. By providing clear and concise explanations of the code structure, developers can quickly grasp the purpose of the code and begin contributing to the codebase [75].
- Better code quality: By improving the understandability, maintainability, and collaboration of the codebase, code documentation leads to better code quality overall. This reduces the likelihood of errors and bugs, which improves the stability and reliability of the application
In this project, documentation has been taken extremely seriously. Each functionality, hook and component has been documented using the JSDoc and its best practices. Documentation for the entire project as a whole has also been written in the form of the main ReadMe file and the project
Overall, code documentation is an important practice that leads to better code quality by improving the understandability, maintainability, and collaboration of the codebase. By making it easier for developers to understand, maintain, and work with the code, code documentation reduces the likelihood of errors and bugs and improves the stability and reliability of the application. Therefore, developers should prioritize code documentation as a key practice in their development
3.4.6 Design Patterns
Design patterns are proven solutions to common software development problems that can be reused across different projects [76]. They are important in software development because they can help to improve the quality of the codebase by providing a consistent, reliable and maintainable way of solving problems
These are some reasons why design patterns are important and lead to better code quality:
- Encourage best practices: Design patterns promote best practices in software development. They encourage developers to use well-established and proven solutions to common problems, rather than reinventing the wheel. This leads to code that is more maintainable, reliable, and scalable [76].
- Reusability: Design patterns are reusable solutions that can be used across different projects. By using design patterns, developers can create code that is more modular and easier to maintain, reducing the likelihood of errors and bugs. They also reduce development time by providing a consistent and reliable solution to a problem [76].
- Improves readability: Design patterns help to make the codebase more readable and easier to understand. By using well-established patterns, developers can create code that is easier for other developers to understand and work with, reducing the likelihood of errors and bugs [76].
- Scalability: Design patterns help to promote scalability by providing solutions that can be easily modified and extended. This allows developers to create code that is more flexible and adaptable, reducing the time and effort required to scale the application [76].
- Promotes collaboration: Design patterns help to promote collaboration among developers by providing a common language and approach to solving problems. This allows developers to work together more efficiently, which leads to better code quality and faster development cycles [76].
Design pattern rules have been followed to ensure that the codebase is of high quality ensuring that it meets the requirements listed above. The design patterns used are discussed in detail in the Design Patterns section.
Overall, design patterns are an important practice that leads to better code quality by promoting best practices, reusability, readability, scalability, and collaboration. By providing consistent and reliable solutions to common problems, design patterns reduce the likelihood of errors and bugs and improve the stability and reliability of the application. Therefore, developers should prioritize the use of design patterns as a key practice in their development process.
3.5 Organising Tasks
Tasks have been organized using the built-in features of GitLab.
Issues
The Issues feature has been used to keep track of features that may need to be implemented and what bugs have been found [77]. For each issue, it is possible to discuss possible ways of solving the issue with members of the team (if available) or the supervisor [77]. The issues also keep track of any pull requests, merges or commits that are mentioned that could have possibly fixed the bug or implemented the issue [77]. Once the issue is fixed, it can be closed indicating the bug has been fixed or the feature has been implemented [77]. Moreover, issue templates have been created to force a more consistent structure for issues: a template for bugs was implemented specifically for reporting bugs, this forces issuers to organize their issues in a consistent manner and ensures that all the information required is provided [77]. A feature template was also created the ensuring feature requests are structured in a consistent fashion and important information is provided [77].
Boards
The Boards feature has been used as a todo list to keep track of the features that need to be implemented. This makes it easier to organize code and help the supervisor and the developer understand what features have been implemented and what is yet to be implemented [77]. Additionally, each entry creates an issue which can then be used to discuss and document strategies to implement said features. Furthermore, once a pull request is merged, this issue can be closed, hence keeping track of what pull requests (and collections of commits) were used to resolve the issue [77].
Milestones
Other GitLab features can potentially be used in the future for organizing and keeping track of tasks and milestones even more efficiently [78]. For example, GitLab's Milestone feature can be used; each time there is a major milestone that is met (such as features), and the code is merged for it, a milestone can be ticked off, these milestones can be a group of features, for example, the communities milestone has multiple features such as creating a community, deleting a community, subscribing to a community and unsubscribing to a community, all these can be grouped into a single major milestone
Requirements
Another GitLab feature that can be implemented is the Requirements feature [78]. The requirements of the project can be specified here and the progress of the features can be compared against the requirements. This helps ensure that the project is meeting the original scope of the project and that all the criteria are met without implementing any unnecessary features first
3.6 Deployment
Deploying a website is the process of making a website accessible to the public on the internet [79]. It is done to share information, products, services or other content with a wider audience [79]. To deploy a website, one needs to have a domain name, a web hosting service and the website files. The domain name is the address of the website that users type in their browsers [79]. The web hosting service is the provider that stores the website files on a server and delivers them to the users' browsers. The website files are the code and content that make up the website
Self Hosting
Self-hosting is the process of setting up and managing your own server to host your website [80]. This option provides complete control over the server and the website, but also requires a high level of technical expertise and can be time-consuming and expensive to set up and maintain. Some popular self-hosting providers include DigitalOcean, Vultr, and Linode [80]. The advantages of self-hosting include complete control over the server and the website, the ability to customize the server and website to meet specific needs, and the ability to scale resources as needed [80]. The disadvantages include the need for technical expertise to set up and maintain the server, the cost of hardware and software, and the time required to manage and maintain the server
Shared Hosting
Shared hosting is a cost-effective solution for hosting a website, where the resources available on the server are shared among multiple users [80]. Some popular shared hosting providers include Bluehost, HostGator, and SiteGround [80]. The advantages of shared hosting include low cost, ease of use, and no need for technical expertise. The disadvantages include limited performance and stability due to shared resources, limited customization options, and limited scalability
Virtual Private Server (VPS)
A virtual private server (VPS) is a type of hosting that provides more resources and stability than shared hosting, but still requires a high level of technical expertise to set up and maintain [80]. Some popular VPS providers include AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure [80]. The advantages of a VPS include better performance and stability compared to shared hosting, the ability to customize the server and website to meet specific needs, and the ability to scale resources as needed [80]. The disadvantages include the need for technical expertise to set up and maintain the server, the cost of hardware and software, and the time required to manage and maintain the server
Managed Hosting
Managed hosting is a fully managed solution for hosting a website, where the provider takes care of all the technical details, including server setup, maintenance, and security. Some popular managed hosting providers include Heroku, WP Engine, and Pantheon [80]. The advantages of managed hosting include ease of use, no need for technical expertise, and the ability to focus on developing and promoting the website rather than managing the server [80]. The disadvantages include higher costs compared to other options, limited customization options, and a lack of control over the server and website
Vercel is a managed hosting provider that specializes in hosting and deploying modern web applications, including Next.JS applications [80]. Vercel offers a fully managed solution for hosting and deploying websites, and it provides a number of advanced features and functionalities that make it well suited for modern web development [80]. The advantages of using Vercel include ease of use, seamless integration with Next.JS, and a range of advanced features and functionalities [80]. The disadvantages include limited customization options and a higher cost compared to other options
Chapter 4: End System Development
4.1 Architecture of End System
4.1.1 Design Patterns
Design patterns are general solutions to common problems that arise in software development [76]. They provide a reusable and flexible way of structuring code, making it easier to maintain, extend and test [76]. Design patterns also help developers communicate their design ideas more effectively, as they can refer to well-known and established concepts instead of explaining every detail [76]. Design patterns are important because they improve the quality and efficiency of software systems, as well as the productivity and collaboration of developers
React Components (Composite Pattern)
React components follow the design pattern of the Composite pattern [82]. The Composite pattern is a structural design pattern that is used to represent a part-whole hierarchy [82]. In the Composite pattern, individual objects are treated the same as compositions of objects, making it easier to manage a tree-like structure of objects
In React, components can be nested within each other to form a hierarchy of components [82]. Each component can be treated as an individual object, or a composition of smaller components [82]. This allows for complex UI to be constructed from simple building blocks and makes it easier to reuse and manage components
Below is an example that demonstrates a parent navbar component which has several children components that are its building blocks [82]. State is passed down from this parent component down to its children which allows this navbar to be more modular
const Navbar: React.FC = () => { const [user, loading, error] = useAuthState(auth); const { onSelectMenuItem } = useDirectory(); return ( <Flex bg="white" height="50px" padding="6px 10px" justify={{ md: "space-between" }} position="sticky" top="4px" zIndex="999" //Rounded props border="1px solid" borderColor="gray.300" borderRadius={10} m={{ base: 1, md: 1.5 }} shadow="lg" > <Flex align="center" width={{ base: "40px", md: "auto" }} mr={{ base: 0, md: 2 }} onClick={() => onSelectMenuItem(defaultMenuItem)} cursor="pointer" > {/* Logo which is always visible */}{" "} <Image src="/images/logo.svg" height="30px" alt="Website logo" ml={1} /> {/* Logo name not visible on mobile */}{" "} <Image src="/images/logo_text.svg" height="30px" display={{ base: "none", md: "unset" }} alt="Website text logo" /> </Flex> {/* Community directory only visible when user is logged in */} {user && <Directory />}{" "} <SearchInput /> {/* Changes depending on whether user is authenticated or not */} <RightContent user={user} /> </Flex> ); };
The use of the Composite pattern in React components allows developers to think about the UI in terms of small, reusable components, rather than a single, monolithic structure. This makes it easier to build and maintain applications, as changes can be made to individual components without affecting the rest of the application.
This design pattern is important because it promotes the reuse of code and makes it easier to manage the structure of an application [82]. It also makes it easier to test components in isolation, as each component can be treated as a separate entity [82].
React Hooks (Higher-Order Components)
React Hooks follow the design pattern of Higher-Order Components (HOCs) and Render Props [83]. These design patterns are used to share logic between components, making it easier to reuse code and manage the state of an application [83].
- Higher-Order Components (HOCs): An HOC is a function that takes a component as an argument and returns a new component with additional props. HOCs allow developers to wrap a component with additional functionality, such as data fetching or theme management, without having to modify the original component. In React Hooks, the useState and useEffect hooks can be considered as HOCs that provide state management and side-effect logic to a component [83].
- Render Props: Render Props is a design pattern that allows a component to pass a function as a prop to another component, which then gets called to render the UI. In React Hooks, the useContext hook provides similar functionality, allowing components to access and update the context data [83].
Both of these design patterns are beneficial because they provide a way to share logic between components, making it easier to manage the state of an application and reuse code. They also make it easier to test components in isolation, as the state management and side effects are separated from the UI logic.
Below is an example of a hook that handles selecting a file from the user's file system. This hook is used in various places such as when selecting an image for a post, community icon and user's profile picture. Because of this common functionality, a singular hook has been created that handles selecting the file, checking whether it is an image, checking whether it is within the file size limits and checking whether it is the correct size (profile pictures are smaller than post images). This hook is then called in the required places.
const useSelectFile = (maxHeight: number, maxWidth: number) => { const [selectedFile, setSelectedFile] = useState<string>(); const onSelectFile = (event: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>) => { const onSelectFile = (event: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>) => { // Logic for uploading and handling files removed due to length of the code }; }; return { selectedFile, setSelectedFile, onSelectFile, }; }; export default useSelectFile; const { selectedFile, setSelectedFile, onSelectFile } = useSelectFile(300, 300);
Selecting a file when changing community icon
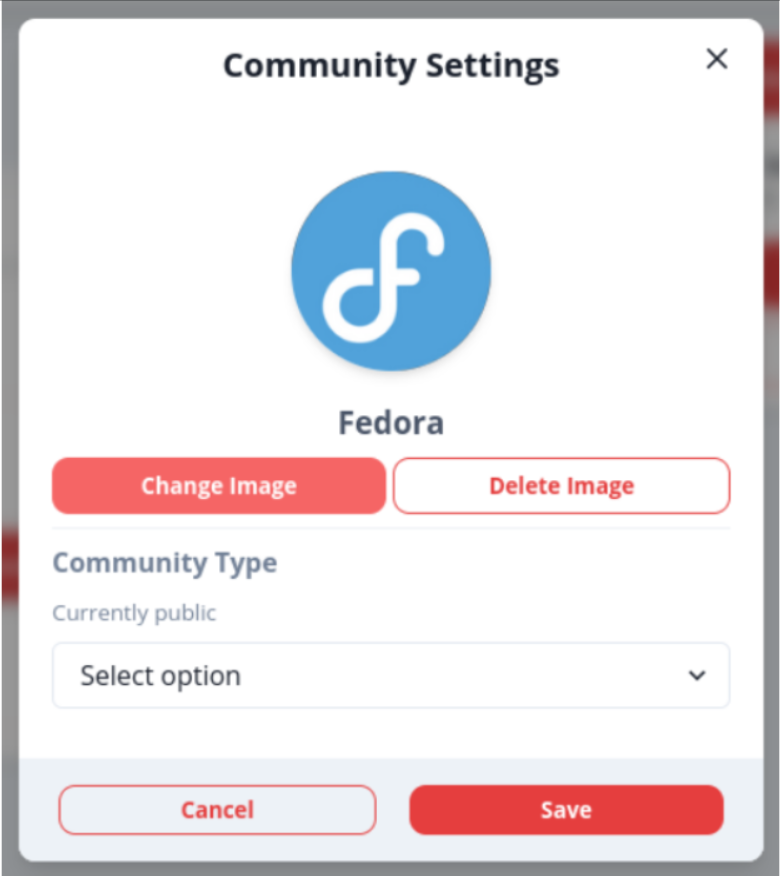
Selecting a file when changing user profile picture
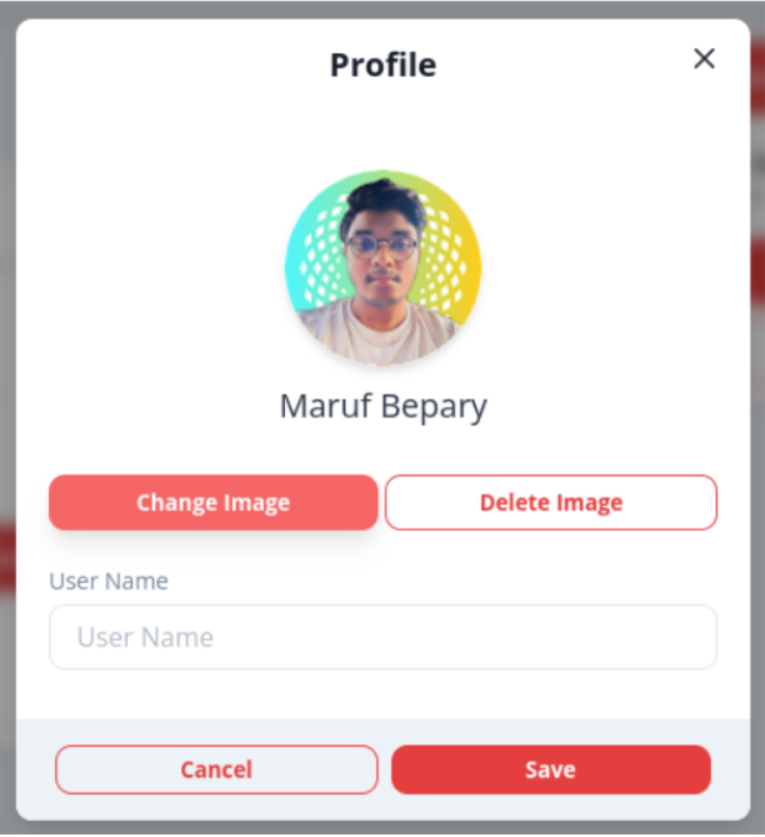
In conclusion, React Hooks provide a more concise and flexible way to manage state and share logic between components compared to the traditional HOCs and Render Props design patterns. By using React Hooks, developers can write cleaner and more maintainable code, making it easier to build and scale applications
State Management (Flux Design Pattern)
The design pattern used for managing the state in React is the Flux design pattern [84]. The Flux design pattern is a unidirectional data flow architecture that is used to manage the state of applications
In Flux, the state of the application is stored in a centralized store, and components can only update the state through actions that are dispatched to the store [84]. The store then updates its state, and the components that depend on the state are re-rendered to reflect the changes. This ensures that the state of the application is always consistent and predictable
React implements this design pattern through its use of the setState function, which allows components to update their state and trigger a re-render of the UI [84]. The useState hook provides a convenient way to manage the state in functional components, making it easier to write clean and maintainable code
This design pattern is important because it helps to maintain the integrity of the state of an application and ensures that the state updates in a predictable manner [84]. It also makes it easier to debug and test applications, as the state is managed in a centralized store and the flow of data is unidirectional
The example below demonstrates how Recoil was used as a centralised system for managing the state of the authentication modal across the app. Some user interactions or events would cause the state to change, opening or closing it. This is because multiple events can trigger it open for example, clicking the authentication buttons (in the navbar), voting on a post without being signed in, trying to comment without being signed in or creating a post without being signed
import { atom } from "recoil"; export interface AuthModalState { open: boolean; view: "login" | "signup" | "resetPassword"; } const defaultModalState: AuthModalState = { open: false, view: "login", }; export const authModalState = atom<AuthModalState>({ key: "authModalState", // unique identifier for the atom default: defaultModalState, });
State Management (Observer)
The Observer design pattern is a behavioural pattern that enables communication between objects in a way that is loosely coupled and easy to maintain [76]. This pattern is useful in situations where one object needs to notify a group of other objects of changes in its state, without having to know anything about those objects
The Observer pattern is used extensively in modern web development, particularly in the context of user interfaces. In a web application based on React, the Observer pattern can be used to manage the state of the application and ensure that changes to the state are reflected in the user interface
The basic idea behind the Observer pattern is that there is a Subject object that maintains a list of Observers [76]. When the Subject changes state, it notifies all of its Observers of the change, allowing them to update their state accordingly
In a React application, the Subject object can be represented by a state manager, such as Recoil or the Context API. The Observers can be represented by React components that are interested in changes to the state managed by the state manager. In this example, the auth state defined by Firebase tracks the authentication status of the user (whether a user is signed in or not) and the entire application would observe it and depending on this status, the application components would behave differently. An example of such behaviour is displaying the authentication buttons if the user tries to create a post when signed
const [user, loading, error] = useAuthState(auth);
Trying to create a post without logging in
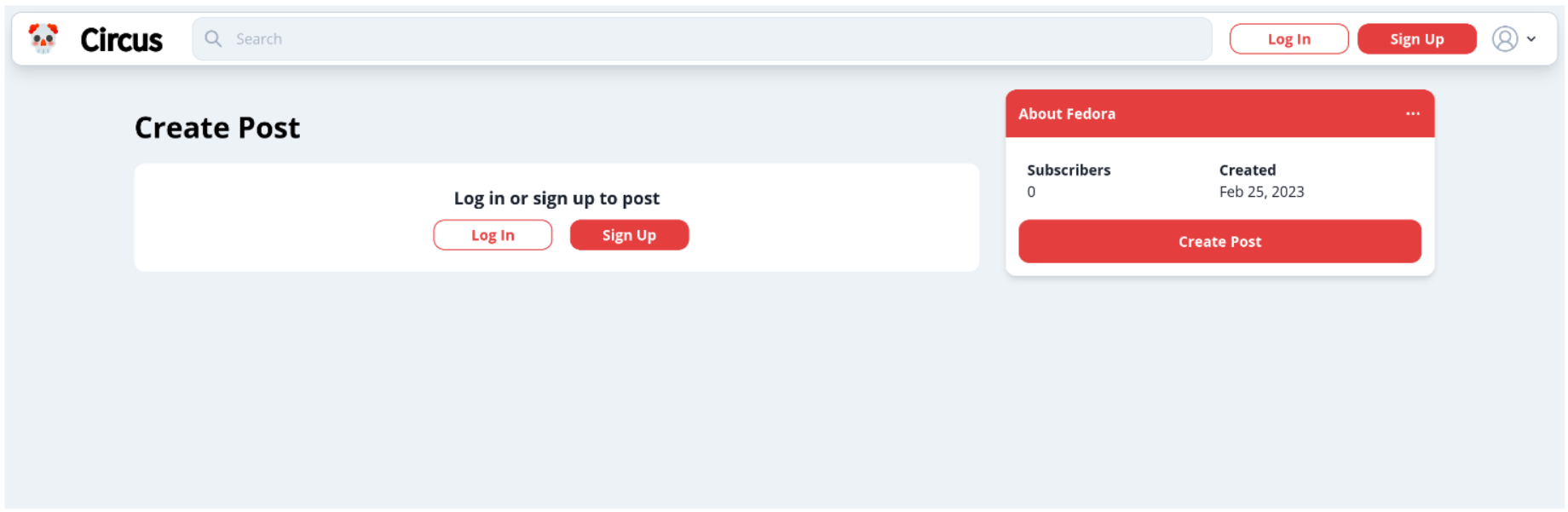
Trying to create a post while logged in
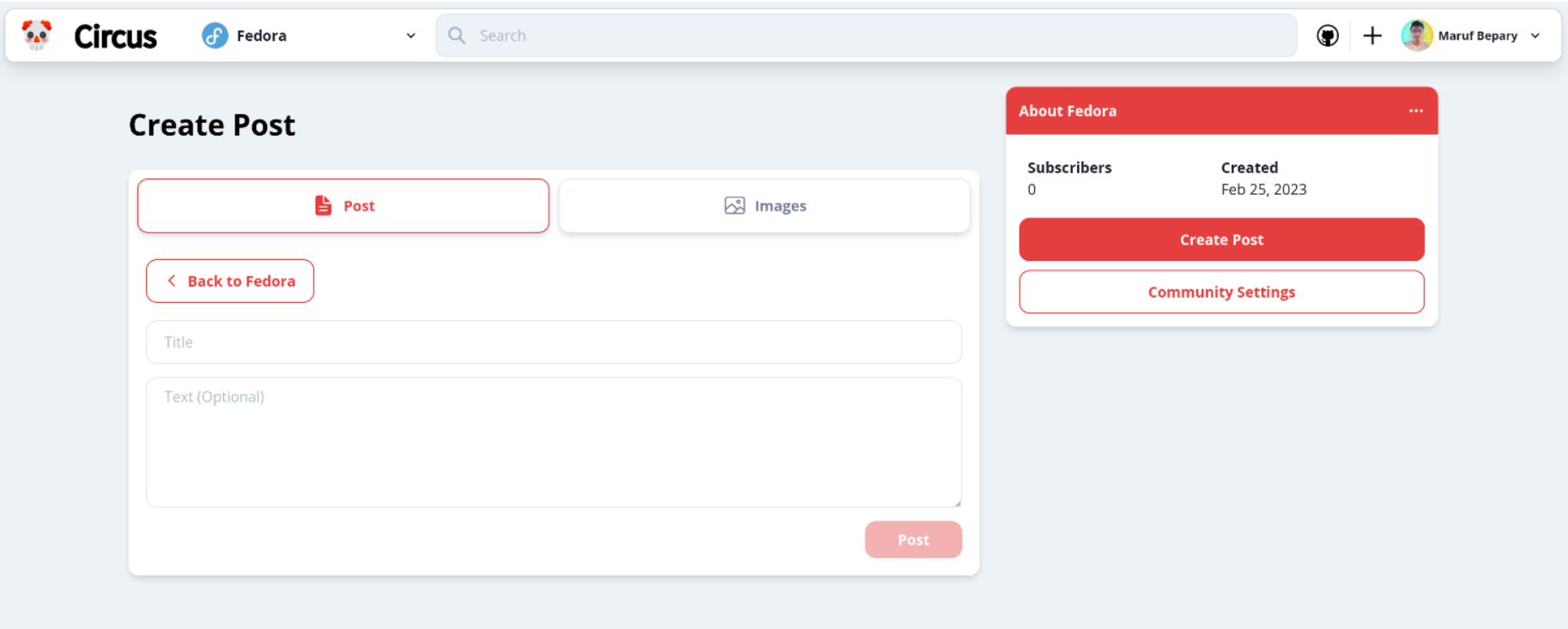
Multiple Items using the Same React Component (Iterator)
The iterator pattern is a software design pattern that provides a way to access the elements of an aggregate object sequentially without exposing its underlying representation [76]. This pattern is commonly used to iterate over a collection of objects and perform some operation on each element
In the context of rendering a single React component multiple times with new data, the iterator pattern can be used to simplify the process of rendering a list of items [76]. Instead of manually creating individual components for each item in the list, we can create a single generic component and use iteration to render it with the data for each item
For example, let's consider a PostItem component that displays a single post with its title, content, post votes and author. To render multiple posts using this component, we can fetch the post data from Firestore and create an array of post objects. We can then use the map function to iterate over the array and render a PostItem component for each post object, passing in the data for that post as
<Stack spacing={3}> {postStateValue.posts.map((item) => ( <PostItem key={item.id} post={item} userIsCreator={user?.uid === item.creatorId} userVoteValue={ postStateValue.postsVotes.find((vote) => vote.postId === item.id)?.voteValue } onVote={onVote} onSelectPost={onSelectPost} onDeletePost={onDeletePost} /> ))} </Stack>
Multiple posts being rendered using the same component by iterating over available posts objects
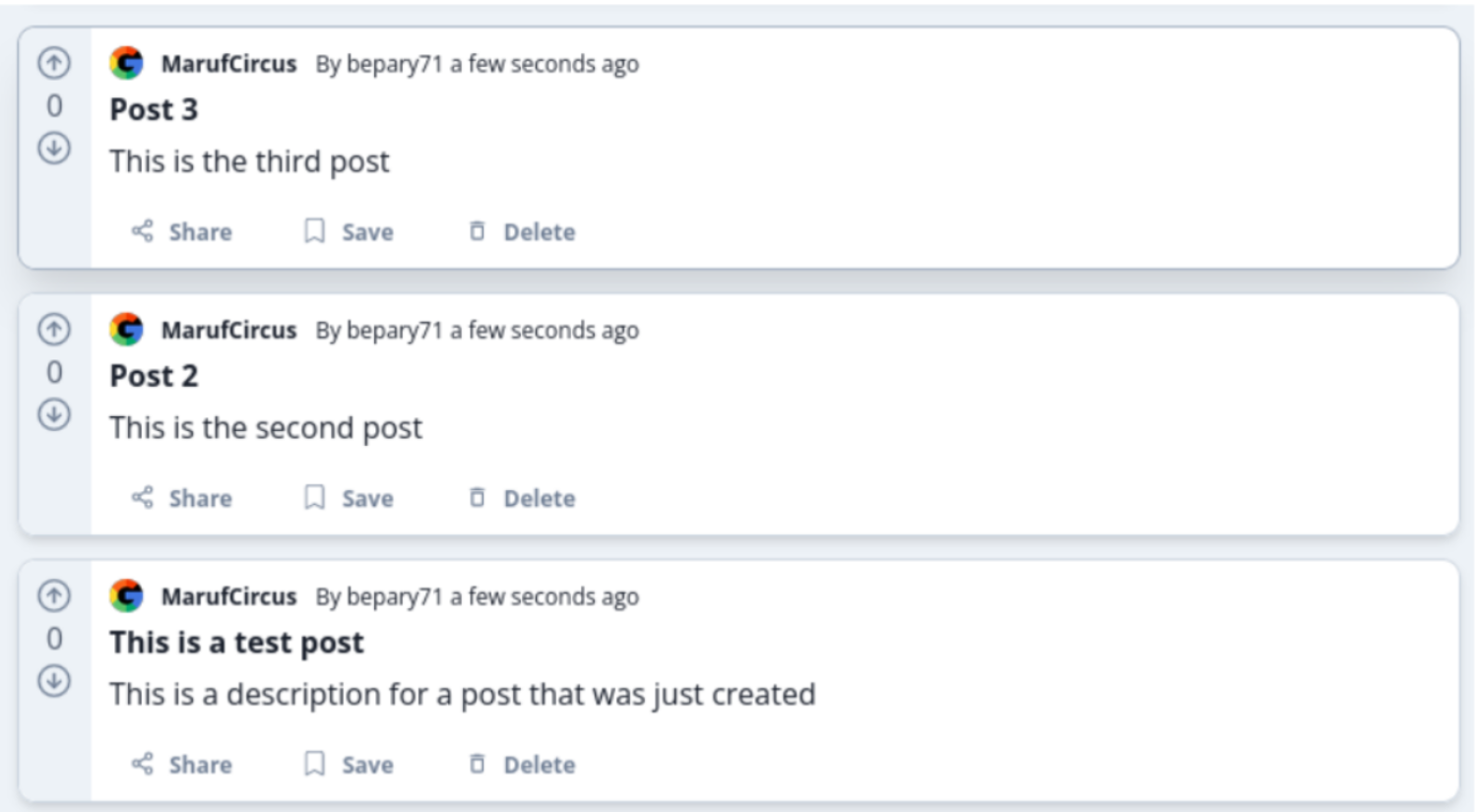
The same approach can be used to render comments within posts and lists of communities, using a generic component for each type of item and iterating over an array of objects to render multiple instances of the component with different
4.1.2 Diagram Detailing Architecture of the Whole System
The system architecture diagram depicts how the various sub-systems in the project function independently to deliver the required functionality. The three primary services that have been used in the project are Authentication, Firestore Database, and Storage. The logic implemented using TypeScript interacts with these Firebase services to perform specific actions, such as creating a new user in Firebase and adding a corresponding user object in the database when a user signs
To illustrate how a particular functionality, such as creating a post, works in this architecture, let's consider the following steps:
- The user interface captures the data for the new post through a form. This data is used to update the state of the form.
- The community logic then captures the updated form state and tries to create a new post. It performs any necessary checks and validation to ensure the data provided is valid.
- Once the post data is validated, the post's title and description are stored in the Firestore database. If there is an image associated with the post, it is uploaded to Firebase Storage, and the image link is stored in the database as
- The view posts logic then updates the Recoil state of the application to reflect the new post's addition. This update is observed by the components and pages in the user interface, which update themselves
By implementing this architecture, the system functions efficiently, and changes to data or state are propagated to all relevant components without any manual intervention. The system remains loosely coupled and easy to maintain, with each sub-system handling its responsibilities independently. Overall, this architecture ensures that the application is scalable, robust, and capable of meeting the evolving needs of the user
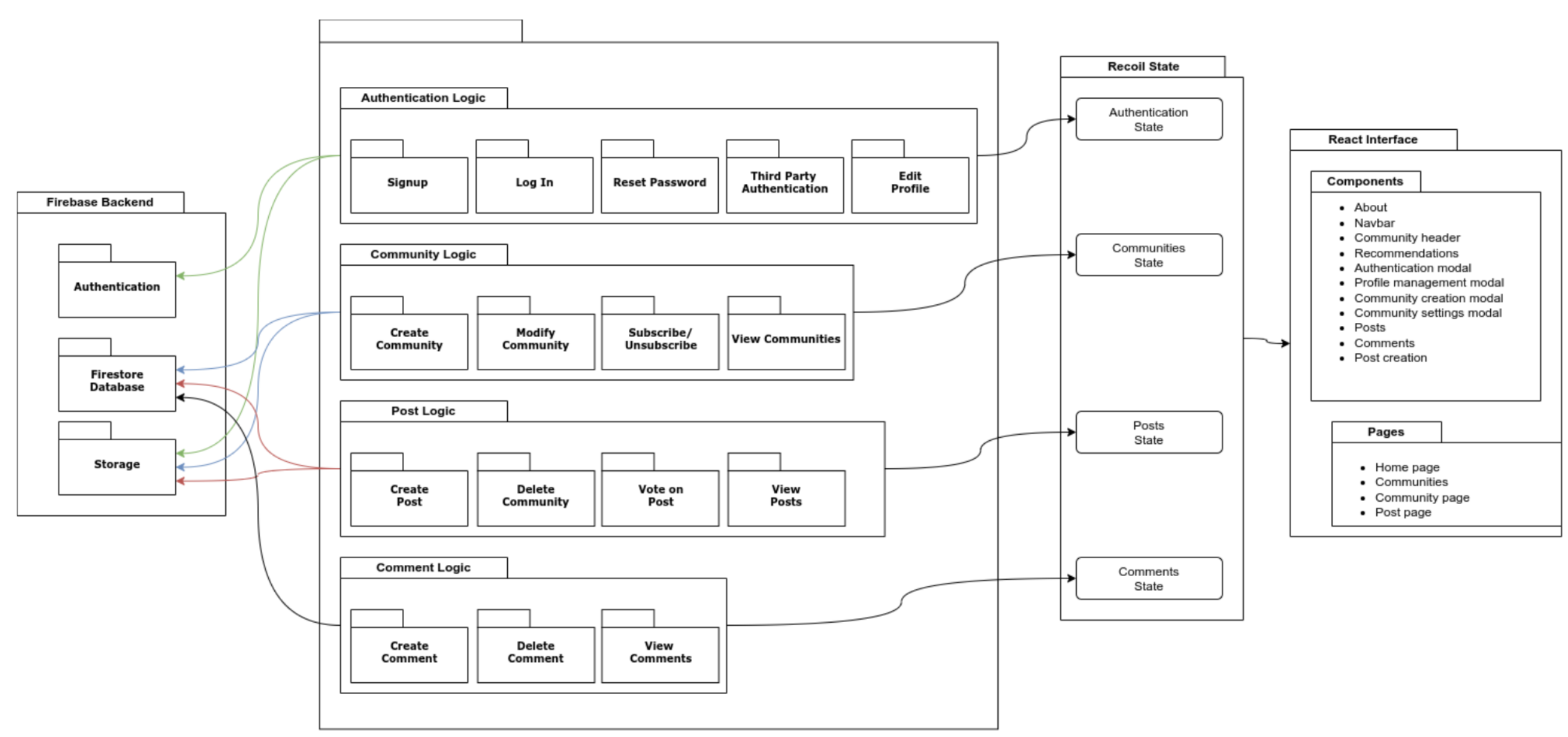
4.2 Database
4.2.1 Relational Database (SQL)
As mentioned before, the first ‘prototype’ system used a relational database for modelling the data (see Back-End Technologies for the rationale behind the choice).
Below is the original relational database that was used with the first system [48]. This can potentially be useful as it can be reused if the system is migrated again to a relational database, for example if switching to Supabase (see Back-End Technologies). In this case, this schema would be used as a baseline as it not feature complete to allow for implementing the rest of the features. This database has not been expanded as a non-relational database was used for the final system.
Achieving ACID compliency is extremely important to ensure the database is robust [85]. ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) is a set of principles that ensures the reliability and consistency of data in a database [85]. A database that adheres to ACID properties provides several benefits, including: allowing multiple people to work on the database without any concerns, reducing the need for manual debugging, and providing an error-free database at all times [85].
Atomicity requires that transactions (such as the insertion or deletion of data) are executed completely or not at all, and that the transaction is only visible to other users when it is fully executed [85]. Consistency requires that each transaction moves the database from a consistent state to another consistent state, ensuring that the database does not contain any conflicting data [85]. Isolation ensures that multiple transactions occurring simultaneously result in the same outcome as if they had taken place one after the other, without affecting the final state of the database [85]. Durability requires that data within the database can only be changed as a result of a transaction and is not changeable by external influences, such as power failures or software updates [85].
In conclusion, compliance with ACID properties makes a database reliable and consistent, allowing multiple users to access and work on the database without any concerns, reducing manual debugging, and protecting the data from external influences [85].
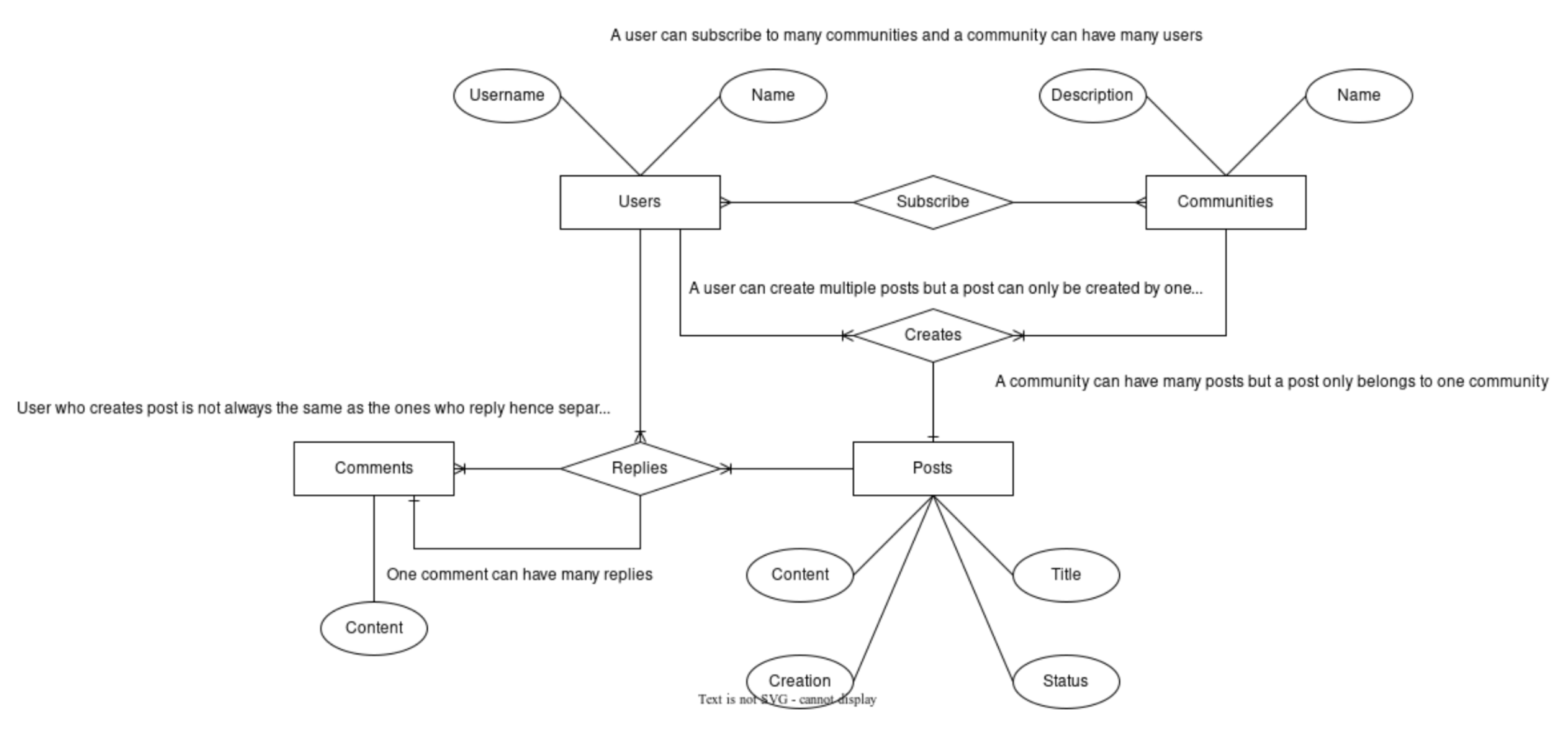
Explanation of the Database
other fields such as email, password and authentication provider but here the base dependencies will be discussed. Each user will have a username which will be publicly viewable by other users
The community entity in the database allows users to create and subscribe to multiple communities. These communities can have multiple users who can subscribe to them, giving them access to the community's posts. The communities can have different visibility settings, including public (where anyone can view and post), restricted (where anyone can view but only subscribers can post), or private (where only subscribers can view and post). However, this feature was not implemented in the database to capture the different visibility
The posts entity in the database represents the content created by users in the communities. Each community will have many posts, but each post only belongs to one community. The posts contain a title, content, and other metadata. Users create posts in a community, which other users can then comment on. This means that a post is created by one user, but a user can create many posts, each belonging to a different community. However, this version of the database does not account for users voting on the post or allowing
The comments entity in the database allows users to respond to the posts. Each comment belongs to both the user who created it and the post it is commenting on. Additionally, each comment can be replied to by another comment, creating a hierarchy of comments. This means that a comment can only belong to a post and optionally to one other comment. The functional dependencies described capture the use cases of the site, including the relationship between the comments, users, and
Normalization
Normalisation is a process of organising the data in a database to avoid redundancy, inconsistency and anomalies [85]. Normalisation involves dividing the data into smaller and simpler tables that are linked by relationships. The benefits of normalisation are:
- It reduces the amount of storage space needed for the data [85].
- It improves the performance and efficiency of queries and updates [85].
- It ensures the integrity and consistency of the data by avoiding duplication and conflicts [85].
- It facilitates the design and maintenance of the database schema by following a set of rules and principles
below is the Mathematical calculations used to normalize the database design to achieve ACID complacency. First Normal Form (1NF) is achieved simply by splitting cells in the database and does not require any mathematical
Functional Dependencies
Functional dependencies are a way of expressing constraints or rules that apply to the data in a database. A functional dependency means that the value of one attribute (or a set of attributes) determines the value of another attribute (or a set of attributes) [86]. For example, if we have a table with student names and IDs, we can say that the student ID functionally determines the student name, because each ID is associated with exactly one name. Functional dependencies are useful for designing and normalizing databases, as they help to avoid data redundancy and
These are the functional dependencies for modelling the data in the database. This will be normalized using various normalization techniques such as Second Normal Form (2NF), and Third Normal Form
R(user_id, username, user_name, community_id, community_name, community_description, post_id, post_content, post_edit_status, post_creation, comment_id, comment_content, tag_id, tag_name) FD = { user_id → username, user_name community_id → community_name, community_description, user_id (Creator), post_id → user_id (Author), post_content, post_edit_status, post_creation, community_id comment_id → comment_content, post_id, user_id tag_id → tag_name, community_id, post_id post_id, comment_id → post_id, user_id post_id, tag_id → post_id, tag_name comment_id, user_id → comment_id (Comment), comment_id (Sub-comment) }
Closures
Closures are a property of relational databases that allow queries to be composed and nested without losing information. A closure means that applying a relational operator to one or more relations produces another relation as a result. This allows complex queries to be built from simpler ones using operators such as selection, projection, join, union, intersection and
(user_id)+ = {user_id, username, user_name} (community_id)+ = {community_id, community_name, community_description, user_id, username, user_name} (post_id)+ = {post_id, post_content, post_edit_status, post_creation, community_id, community_name, community_description, user_id, username, user_name} (comment_id)+ = {comment_id, comment_content, post_id, post_content, post_edit_status, post_creation, community_id, community_name, community_description, user_id, username, user_name} (tag)+ = {tag_id, tag_name} (comment_id, tag_id)+ = {comment_id, comment_content, tag_id, tag_name, user_id, username, user_name, community_id, community_name, community_description, post_id, post_content, post_edit_status, post_creation}
Second Normal Form (2NF)
Helps achieve Consistency by organising the data such that each non-key attribute is dependent on the entire primary key, rather than just a part of it [87]. This helps to eliminate redundancy and ensure that each piece of data is stored in a single location, making it easier to maintain the consistency of the data over time. In other words, 2NF helps to ensure that a database satisfies the consistency property of ACID by reducing the chances of inconsistencies and anomalies that may arise from duplicate data
Requirement: Every non-primary-key attribute is fully functionally dependent on the primary
R(comment_id, tag_id, comment_content, user_id, username, user_name, community_id, community_name, community_description, post_id, post_content, post_edit_status, post_creation)
Closures
Original
(comment_id, tag_id)+ = { comment_id, comment_content, tag_id, tag_name, user_id, username, user_name, community_id, community_name, community_description, post_id, post_content, post_edit_status, post_creation }
Partial Functional Dependency
(comment_id)+ = { comment_id, comment_content, user_id, username, user_name, community_id, community_name, community_description, post_id, post_content, post_edit_status, post_creation } (tag_id)+ = { tag_id, tag_name, }
Relations
R(comment_id, tag_id) R1(comment_id, comment_content, user_id, username, user_name, community_id, community_name, community_description, post_id, post_content, post_edit_status, post_creation) R2(tag_id, tag_name)
Third Normal Form (3NF)
Helps achieve the Consistency property by reducing data redundancy and eliminating inconsistencies in the data [88]. By removing redundant data and ensuring that data is stored only once, 3NF helps prevent data anomalies and ensures that data is always consistent. In other words, 3NF ensures that the data in a database is accurate, consistent, and in a well-structured format, which helps to maintain the overall reliability and integrity of the data in the database
Requirement: There is no transitive dependency for non-prime attribute
R(comment_id, tag_id) R1(comment_id, comment_content, user_id, username, user_name, community_id, community_name, community_description, post_id, post_content, post_edit_status, post_creation) R2(tag_id, tag_name)
Closures
(comment_id)+ = { comment_id, comment_content, user_id, username, user_name, community_id, community_name, community_description, post_id, post_content, post_edit_status, post_creation } (post_id)+ = { post_id, post_content, post_edit_status, post_creation, community_id, community_name, community_description } (community_id)+ = { community_id, community_name, community_description, user_id, username, user_name } (user_id)+ = {user_id, username, user_name}
Relations
R(comment_id, comment_content, post_id) R1(post_id, post_content, post_edit_status, post_creation, community_id) R3(community_id, community_name, community_description, user_id) R4(user_id, username, user_name)
Final Relations
One to Many / Many to One
Users(user_id, username, user_name) Communities(community_id, community_name, community_description, user_id (Creator)) Posts(post_id, post_content, post_edit_status, post_creation, community_id, user_id (Creator)) Comments(comment_id, comment_content, user_id (Creator), comment_id (Reply), post_id (Reply))
Many to Many
Subscribe_Communities_Users(community_id, user_id) Likes_Posts_Users(post_id, user_id) Likes_Comments_Users(comment_id, user_id) Filter_Tags_Posts(post_id, tag_id)
4.2.2 Non-Relational Database (NoSQL)
As mentioned before, the final system uses a non-relational database provided by Firebase called Firestore. The rationale for using Firestore was discussed in Non-Relational Database using on Final System. Firestore is a document database, meaning that it is structured similar to a file system [51]. A collection in Firestore is similar to a folder and can store many related documents, for example, a collection of "users" can store many user objects [51]. These objects, collected into collections, are called "documents" [51]. Documents can also contain sub-collections, which were used in this project to capture certain types of relations when metadata was involved [51]. Since Firestore is a non-relational database, there was no normalization involved in the design
User object in the users collection
The user entity in the system represents the users who interact with the website. Although there are other fields that exist for the user, they are not relevant for the purpose of this description. The user performs various actions within the system, such as creating and deleting posts and creating and deleting comments. This entity is the central piece for the user's interaction with the
- uid: identifies the user
- email: email for the user
- disabled: whether the account is banned
- displayName: name of the user
- emailVerified: whether the email was verified
- passwordHash: hashed password of the user
- providerData: metadata provided if the user signed up using 3rd party provider
Communities object in the communities collection
The communities entity in the system represents the communities that a user can interact with. Each community has a unique name, which serves as its identifier. Each user can subscribe to multiple communities, and communities can have many subscribers. The numberOfMembers field captures the number of subscribers in a community. In a relational database, this would be a derived field, calculated by counting the number of users that are subscribed, but in this case, it is a stored field. This means that the data must be manually updated each time a user subscribes or unsubscribes, but it also means that there is no need for extra computation if only the number of members in a community is needed. The users who have subscribed to a community are stored in the "users" document. The privacyType field stores the type of community, with options for "public" (where any user can view and post), "restricted" (where any user can view posts but only subscribers can post), and "private" (where only subscribers can view and
- createdAt: when the community was created
- creatorId: user who created the community
- imageURL: URL (from Firebase Storage) for the community logo
- numberOfMembers: number of users subscribed to the community
- privacyType: whether the community is ‘public’, ‘private’ or ‘restricted’
Posts object in the 'posts' collection
The posts entity in the system represents the content created by users within the communities. Users can create posts in communities, and other users can view them. Each post belongs to a single community and is created by one user. Posts can be commented on, resulting in many comments for a single post. The number of comments for a post is stored directly for the same reason as storing the number of subscribers in a community. The comments themselves are stored in the "comments"
A post has a title, the body storing the contents of the post, and an optional image, which is stored in Firebase Storage. Posts can also be voted on by other users, with a vote status captured by the field "voteStatus." The overall vote status is stored for the same reason as storing the number of subscribers in a community. When a post is created, its vote status is initialized to 0, as no user has liked or disliked the post. When a user votes on a post, the vote status is incremented or decremented depending on whether the user liked or disliked the post, respectively. The users who voted on a post are stored in a sub-collection in the "users"
- uid: uniquely identifies a post
- title: stores the title of the post
- body: stores the extra description/content of the post
- imageURL: optional image that can be posted
- creatorId: stores the unique identifier of the user who created the post
- creatorUsername: stores the username of creator of the post for quick access
- createTime: when the post was created
- voteStatus: overall vote of the post
Comments object in the 'comments' collection
The comments entity in the system represents the responses to the posts created by users. Users can comment on posts, which can be viewed by other users. Each comment belongs to a single post, and a post can have many comments on it. This entity captures the conversation and discussions related to the posts within the
- id: unique identifier of the post
- postId: identifier to the post the comment belongs to
- postTitle: title of the post the comment belongs to for quick access
- creatorId: identifier of the user who created the comment
- creatorDisplayText: username of the user who created the comment for quick access
- text: comment text itself
- createdAt: time when the comment was created
communitySnippets sub-collection in the users collection
The relation between a user and a community is represented in the database. As mentioned earlier, a user can subscribe to multiple communities, and a community can have many users subscribed to it. The user objects are stored in the "users" collection, and these objects contain a "communitySnippet" collection that represents the relations between the user and the communities. The community snippet objects are stored in the following format: "user/userId/communitySnippet/communitySnippetObject". This means that a user can have many community snippet objects, representing multiple
There is some data repetition in this structure for data that is frequently used, such as the relation between a user and a community. If a user is the creator of a community, they are considered the admin. This information is stored in the community snippet object, allowing for quick access to the information without the need for complex computations or
- communityId: identifier of the community the user is subscribed to
- imageURL: logo of the community for quick access
- isAdmin: specifying if the user is the admin of this community
postVotes sub-collection in the users collection
As mentioned earlier, a user can vote on posts in the system. This means that multiple users can vote on multiple posts. The information about a user's votes is stored in a sub-collection within the "users" object, representing the list of all votes the user has made for posts. The overall post vote status is stored in the post object. Whether the post was liked is stored in "postVotes," and the value of "voteValue" is used to calculate the overall value of the post votes. This structure allows for easy tracking of the votes made by each user and the overall vote status of each
- communityId: identifier of the community the post being liked belongs to
- postId: identifier to post being voted on
- voteValue: whether the post was liked (+1) or disliked (-1)
4.3 Features of the End System
All the features and todos have been kept track with using GitLab’s built-in features. Boards was used to keep track of the planned features that need to be implemented. Issues was used to keep track of new feature requests or bugs.
Many of the planned features have been implemented. Features have been implemented in order of priority specified in the User Stories section. Tags have been created for keeping track of the fully functional features and sub-features.
4.3.1 Authentication and Account Management
The system has several key user authentication and account management features designed to ensure that users have a seamless and secure experience:
- Users can sign up using email and password
- Users can sign up using third party authentication providers such as Google and GitHub
- Users can log in using email and password
- Users can log out
- Users can reset their password
- Users can modify their profiles (profile image and username)
Sign Up Screen / Modal
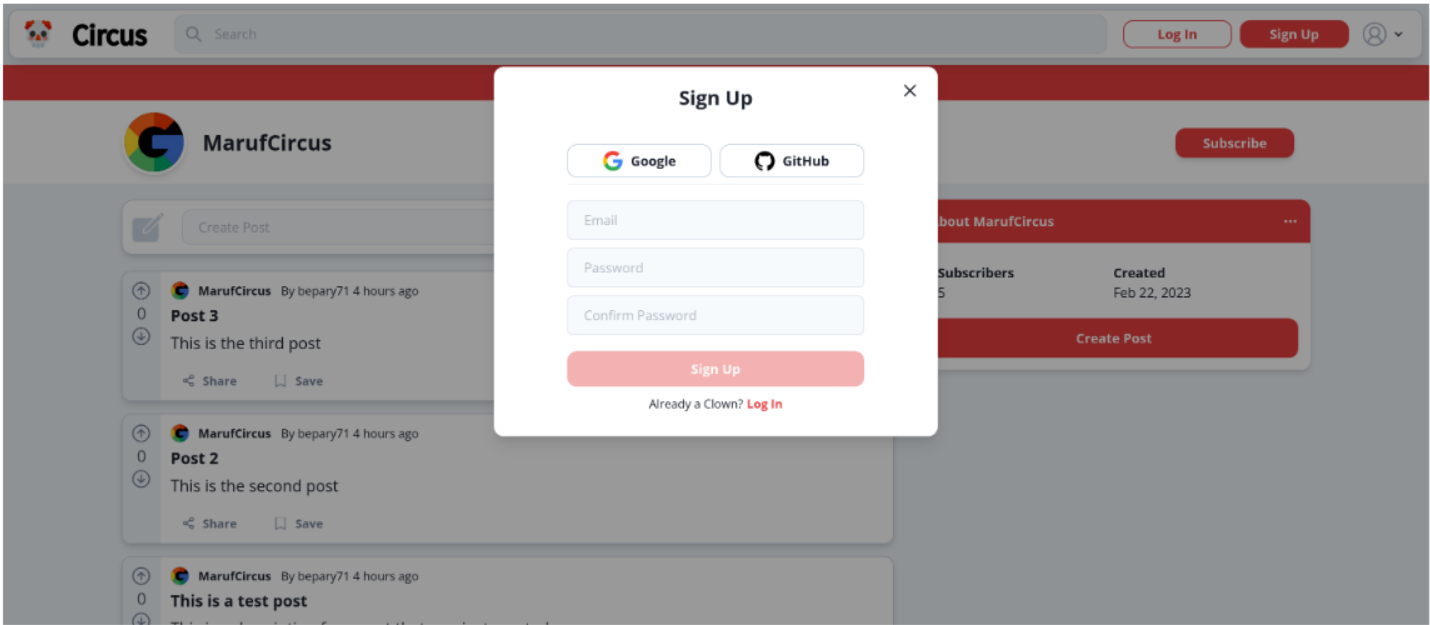
Users can sign up using their email address and a secure password, providing them with access to all of the application's features and functionality.
To make the sign-up process even more convenient, users can also sign up using third-party authentication providers such as Google and GitHub. This approach saves users time and effort, as they can quickly log in using their existing credentials and start using the application right away.
Log In Screen / Modal
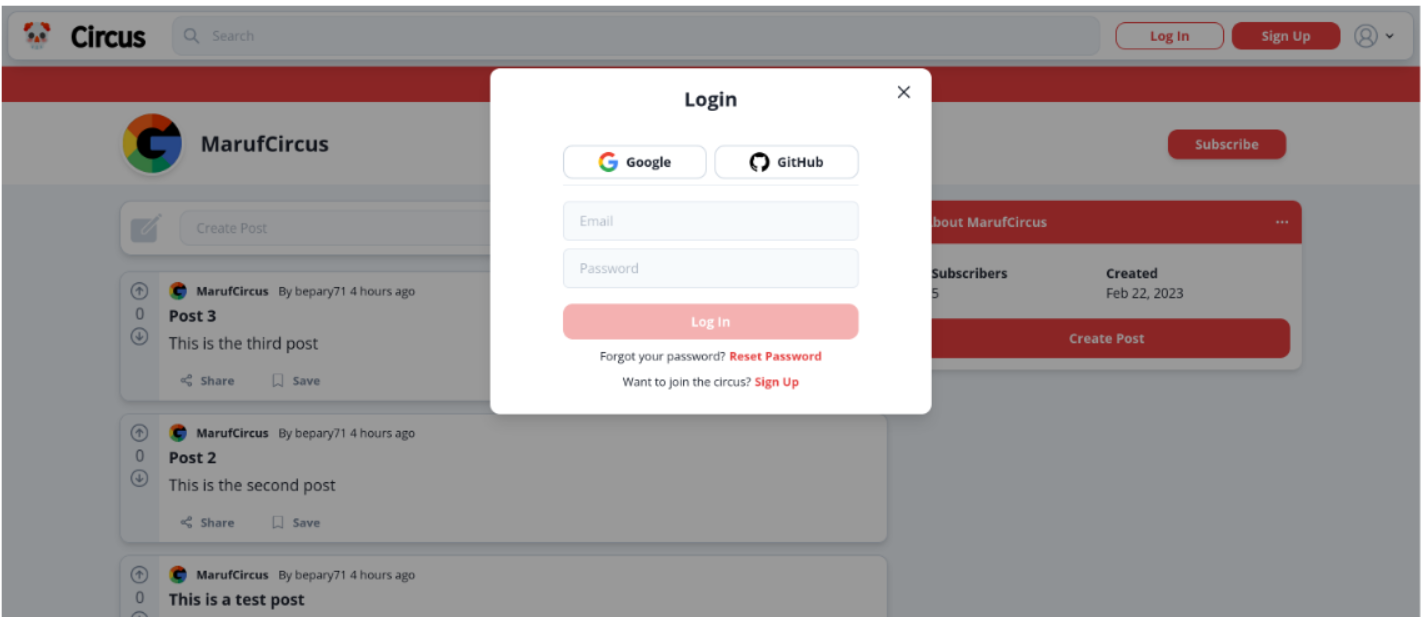
For users who have already created an account, they can easily log in using their email and
Profile Management Screen/Modal
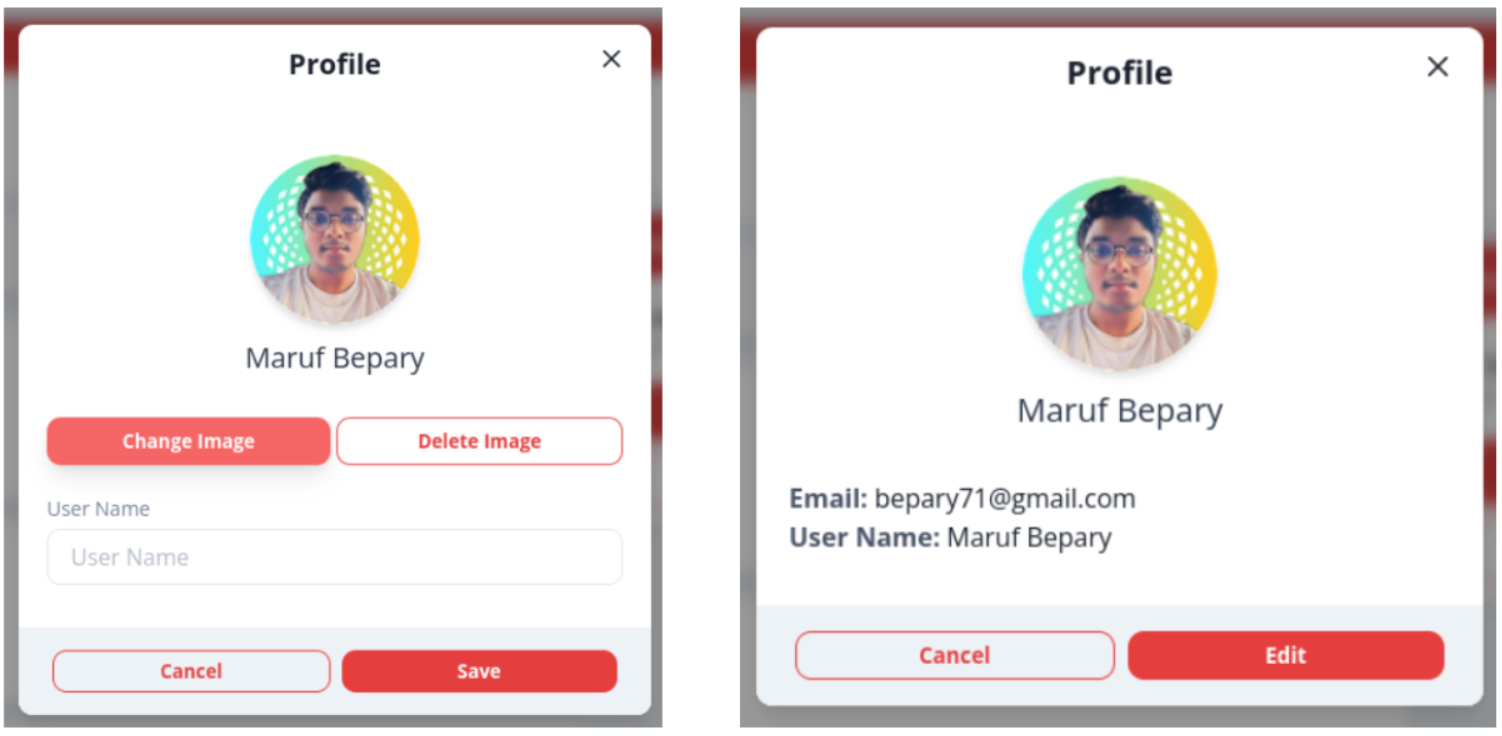
Once logged in, they can access all of their account information and settings, including the ability to modify their profile information such as their profile image and
Logging Out
To ensure the security of user data, users can also log out of their account at any time.
Resetting Password
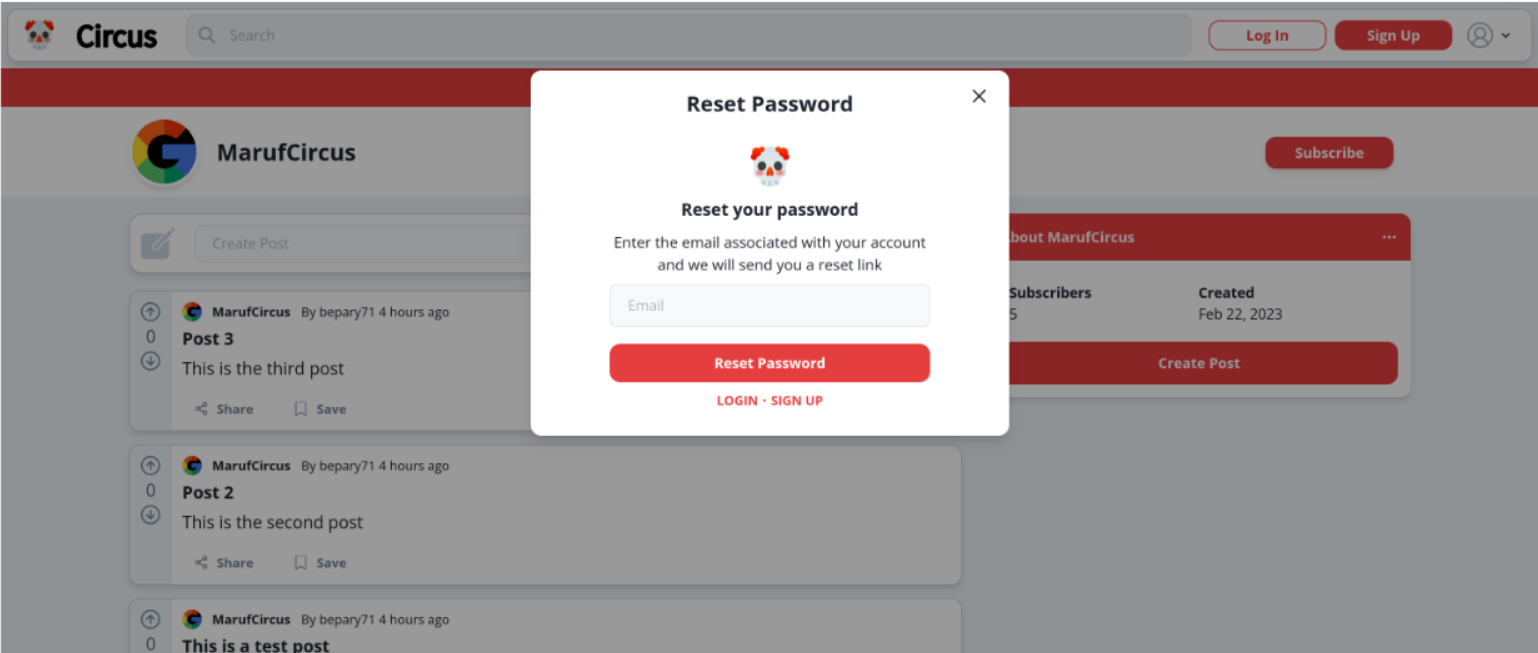
In addition, if users forget their password, they can reset it easily using the password reset functionality, which sends them an email with instructions on how to reset their
4.3.2 Community
The system has several key community management features designed to promote engagement and collaboration among
- Users can create communities (different types)
- Users can subscribe and unsubscribe to and from a community
- Admins can change the community logo
- Admins can change community visibility
- Users can view all public and restricted communities
Creating Community
Creating Community
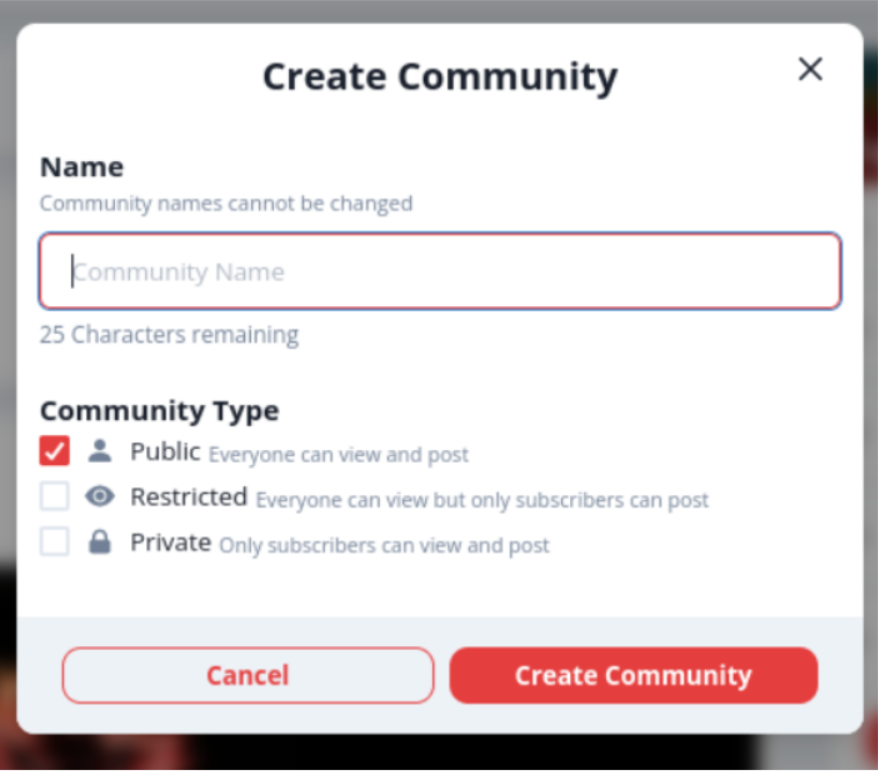
Users can create different types of communities, allowing them to connect with others who share similar interests, goals, or
Subscribing & Unsubscribing
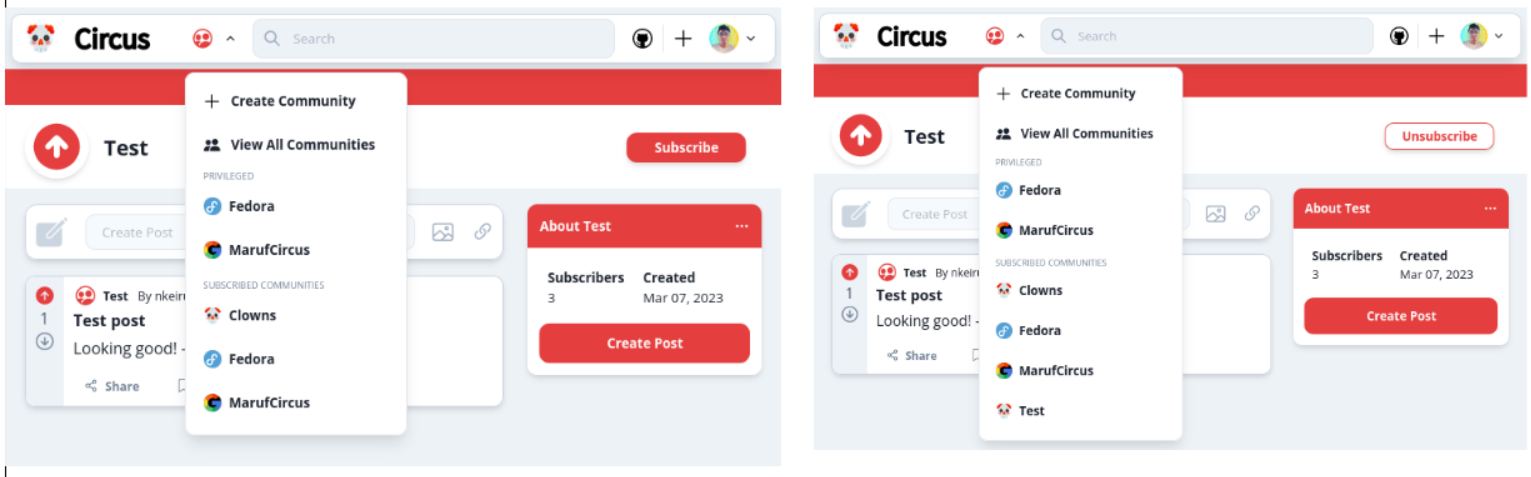
To participate in a community, users can subscribe or unsubscribe to and from it. This approach provides users with control over their community involvement, allowing them to focus on communities that are most relevant to their
Community Settings

Community administrators have additional functionality, such as the ability to change the community logo. This feature allows administrators to customize the community's appearance, making it more visually appealing and recognizable to
Administrators can also change community visibility, allowing them to control who can see and access the community. This feature is particularly useful for communities that have specific membership criteria or that deal with sensitive or confidential
To make it easy for users to discover and join communities, the web application provides a comprehensive view of all public and restricted communities. Users can browse and search for communities based on various criteria, such as topic, size, and membership
4.3.3 Posts
The system has several key features designed to make it easy for users to create and view posts within communities:
- User can create a post in a specific community with an optional image
- User can view all posts from a community
- User can view posts from subscribed communities
- User can delete a post they have created
- User can vote on a post
- User can share a post
Creating New Posts
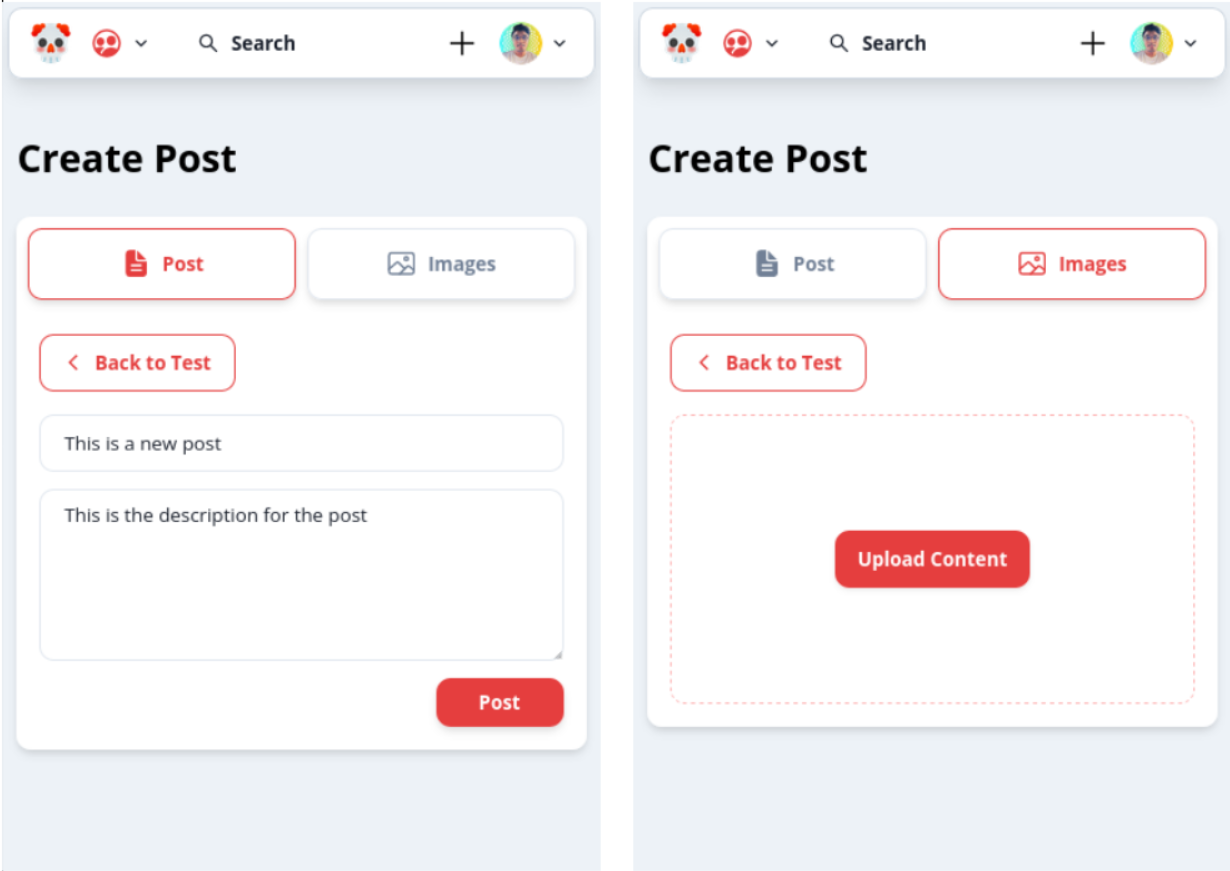
Users can create a new post in a specific community, providing them with a targeted audience for their content. They can also add an optional image to their post to make it more visually appealing and
Viewing Posts from Community Page
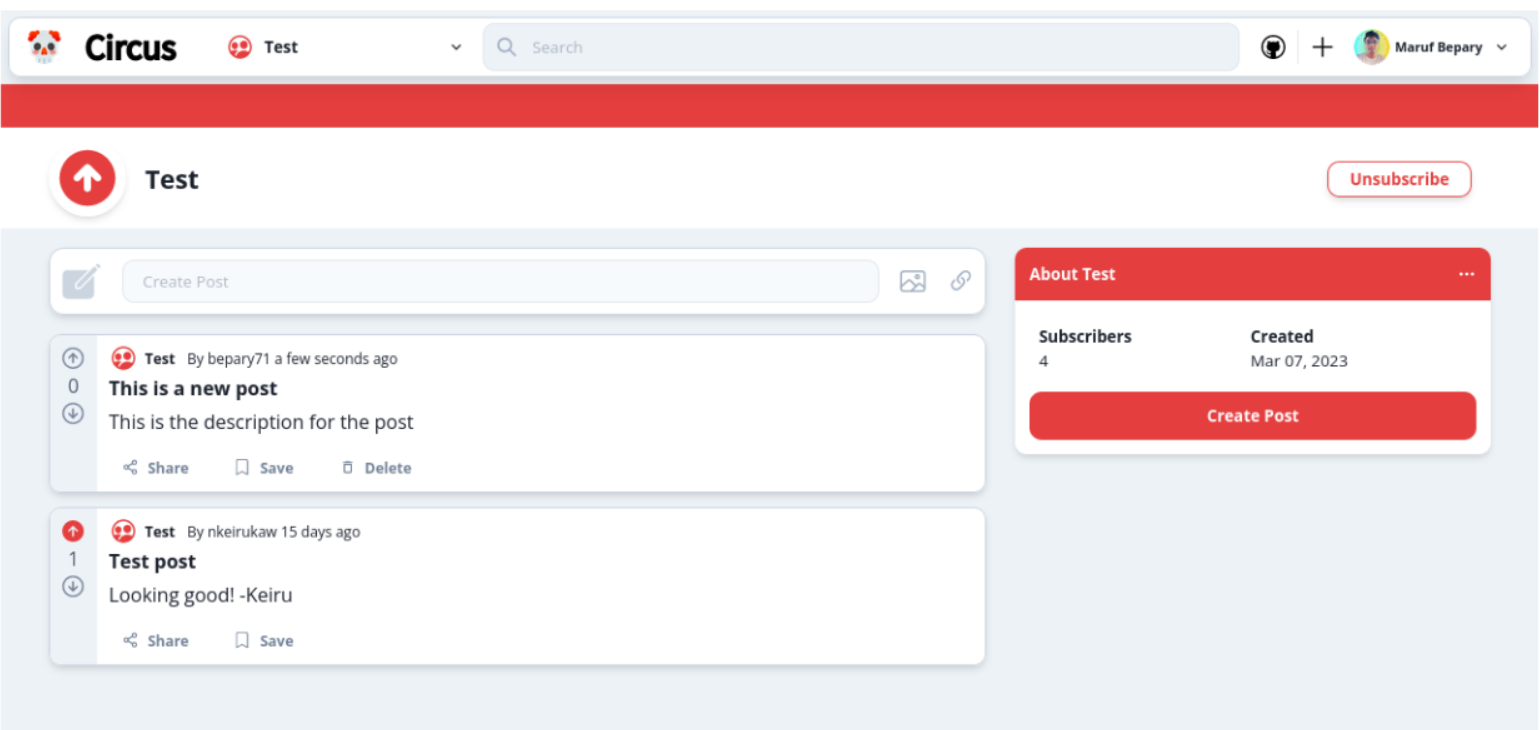
To stay up-to-date with the latest posts in a community, users can view all posts from a specific community. This feature provides users with an overview of the latest content in the community, enabling them to engage with others and stay informed on relevant
Viewing Posts from Subscribed Communities in the Home Page
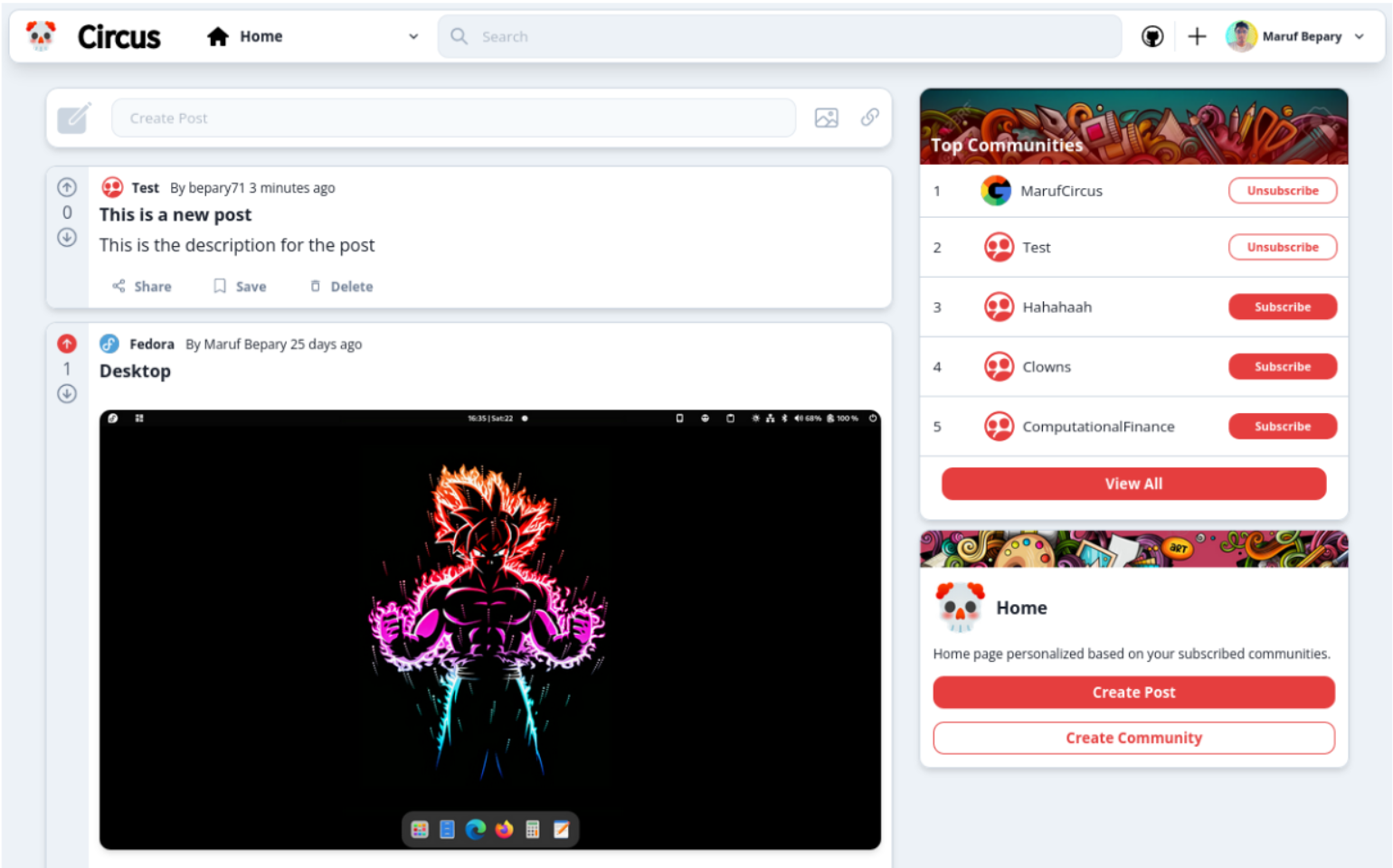
Users can also view posts from subscribed communities in their home feed, ensuring that they never miss an important post from a community they are interested in. This feature helps users stay connected to the communities they care about, without having to manually check each community for new
Deleting Posts
Users can delete posts that they have created. This feature is particularly useful for managing content that is no longer relevant or accurate, ensuring that communities stay up-to-date and relevant. Other users cannot delete a post they have no
Voting (Liking & Disliking)
Users can also vote on posts, indicating their approval or disapproval of the content. This feature provides valuable feedback to post creators, helping them to understand what type of content resonates with their audience and what does
Sharing Posts
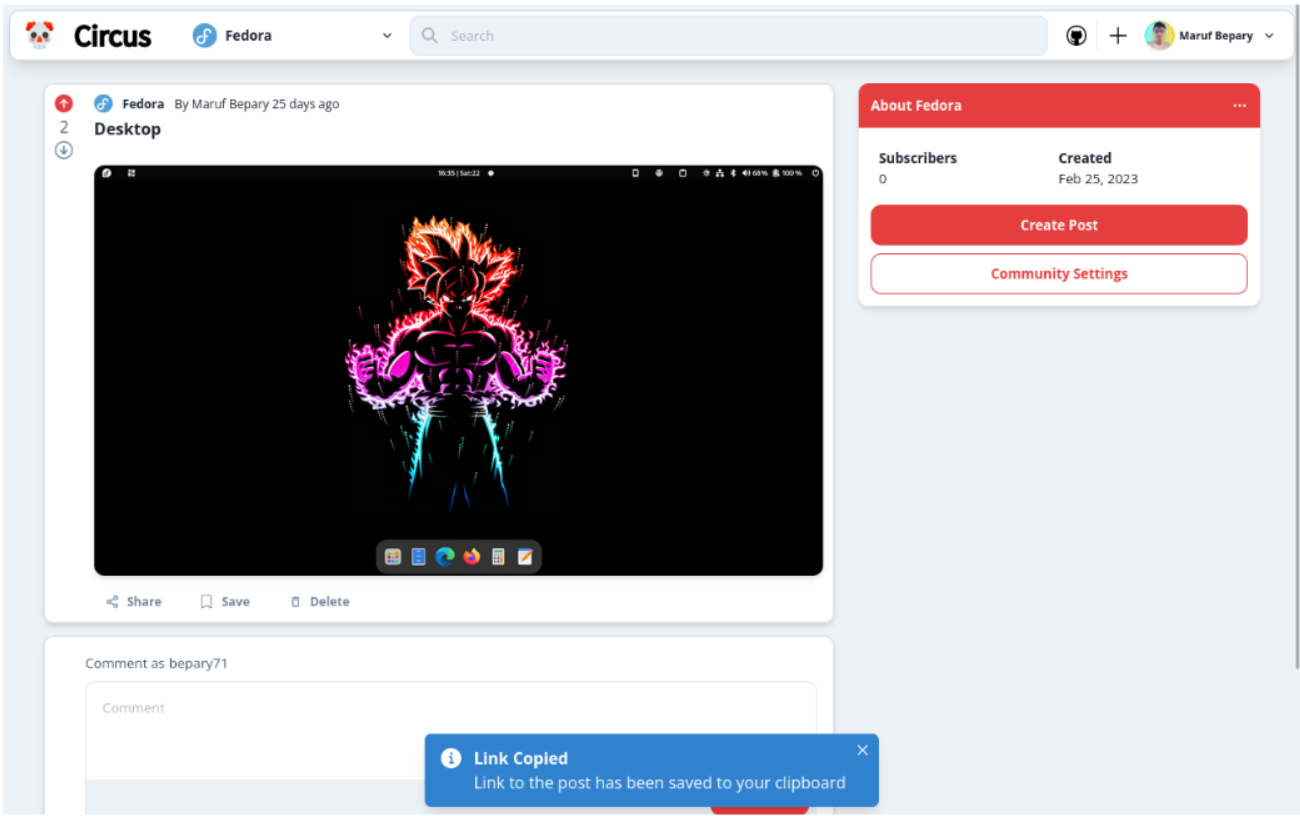
Users can share posts (by sending links to posts), enabling them to share valuable content with others and promote meaningful engagement within communities. This feature provides users with an easy way to share relevant content with their network, contributing to a vibrant and engaged
4.3.4 Comments
The web application has several key features designed to make it easy for users to engage with others by creating and viewing comments:
- User can create a comment to reply to a post
- User can view comments in a post
- User can delete a comment they created
Creating Comments
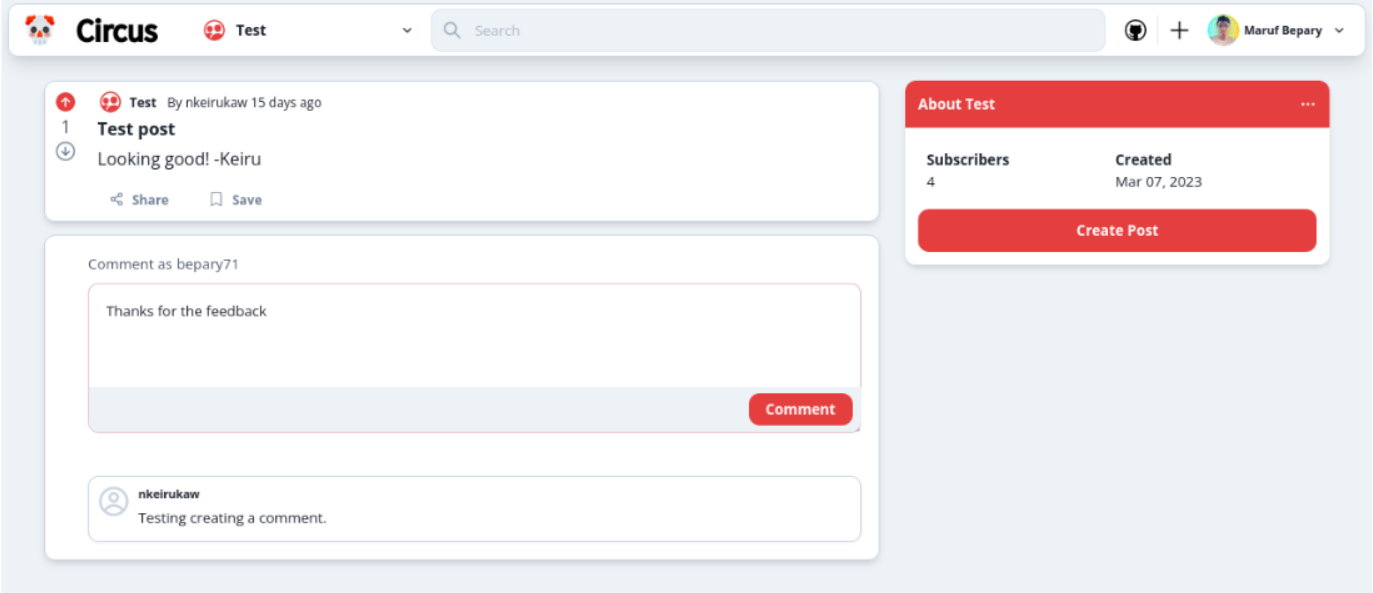
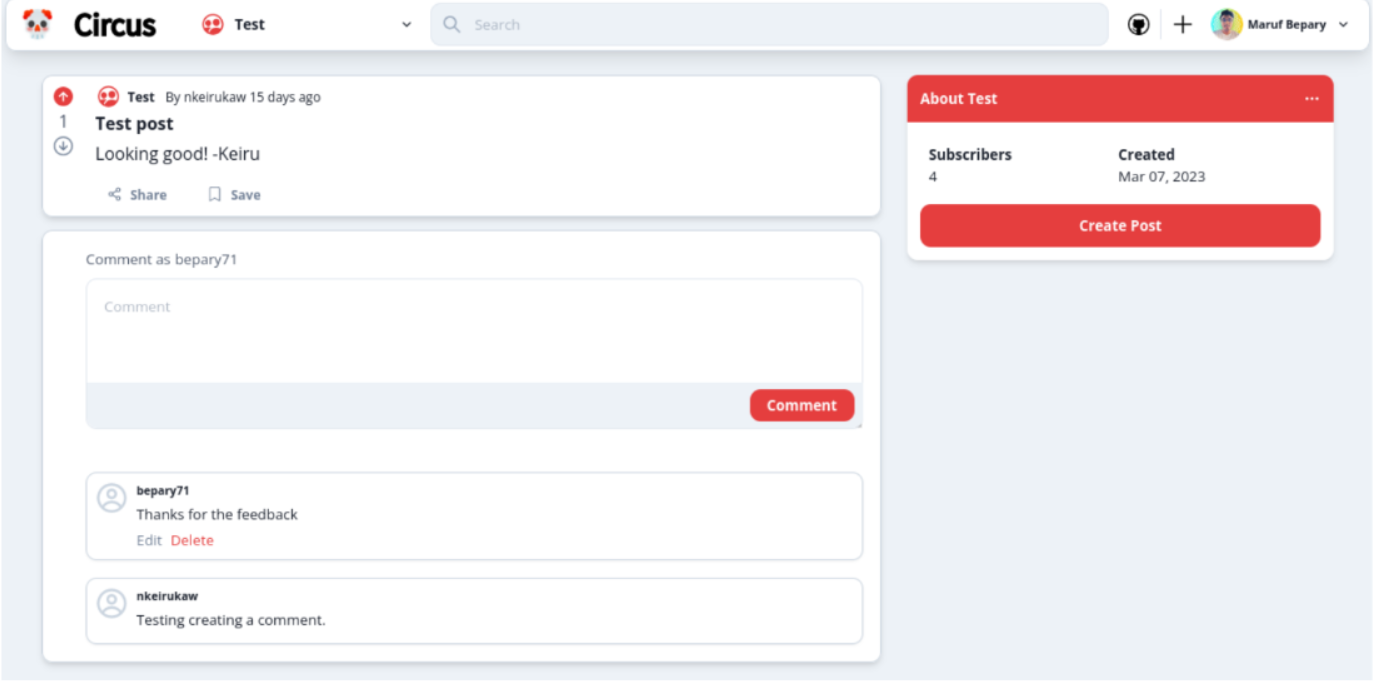
Users can create a new comment in response to a post, enabling them to share their thoughts and feedback with
Viewing Comments
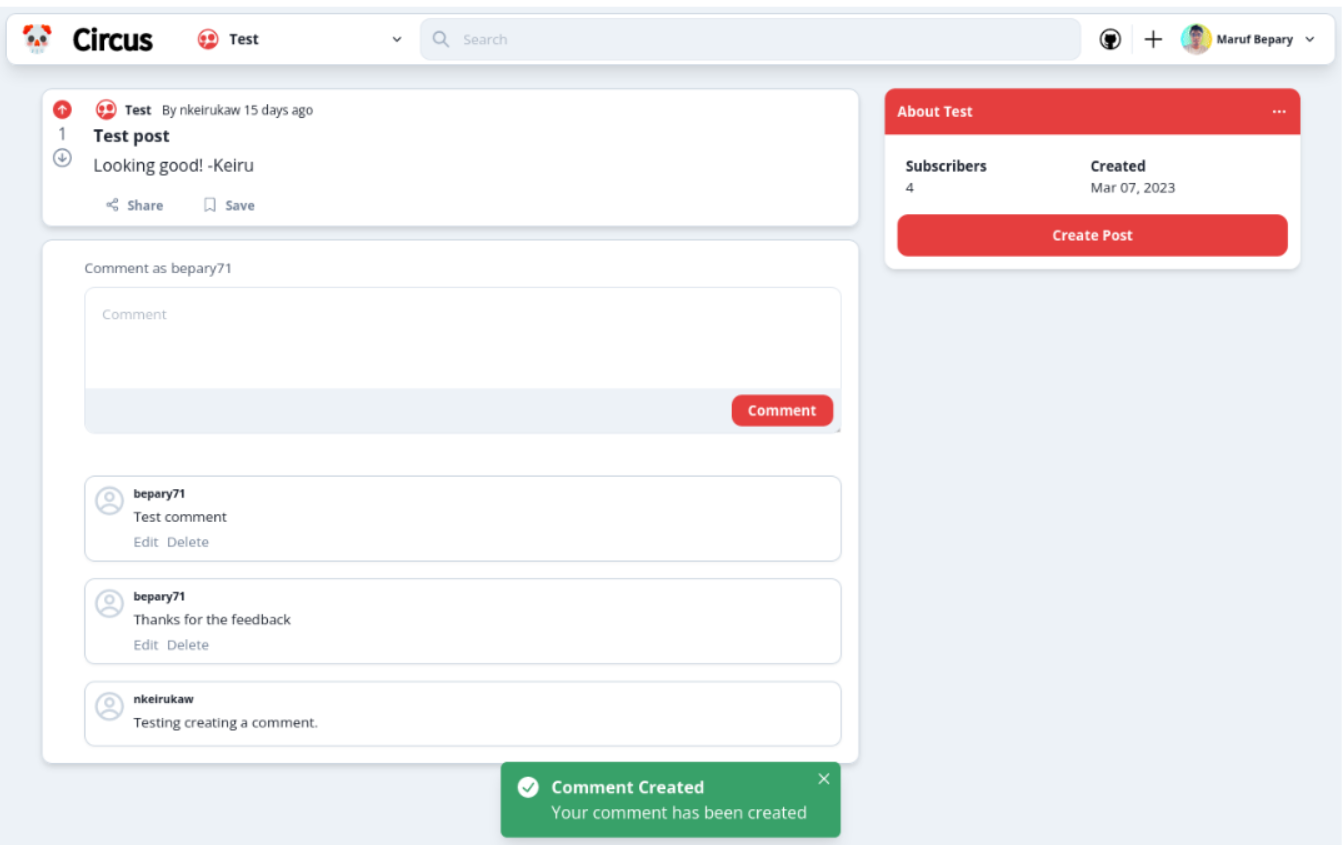
To view comments associated with a post, users can access the post and see all of the comments that have been created in response. This feature provides users with a comprehensive view of the conversation around the post, allowing them to engage with others and stay informed on relevant
Deleting Comments
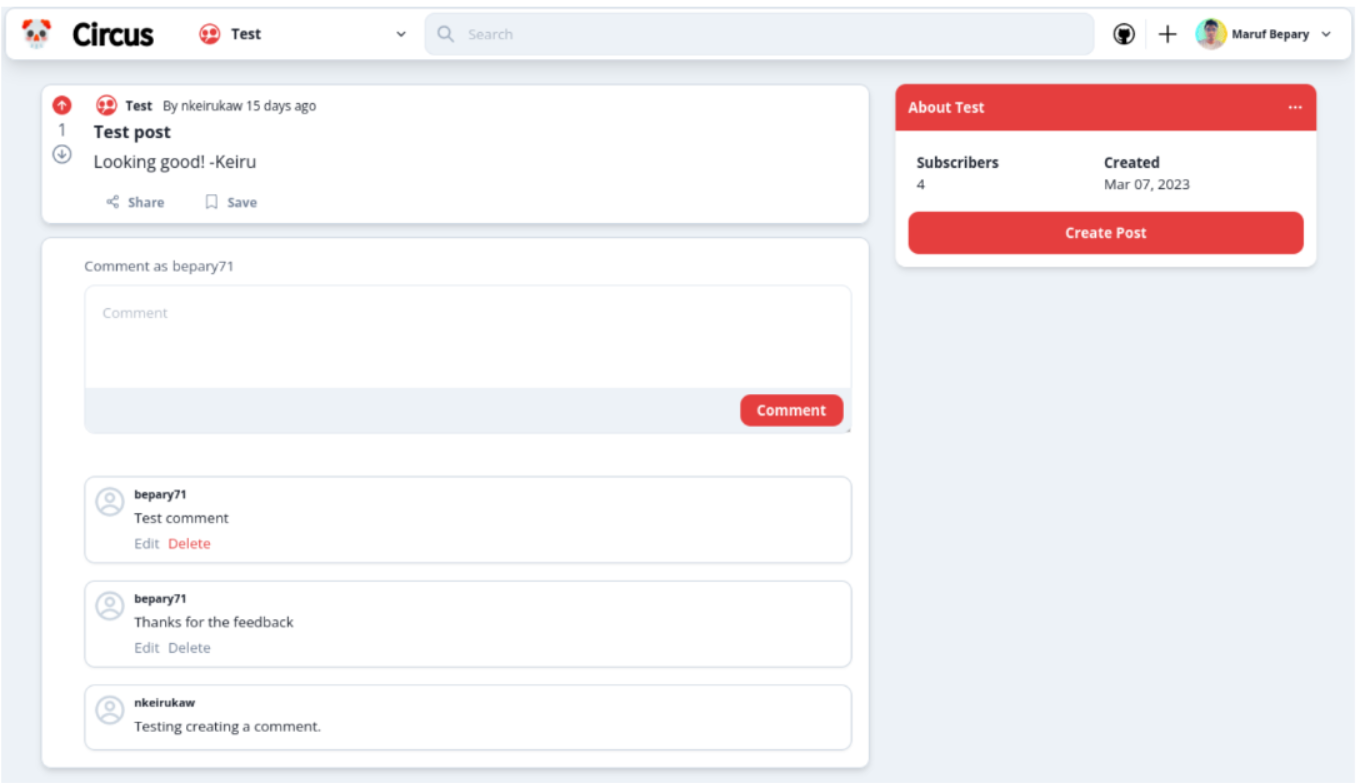
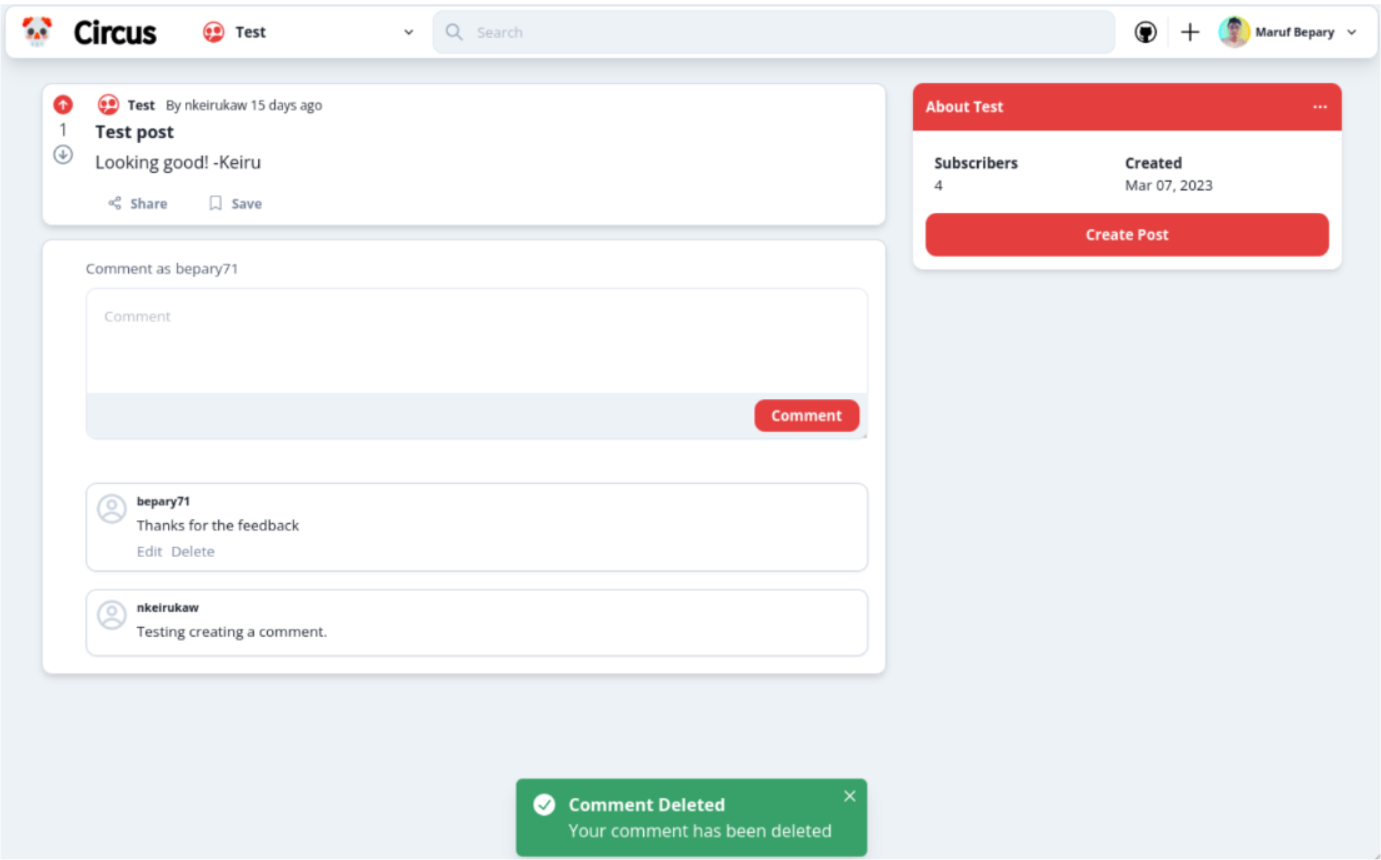
Users can also delete comments that they have created. This feature is particularly useful for managing content that is no longer relevant or accurate, ensuring that comments stay up-to-date and relevant. Other users cannot delete comments they have not
4.4 General:
The system has several general features to make the site user friendly and accessible
- Logged in users can view posts from various communities they are subscribed to in the home feed
- Logged out users can view posts from all communities in order of likes
- System UI is responsive hence it can be used on smartphones, tablets or computers
Home Feed for Logged in Users
Users can also view posts from subscribed communities in their home feed, ensuring that they never miss an important post from a community they are interested in. This feature helps users stay connected to the communities they care about, without having to manually check each community for new
Home Feed for Users Who Are Not Logged In
For users who are not logged in, they can still view posts from all communities in order of likes. This feature enables non-logged-in users to browse and search through the most popular posts across all communities, providing them with valuable insights and information even if they are not subscribed to any specific
Responsive Interface
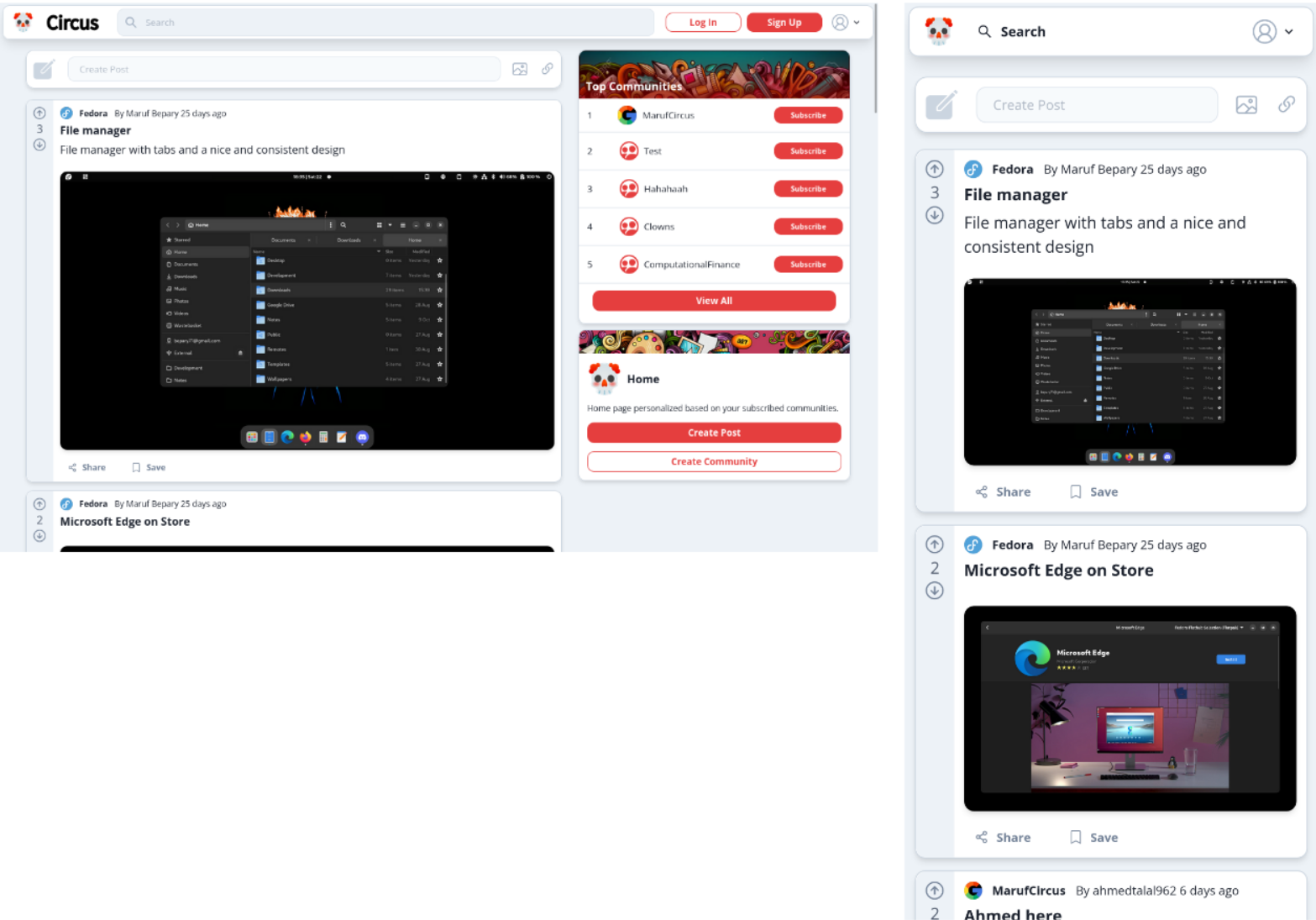
To ensure that the user interface is accessible to all users, the system UI is responsive and can be used on smartphones, tablets, or computers. This feature ensures that users can access and use the application regardless of the device they are using, enhancing the overall user experience and
4.4 User Interface
e has been designed using usability principles while making
g it visually
4.4.1 Background Blur
Background blur has been used for modals and popup windows in this application for many different reasons:
- Improved focus: Blur backgrounds help to draw the user's attention to the content within the modal or window by creating a visual separation from the main interface. This can make it easier for users to focus on the task at hand, and can also reduce distractions from other elements on the screen [94].
- Enhanced readability: Blur backgrounds can also help to improve the readability of text and other content within the modal or window. This is because the blurred background acts as a subtle backdrop that reduces the contrast between the text and the background, making it easier on the eyes and reducing eye strain [94].
- Increased perceived depth: Blur backgrounds can add a sense of depth to the interface, making it feel more three-dimensional and immersive. This can help to create a more engaging and visually appealing experience for users.
- Improved aesthetics: Blur backgrounds can also contribute to the overall aesthetic appeal of the interface, making it look more polished and professional. This can help to increase user trust and confidence in the application, and can also make the interface more enjoyable to use
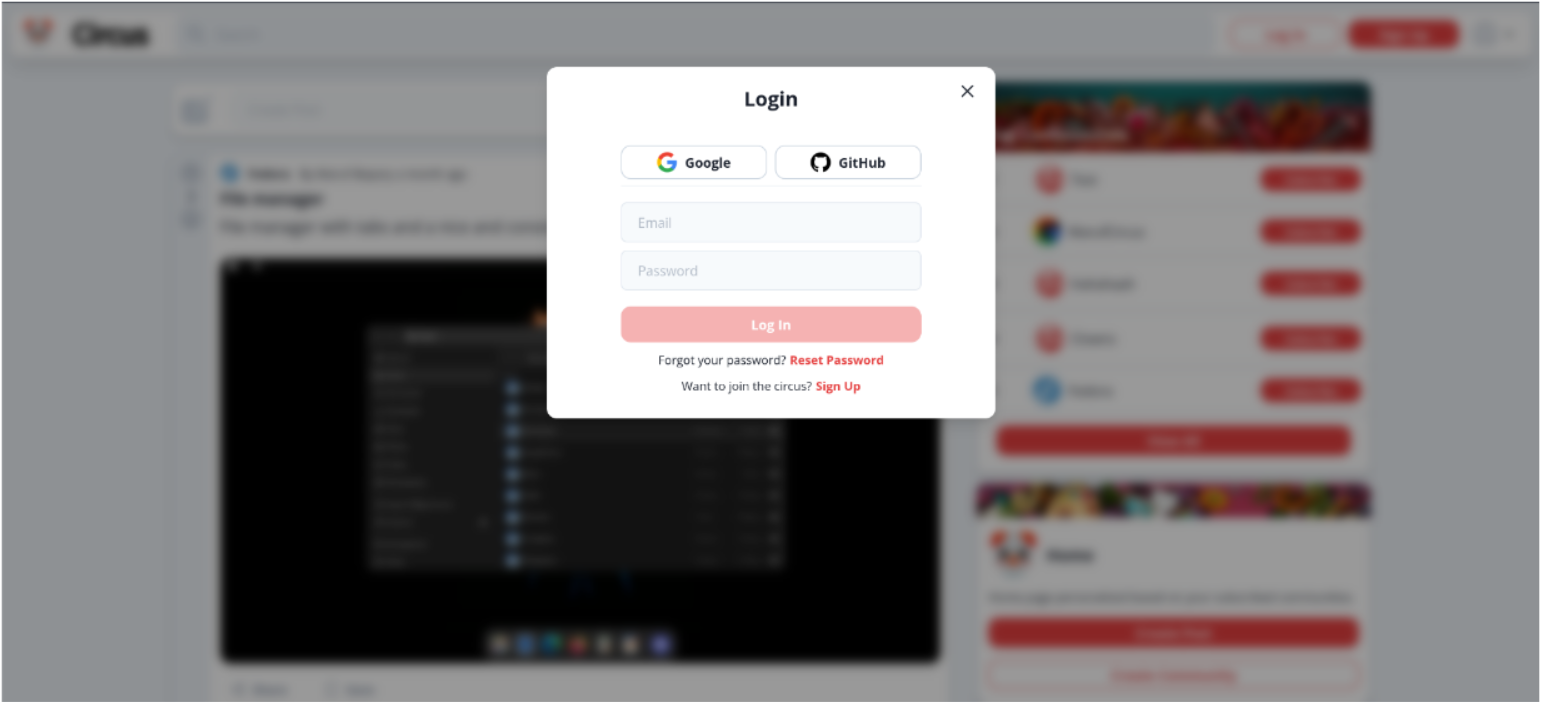
4.4.2 Typography
Typography is also a technique that was used for making the system more accessible and visually pleasing:
- Bold headings: By using bold headings, the designer is emphasizing the most important information on the page and making it easy for users to quickly identify the main sections of content. This can help to create a visual hierarchy and make the interface more readable and accessible [95].
- Gray for less important information: The use of gray for less important information helps to de-emphasize this content and create a clear distinction between what is most important and what is secondary. This can make it easier for users to quickly understand the structure of the page and find the information they are looking for
- Bold links with red accents: By making links bold and using a red accent color, the designer is making them stand out and easy to find. This can help to improve the discoverability of links and encourage users to interact with them. The use of red also helps to reinforce the color theme of the application and create a consistent visual style
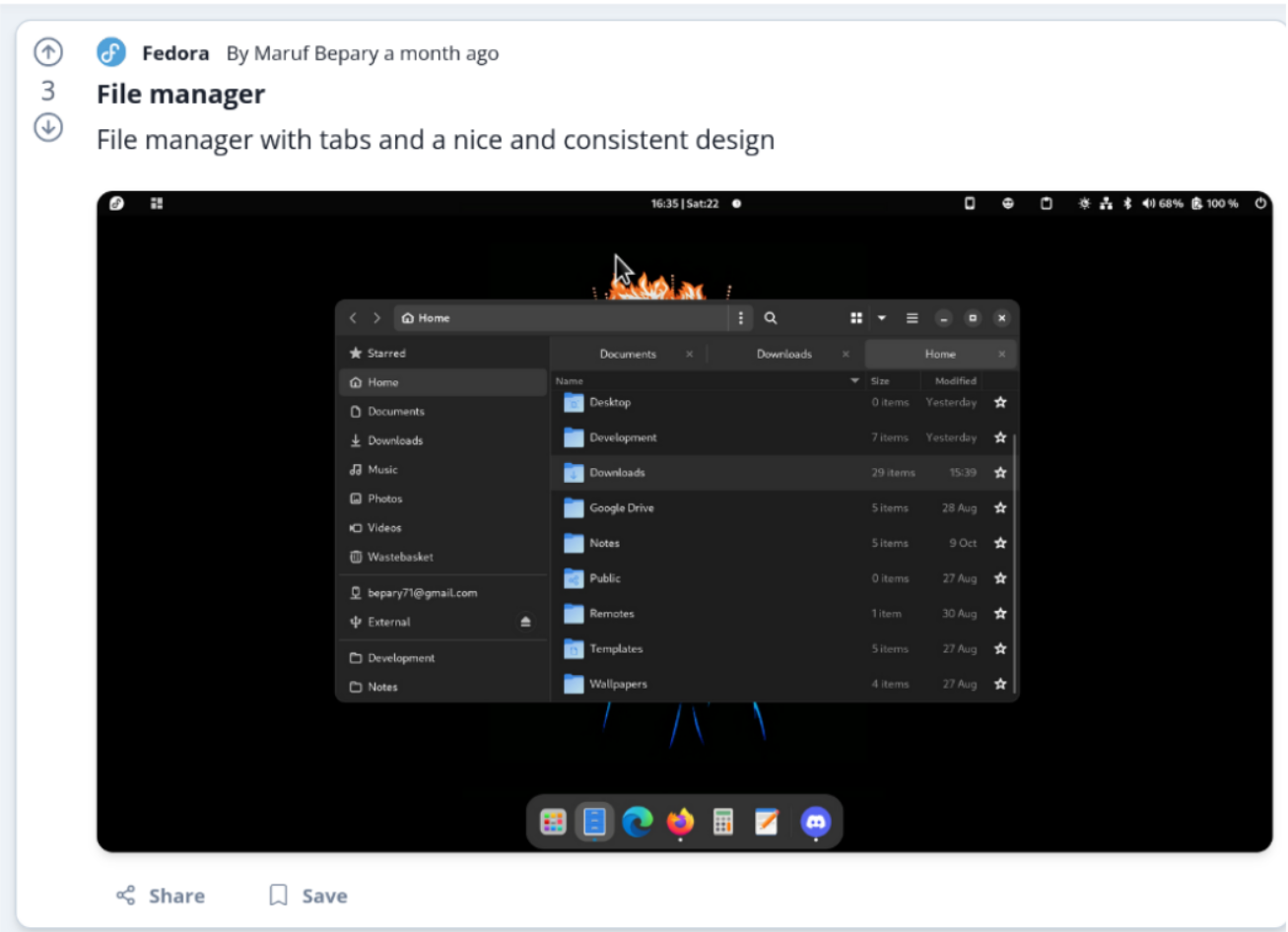
4.4.3 Responsive UI
Responsiveness is a technique that was used in this project to adapt the interface to different form factors, such as computers, phones, and tablets [96]. The goal of responsiveness is to create a seamless user experience regardless of the device being used, and to ensure that the content and functionality of the website are accessible and usable on a variety of devices and screen sizes [96]. In this project, Chakra UI was used as discussed in the Front-End Technologies section. This is discussed in more detail in the Features of the End System
In this project, flexible grids systems were utilised to structure the content on the page. The grid adjusts dynamically based on the size of the screen, ensuring that the content is rearranged in the most optimal way for the available space
Media queries were also utilised to apply different styles to the website based on the characteristics of the device being used [96]. For instance, when changing the font size and hiding certain elements on smaller screens to provide a better user experience
Finally, for touch devices, touch-friendly interactions like tap targets, swipe gestures, and pinch-to-zoom were designed [96]. These interactions provide an intuitive and accessible experience for users, making the website easy and enjoyable to use on all devices
4.5 Future Enhancements
There are some features that are yet to be implemented which hold lower priorities, these are mostly priority 3(least important) according to the user stories. Most of these were not captured by user
These functionalities can be assigned a difficulty rate giving a rough estimation of how difficult it would be to implement such features:
- Low Difficultly
- Medium Difficultly
- High Difficulty
below is a list of features, functionalities and enhancements that can be added for the future:
- Only allow verified users to create create content (post or comment)(2)
- Add functionality for users to manage communities such as add and change descriptions to clarify what the community is about (1)
- Add functionality for users to reply to other comments to have deeper and more organised discussions (3)
- Add functionality for users to edit posts and comments if they want to change any mistakes (1)
- May lead to abuse if the content is changed too much hence it is not certainty
- Will lead to less transparency in the community
- Add functionality to save and add tags to post for better organisation and reference of content (2)
- Add funtionality to manage user profile to modify usernames, password or change profile picture (2)
- Add functionality for users to moderate content if there is inappropriate or offensive content (3)
- Users report of on a post or comment and at a certain point, it will automatically be deleted
- Add a search functionality to quickly search for communities and posts in a community (3)
- Adding notifications if other users reply to a post created by a user or for other updates (3)
4.6 Running the Site
The site has been deployed on Vercel and it is fully operational:
https://circus-discussion.vercel.app
Chapter 5: Assessment & Evaluation
5.1 Profession Considerations for this Project
developer wanted to ensure that our users could create and access their accounts securely and conveniently. Proper password security measures were handles by Firebase who already tested their system and ensured that it meets the technical and legal requirements. Features such as password strength were implemented forcing the user to create appropriately strong passwords.
5.1.1 Security & Privacy
information of its users [89]. When a website stores passwords in an insecure manner, such as saving them in plain text or using a weak encryption method, it leaves them vulnerable to attacks like hacking or data breaches [89].
Hackers can gain access to sensitive information like user names, passwords, email addresses, and other personal details, which can be used for identity theft, fraud, or phishing attacks. This can
using secure password storage methods, such as hashing and salting, and implementing robust authentication and authorization systems. Additionally, developers should also consider using tools like password managers and two-factor authentication to further strengthen the security of the website [89].
passwords using an outdated encryption method that was easily crackable [90]. This resulted in the personal information of all three billion of its user accounts being compromised, leading to
using secure password storage methods, implementing robust authentication and authorization systems, and considering tools like password managers and two-factor authentication to strengthen the security of the website. This helps to protect user information and avoid the serious
5.1.2 Legal
Good password management is also important from a legal perspective, as failing to properly manage user passwords can result in serious legal consequences [91].
(GDPR) in the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, that require organizations to protect the personal information of their users . If a website fails to properly manage user passwords and a data breach occurs, the organization may be held legally responsible for the loss of sensitive information and may face fines, lawsuits, and negative publicity [91][92].
application [91][92]. For example, if a developer is building a web application and fails to implement proper security measures, such as using secure password storage methods or
implementing robust authentication and authorization systems, they may be held liable for any security breaches that occur as a result
The 2013 data breach at Yahoo had significant legal consequences in addition to its impact on the company's reputation and finances. Due to the nature and scale of the breach, Yahoo faced multiple lawsuits from affected users and state attorneys general, who accused the company of failing to properly protect user information. The company was also required to pay substantial fines as part of settlement agreements [90][92]. In addition, the data breach at Yahoo was a clear violation of privacy and data protection laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States. These laws require organizations to protect the personal information of their users and impose significant fines and penalties for data breaches
Therefore, it was important to be aware of the legal implications of poor password management and to prioritize security measures when building a web application. This includes following industry best practices and implementing the necessary security measures to protect user information and avoid legal
5.1.3 Ethical
Good password management is also important from an ethical perspective, as failing to properly manage user passwords can have significant ethical
In an ethical context, organizations have a responsibility to protect the personal information of their users and ensure that their data is handled in a responsible and trustworthy manner [92]. If a website fails to properly manage user passwords and a data breach occurs, this can result in the loss of sensitive information and a breach of trust between the organization and its users
The ethical consequences of poor password management can also extend to the development process of a web application [92]. If a developer is building a web application and fails to implement proper security measures, such as using secure password storage methods or implementing robust authentication and authorization systems, they may be contributing to the loss of sensitive information and violating the trust of users
Therefore, it was important to prioritize ethical considerations when building the system and to take the necessary steps to protect user information and maintain the trust of their users. This includes following industry best practices and implementing the necessary security measures to ensure the confidentiality and privacy of user
5.1.4 Improvements for the Current System
There are several security improvements that can be made to enhance the security of the system:
- Email Verification: Adding email verification to your website can help prevent the creation of fake accounts and reduce the risk of spam and malicious activity. This can be accomplished by requiring new users to confirm their email address before they can access their account.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Implementing 2FA can add an extra layer of security to user accounts by requiring users to provide a second factor of authentication, such as a code sent to their phone, in addition to their password. This can help prevent unauthorized access to user accounts even if their password is compromised
Implementing these features can help ensure the security and stability of the website and provide a safer environment for your users. However, it is important to continuously monitor and update the system's security measures to stay ahead of evolving security
It's worth noting that as an open source project, users are ultimately responsible for their own security and should take steps to protect their own personal information and
5.2 Diary
5.2.1 August 2022
technology has become increasingly important in the development world, as it allows for applications to be packaged and run consistently across different environments. I was able to understand how containers can be used to isolate and manage dependencies, making it easier to deploy and maintain applications.
testing, and deployment of applications. This technology is becoming more and more popular, as it can help to speed up the development process and reduce errors. I was able to understand the
different systems, and how routing can be used to control the flow of requests in an application. This knowledge will be useful as I continue to develop and maintain websites, as APIs and routing
5.2.2 September 2022
In September 2022, I had an idea for a new project and decided to pursue it. I spent some time researching and planning, making sure that I had a clear understanding of what I wanted to achieve
Python framework for web development, and I was eager to learn more about it. I was impressed by its simplicity and flexibility, and I felt confident that it would be the right choice for my project.
JavaScript library for building user interfaces, and it has become one of the most popular choices for front end development. I was excited to learn about its component-based architecture and how it can be used to create dynamic and interactive user experiences.
5.2.3 October 2022
for Python that makes it easier to manage dependencies and packages for a project. I found it to be a useful tool for organizing and maintaining my project, and I was able to start experimenting with different ideas and technologies.
clear roadmap for the project and that I knew what steps I needed to take to reach my goals. I spent some time researching and brainstorming, and I was able to come up with a comprehensive plan.
I had done so far, and I felt confident that I was on the right track. I was excited to move forward with the project and start bringing my ideas to life.
5.2.4 November 2022
how to implement CI/CD pipelines with Docker containers, and GitLab CI seemed like the perfect tool for the job. I was able to understand how to set up pipelines and automate the deployment of my application.
I also realized that I needed to learn data mocking for testing APIs. This is an important technique in software development that allows developers to simulate the behaviour of an API without actually calling the real API. I understood that this would be essential for testing the APIs that I was developing for my project. Mocking using PyTest was relatively simple, especially compared to Jest in
On the 29th of November, I finished experimenting with the Material React library for the front end. I was pleased with what I had learned, but I was also exploring other options as it was not giving the flexability I needed. I was interested in Flutter Web and Svelte, two relatively new technologies that are gaining popularity in the web development community. I wanted to learn more about them and see if they could be a good fit for my
5.2.5 December 2022
In December 2022, I started a new project using Next.JS, TypeScript, Firebase v9, and Recoil3. I wanted to use Next.JS because it provides a more structured development experience and offers features that are not available with regular React. I also wanted to use TypeScript for its static type checking capabilities, which can help catch errors early in the development process. The rational behind choosing these tools is discussed in Technologies (Web Frameworks)
Lastly, I decided to use Recoil for state management. I learned that Recoil provides more advanced state management than React, which is required for this complex application. I was able to understand how Recoil works and how it can be used to manage state in a scalable and efficient way. This was extremely useful to make the site more responsive and it was very simple to
Overall, I was excited to start this new project and put my skills to the test. I was confident that the combination of Next.JS, TypeScript, Firebase v9, and Recoil would help me to create a high-quality, robust
5.2.6 January 2023
In January 2023, I made significant progress on my project. On the 12th, I successfully implemented authentication via Firebase, including log in and sign up, as well as third-party authentication providers. I was pleased with my progress and felt confident in my ability to add more features to the application. The documentation provided by Firebase and react-firebase-hooks was very simple to understand and using Chakra UI to build the frontend was a
However, on the 13th, I encountered a major setback. I attempted to implement password reset, but I ran into a bug that caused the whole project to fail. The bug was too difficult to fix, and I was forced to start over from
Despite this setback, I was determined to keep going. On the 30th of January, I started reimplementing the whole project from scratch. This time, I was able to fully implement authentication, including sign up with email and password, log in with email and password, and the ability to continue with Google and GitHub. I also successfully implemented password reset, which had been a challenge for me
I was proud of my progress and felt that I had learned a lot from my experiences. I was eager to continue building and improving the application, and I was confident that I would be able to overcome any future challenges that came my
5.2.7 February 2023
In the month of January 2023, a lot of progress was made on the project. On the 1st, I implemented the functionality to create a community via a modal. The modal allowed the user to select which type of community should be created (public, private, or restricted) and added checks for the character limit and length of a community name. I also prevented special characters in community
names, as they could be used to create weird communities. Community names are unique and are used as keys. Creating communities was very simple both in the frontend and
On the 5th, I added a project wiki with instructions on how to set up and run the project. This can be used by other people to configure the project and for my future reference. I also added issue templates for bugs and features, which provides a consistent structure for issues and makes it easier to track them. I also added a license. I implemented the functionality to subscribe and unsubscribe to and from
I started adding documentation for community functionality on the 6th and researched about testing techniques for the current stack (Next.JS + Firebase) on the 8th. On the 14th, I added proper password verification which was simple but it required me learning regex, using a library would have been simpler. On the 15th, I finished the implementation and documentation of community functionality. Writing the documentation was tedious but an important step that had to be
On the 16th, I created a post page where users could create posts for a specific community. I also allowed uploading and removing images, which is required for creating posts with images. I added functionality to create posts in the backend and display the posts for a community in the main community page. I also added functionality to delete a post if the user is the creator of the post. This functionality was simple for the most part, but it required a lot of work and it would have been impossible to
On the 18th, I created an "about" component for the community page, which displays information about the community. I made the navbar always visible while scrolling and refactored the upload and delete image into its own hook as it is used by multiple components. I also added functionality for community admins in the "about" component. This was also simple to implement as only some simple data from Firebase had to be fetched. Adding community description would have also been a nice feature but this would have required me to allow the user to insert this description, it would have also required the community state to be updated which could result in complications (since it is a foundational part of the
I fixed a bug with the navbar on the 19th and implemented the functionality to vote on posts on the 20th, this was the most difficult part of the project. This is because implementing voting functionality is a highly relational operation which as discussed in Non-Relational Database using on Final System is not simple to do with Firestore. I was required to store the total number of likes in the post document, store every post the user has voted to in the users, whether they liked or disliked to post and use this to update the overall vote. For example, if the user disliked the post, the vote status of the post (which is stored in the post) would be decremented by fetching the vote (+1 for like or -1 for dislike) from the users collection. If the post was already liked by a user, and the same user dislikes it, then it would be decremented by 2 (to undo the like and then dislike). In contrast, the frontend functionality for this was extremely simple. Furthermore, I also allowed the user to comment which was very simple on a post and fixed a bug where the border for the post item did not match the comment input
On the 21st, I fixed the styling for comments in the single post page and added community functionality to the previous community directory menu component. I also implemented a home feed for unauthenticated users and a homepage for authenticated users. All these functionalities were not difficult to implement as they are continuations of previous
I deployed the site to Vercel on the 22nd after fixing build errors and linting issues, these were very easy to fix but they had to be located from across the application. I fixed a bug where the user would not be able to open a post if they were not authenticated and added documentation up to this point, this was simple to implement by making the user status
In the following days, I worked on general styling for the application, including the user menu, the navbar, the modals, and the page layout. I refactored code to make it more modular and added
missing input field styling. I also implemented the functionality for the admin to delete the community image and added a button to take the user back from the create post page to the corresponding
5.2.8 March 2023
In March, several improvements and bug fixes were made to the website. The UI was refined by adjusting shadows to make the site more legible and improve its overall look. The shadows were used to provide user feedback on focused elements and highlight the importance of certain actions. Implementing these changes was straightforward, as the app was already following accessibility guidelines. Modifications were also made to ensure that the theming of the app was consistent. For instance, the post link and text form for post creation were adjusted to better align with the app's overall
Other enhancements included centering the 'view more communities' button for added symmetry, displaying the user's profile picture in the navbar, and adding a profile modal for users to view details such as their profile picture, email, and username. These features were relatively easy to implement, as they mainly involved fetching data already available in the database. The post creation time display was also updated to show how long ago a post was created rather than the exact time, making it more
The option for users to edit the current community they are visiting was added if they are the admin. While updating the privacy type of the community was easy to implement, updating the community image proved more challenging. This required finding all instances of the current community in the user's subscribed communities and changing the image. Another improvement that could be made is verifying if the current user is subscribed to the community before allowing them to navigate to a private
Several bug fixes were also implemented, such as fixing error messages when using third-party authentication, adding custom toast notifications for user feedback, and fixing a bug where the site would crash if the post link was invalid. Additionally, the ability to share posts by copying the post link to the clipboard was added, and a 'not found' page was created to handle invalid
Users were given the ability to update their community, which included changing or deleting their profile image and changing their username. While these updates were relatively easy to implement, updating the email address and creating a state to store details about the currently logged-in user locally could be considered for future
Towards the end of March, configuring testing proved to be difficult due to unclear documentation and fragmented resources. Efforts to set up testing and mock data to remove reliance on the real backend were carried out up to March
5.3 Self-Evaluation
The purpose of this self evaluation is to reflect on what has been improved since the last time and what could be improved in the future. The evaluator will use specific examples and evidence to support their assessment of their strengths and weaknesses. The evaluator will also identify their goals and action plans for further development and
What can be improved:
- The developer could try to optimize the code more. Even after refactoring the code, it is mentioned that some components were 300 lines, which could make it difficult to understand and modify the code.
- The developer could also try to find more efficient ways to implement features. For example, the voting functionality was extremely difficult to implement despite seeming easy.
- The developer may consider Supabase as an alternative to Firebase as it is more appropriate for this project
- The developer could implement better DI/CD pipelines to make the development process more efficient
What was improved from last time:
- The developer has implemented more features at a high standard compared to the original Python based prototype
- The current system is much more robust than the original one as it is more stable and has fewer bugs
- The current system is better designed compared to the original one the components are of higher quality and the overall layout is better structured
- The overall development was more agile (faster and more flexible)
- The developer has significantly improved their skills in various technologies such as React, Next.JS, Firebase, and TypeScript.
- The developer has also made the code base more modular and efficient by refactoring the code.
- The developer has also added several new features such as a page to view all communities, the option to view all communities in the directory menu, and the ability to create a post from the home
Chapter 6: Project Management
6.1 Risks and Mitigations
There are potential risks that can take place which must be accounted for my implementing mitigation techniques if it is no possible to avoid the risk
Not Finishing on Time
The most likely and serious would be not finishing the project on time. The deadline of the project is strict hence the product must be delivered on time. This risk must be avoided. The plan was to allows for extra time in case there are other risk which increase the time of development. There is a soft deadline 3 weeks before the hard deadline which would allow for extra time in case it is required. Almost all of the major functionalities have been implemented by now meaning the project is complete for the most
Project not Meeting the Requirements/Scope
Projects can often go off track, especially if the requirements and scope are not clearly defined. This can lead to wasted time and resources, as well as disappointment from stakeholders. To mitigate this risk, it is important to have frequent reviews of the project and compare it against the requirements and scope. This allows for the team to catch any deviations early on and make necessary adjustments before it becomes a larger
One way to ensure that the project stays on track is by using a Requirements management tool such as the one built into GitHub and GitLab. This tool allows for the team to clearly define and track requirements and makes it easier to see when the project deviates from the original plan. Another way is to have regular check-ins with stakeholders to ensure that the project is still aligned with their needs and
It is also important to have a clear and effective communication plan in place. This helps ensure that everyone is on the same page and that any changes or deviations are discussed and addressed promptly. Additionally, having a flexible project management approach, such as Agile (which was followed in this project), can also help mitigate this risk as it allows for changes to be incorporated
Technical Failures
Technical failures can have a significant impact on the project and its ability to meet its objectives. When components within the codebase fail, it can lead to unexpected behaviour and errors that can negatively impact the user experience. To mitigate this risk, it is important to have a robust testing process in place. This includes incorporating unit testing into the development process to ensure that each component is thoroughly tested before being integrated into the larger
Unit testing is a critical aspect of software development that involves writing tests for individual components or units of code to verify that they work as expected. By conducting unit tests, developers can catch and fix bugs early in the development process, reducing the risk of technical failures. Additionally, unit tests serve as a form of documentation and can provide confidence in making changes to the codebase in the future. Furthermore, user testing was also carried out to capture any faults in the code that were not captured by unit tests and to receive non-technical feedback about the project such as design of the system, usability, etc. More on Testing to see how it helped in this
Conducting user testing has also helped in this project. This has allowed users to try out the system and find any bugs. From the user testing that was carried out, it does not appear there to be any technical failures in functionality. More on User Testing to understand how it has helped.
Another way to mitigate the risk of technical failures is to implement continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. CI/CD pipelines automate the testing and deployment process, reducing the risk of human error and ensuring that the codebase is always in a deployable state. Furthermore, implementing monitoring and logging can also help identify and fix technical failures quickly, reducing the risk of downtime and improving the overall stability of the system. In this project, Vercel (the deployment provider) has carried out build and lint testing automatically every time there was new code pushed to the repository. This insured that there was a certain level of quality with the product and that it would function correctly in production.
Breaches
Security breaches are a major concern for any online system that stores sensitive user information. In the first prototype of this project where the back-end was custom, the risk of a security breach was mitigated by hashing all passwords and not storing personal information such as names, addresses, and dates of birth. This means that even if a breach were to occur, the information stored in the database would not be easily usable for malicious actors.
In the current system based on Firebase, the security and breach protections and mitigations are handled by Google. Google has a team of security experts who are constantly monitoring the Firebase infrastructure to prevent security breaches and other security-related incidents.
However, it is still important to implement additional security measures to further reduce the risk of a security breach. This can include implementing encryption for sensitive data, implementing access control mechanisms (Firestore Rules) to restrict access to sensitive data, and regularly conducting security audits to identify potential vulnerabilities in the system. By implementing these measures, the project can ensure that user data is protected and that the risk of a security breach is minimized.
Disasters
In case of disasters such as natural calamities, power outages, or other events that can impact the infrastructure, the current project has several mitigations in place. Firstly, the codebase is stored on Github and Gitlab, which provide robust version control and disaster recovery capabilities. In case of data loss or system failure, the codebase can be recovered from these platforms.
Moreover, the backend of the system is handled by Google and its Firebase platform, which has a proven track record of providing reliable and secure infrastructure. Google has multiple data centers across the world and employs advanced technologies such as load balancing and automatic failover to ensure that the system remains available even in case of disasters.
Finally, the front-end of the system is handled by Vercel, which is a well-established platform for hosting web applications. Vercel has a robust infrastructure that can handle large amounts of traffic and provides automatic scaling to handle any unexpected spikes in traffic. This means that even in case of disasters, the system is likely to remain available and accessible to users.
In conclusion, while disasters can pose a risk to any system, the current project has several mitigations in place to minimize the impact of these events and ensure that the system remains available and accessible to users even in case of disasters.
Bibliography
[1] StudyBuff. What Is a Discussion Forum? https://studybuff.com/what-is-a-discussion-forum/
[2] Disciple Media. Benefits of Forum. https://www.disciplemedia.com/building-your-community/benefits-of-forum/
[3] Short Fact. What is the purpose of discussion forums? https://short-fact.com/what-is-the-purpose-of-discussion-forums/
[4] Listen and Learn Research. Why Do People Use Forums? https://listenandlearnresearch.com/why-do-people-use-forums/
[5] OpenSource.com. Security, transparency, and open source: Understanding the value of audits. https://opensource.com/article/21/6/security-transparency
[6] Reputation Defender. Top Five Social Media Privacy Concerns. https://www.reputationdefender.com/blog/privacy/top-five-social-media-privacy-concerns
[7] FreeCodeCamp. How to Maintain an Open Source Project. https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-maintain-an-open-source-project/
[8] Javatpoint. Quora. https://www.javatpoint.com/quora
[9] Quora. Why is Quora's user interface not attractive as compared to that of Facebook? Are Facebook designers better? https://www.quora.com/
Why-is-Quoras-user-interface-not-attractive-as-compared-to-that-of-Facebook-Are-Facebook-designers-better [10] Quora. What data does Quora collect on me? How does Quora use my data? https://help.quora.com/hc/en-us/articles/360000839483-What-data-does-Quora-collect-on-me-How-does-Quora-use-my-data
[11] Sethi S, Sharma R. Social media and its role in medical research. J Educ Health Promot. 2019;8:47. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6428478/
[12] How-To Geek. What is Discord, and Is It Only for Gamers? https://www.howtogeek.com/659237/what-is-discord-and-is-it-only-for-gamers/
[13] Codecademy. What is Back End? https://www.codecademy.com/resources/blog/what-is-back-end/
[14] Cloudflare. Backend-as-a-Service (BaaS). https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/serverless/glossary/backend-as-a-service-baas/
[15] GeeksforGeeks. Firebase Introduction. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/firebase-introduction/
[16] Firebase. Products & Solutions. https://firebase.google.com/products-build
[17] Cloudflare. Backend-as-a-Service (BaaS). https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/serverless/glossary/backend-as-a-service-baas/
[18] Back4app. Firebase Advantages and Disadvantages. https://blog.back4app.com/firebase-advantages-and-disadvantages/
[19] DataVersity. NoSQL Databases: Advantages and Disadvantages. https://www.dataversity.net/nosql-databases-advantages-and-disadvantages/
[20] PythonBasics. What is Flask? https://pythonbasics.org/what-is-flask-python/
[21] PythonProgrammingLanguage. Python Flask Example. https://pythonprogramminglanguage.com/python-flask-example/
[22] Allwin Raju. Disadvantages of Flask. https://allwin-raju-12.medium.com/disadvantages-of-flask-95f1ff8f83bf
[23] Back4app. What are the Benefits of Backend-as-a-Service (BaaS)? https://blog.back4app.com/what-are-the-benefits-baas-backend-as-a-service/
[24] Clockwise Software. Choice between Mobile Backend-as-a-Service and Custom Backend. https://clockwise.software/blog/choice-between-mobile-backend-as-a-service-and-custom-backend/
[25] Supabase. Supabase vs Firebase. https://supabase.com/alternatives/supabase-vs-firebase
[26] Blog.LogRocket. Firebase vs Supabase: Choosing the Right Tool for Your Project. https://blog.logrocket.com/firebase-vs-supabase-choosing-right-tool-project/
[27] FreeCodeCamp. What is Front End? https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/what-is-front-end-development/
[28] Wikipedia. React (JavaScript library). https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/React_(JavaScript_library)
[29] C# Corner. What and Why ReactJS? https://www.c-sharpcorner.com/article/what-and-why-reactjs/
[30] Kinsta. React Components Library: A Comprehensive Guide. https://kinsta.com/blog/react-components-library/
[31] Koombea. React Pros and Cons: What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of ReactJS? https://www.koombea.com/blog/react-pros-and-cons-what-are-the-advantages-and-disadvantages-of-reactjs/
[32] WithLoveInternet. Chakra UI vs Material UI: A Comprehensive Comparison. https://withloveinternet.com/blog/chakra-ui-vs-material-ui-a-comprehensive-comparison
[33] SourceForge. Material-UI (MUI) Alternatives. https://sourceforge.net/software/product/Material-UI-MUI/alternatives
[34] Imaginary Cloud. Next.js vs React: What to Choose in 2021. https://www.imaginarycloud.com/blog/next-js-vs-react/
[35] Deepti Sharma. What Is State in React? https://medium.com/@deedee8/what-is-state-in-react-7e4ba938df23
[36] FreeCodeCamp. How to Manage State in Your React Apps. https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-manage-state-in-your-react-apps/
[37] FreeCodeCamp. How to Manage State in React. https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-manage-state-in-react/
[38] Blog.LogRocket. Pitfalls of Overusing React Context. https://blog.logrocket.com/pitfalls-of-overusing-react-context/
[39] tkDodo. React Query as a State Manager. https://tkdodo.eu/blog/react-query-as-a-state-manager/
[40] Rahul Phansen. React Context vs Recoil vs Hawk. https://medium.com/@rphansen91/react-context-vs-recoil-vs-hawk-dfe1be9e8372
[41] OpenReplay. Top 6 React State Management Libraries for 2022. https://blog.openreplay.com/top-6-react-state-management-libraries-for-2022/
[42] Kinsta. Svelte vs React: Which One to Choose in 2021? https://kinsta.com/blog/svelte-vs-react/
[43] Cmarix. React vs Svelte: A Comprehensive Comparison Between JavaScript Libraries. https://www.cmarix.com/blog/react-vs-svelte-a-comprehensive-comparison-between-javascript-libraries/
[44] Blog.LogRocket. SolidJS vs React: How Do They Compare? https://blog.logrocket.com/solidjs-vs-react/
[45] Fulcrum Rocks. Vue.js vs React: Which One to Choose in 2021? https://fulcrum.rocks/blog/vue-vs-react-comparison
[46] Trio. Angular vs React: Which Framework to Choose in 2021? https://www.trio.dev/blog/angular-vs-react
[47] Successive Technologies. Best Database for Web Applications in 2021. https://successive.tech/blog/best-database-for-web-applications/
[48] Oracle. What Is a Relational Database? https://www.oracle.com/uk/database/what-is-a-relational-database/
[49] Sage Answer. What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Relational Database? https://sage-answer.com/what-are-the-advantages-and-disadvantages-of-relational-database/
[50] Jelvix. Relational vs Non-Relational Database: What Is the Difference? https://jelvix.com/blog/relational-vs-non-relational-database
[51] Wikipedia. NoSQL. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NoSQL
[52] Dataversity. NoSQL Databases: Advantages and Disadvantages. https://www.dataversity.net/nosql-databases-advantages-and-disadvantages/
[53] TDWI. Data Modeling for NoSQL Improves Agile Development. https://tdwi.org/articles/2017/10/03/ba-all-data-modeling-for-nosql-improves-agile-development.aspx
[54] Indeed. What Is Project Management Methodology? https://sg.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/project-management-methodology
[55] Asana. What Is Agile Methodology? https://asana.com/resources/agile-methodology
[56] Educba. Advantages and Disadvantages of Agile Methodology. https://www.educba.com/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-agile-methodology/
[57] Forbes. What Is Waterfall Methodology? https://www.forbes.com/advisor/business/what-is-waterfall-methodology/
[58] IBM. What Is Software Testing? https://www.ibm.com/topics/software-testing
[59] Geekflare. A Guide to Unit Testing. https://geekflare.com/unit-testing-guide/
[60] PythonPool. Python Unittest vs Pytest: A Comparison. https://www.pythonpool.com/python-unittest-vs-pytest/
[61] Ricardo Cruz. Why I’m Moving from Jest to Vite — Part 1. https://dev.to/rstacruz/why-im-moving-from-jest-to-vitest-27d7
[62] MarvelApp. The Importance of User Testing in Design. https://marvelapp.com/blog/importance-user-testing/
[63] Microsoft Learn. What Is Version Control? https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/devops/develop/git/what-is-version-control
[64] Atlassian. Why Git? https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/why-git
[65] Atlassian. Using Branches in Git. https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/using-branches
[66] Atlassian. Git Tag. https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/inspecting-a-repository/git-tag
[67] Atlassian. Comparing Workflows. https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/comparing-workflows
[68] Git. Git Basics - Working with Remotes. https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Git-Basics-Working-with-Remotes
[69] Indeed. What Is Code Quality? https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/what-is-code-quality
[70] MakeUseOf. What Is Linting and How to Use It to Write Better Code. https://www.makeuseof.com/what-is-linting/
[71] Real Python. How to Write High-Quality Python Code With Automated Testing and Linting. https://realpython.com/python-code-quality/
[72] SitePoint. A Comparison of JavaScript Linting Tools. https://www.sitepoint.com/comparison-javascript-linting-tools/
[73] FreeCodeCamp. Software Design. https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/software-design/
[74] Wikipedia. Code Refactoring. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Code_refactoring
[75] CodeDam. How to Create Effective Code Documentation in Software Development. https://codedamn.com/news/uncategorized/how-to-create-effective-code-documentation-in-software-development
[76] Shvets, Alexander. Dive Into Design Patterns. https://refactoring.guru/design-patterns/book
[77] GitLab. Issues. https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/project/issues/
[78] GitLab. Milestones. https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/project/milestones/
[79] Hostinger. What Is Web Hosting? https://www.hostinger.com/tutorials/what-is-web-hosting/
[80] Elementor. Types of Web Hosting: Which One Is Right for You? https://elementor.com/blog/types-of-web-hosting/
[81] Vercel. Documentation. https://vercel.com/docs
[82] Better Programming. Compound Component Design Pattern in React. https://betterprogramming.pub/compound-component-design-pattern-in-react-34b50e32dea0
[83] Developer Way. Higher-Order Components in React: The Hooks Era. https://www.developerway.com/posts/higher-order-components-in-react-hooks-era
[84] FreeCodeCamp. How to Use Flux in React: An Example. https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-use-flux-in-react-example/
[85] BMC. ACID: Atomic, Consistent, Isolated, Durable. https://www.bmc.com/blogs/acid-atomic-consistent-isolated-durable/
[86] GeeksForGeeks. Functional Dependency. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/functional-dependency/
[87] GeeksForGeeks. Second Normal Form (2NF). https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/second-normal-form-2nf/
[88] GeeksForGeeks. Third Normal Form (3NF). https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/third-normal-form-3nf/
[89] TechRepublic. How Weak Passwords Could Put Your Organization at Risk. https://www.techrepublic.com/article/how-weak-passwords-could-put-your-organization-at-risk/
[90] BBC News. Equifax Data Breach: What You Need to Know. https://www.bbc.com/news/business-41493494
[91] The Data Privacy Group. Data Breach: The Legal Implications. https://thedataprivacygroup.com/blog/2019-9-17-data-breach-the-legal-implications/
[92] Brightjourney. Legal and Ethical Responsibility to Safely Store Passwords. http://www.brightjourney.com/q/legal-ethical-responsibility-safely-store-password
[93] One.com. What Can I Do to Enhance the Security of My One.com Account? https://help.one.com/hc/en-us/articles/4777447332625-What-can-I-do-to-enhance-the-security-of-my-one-com-account-
[94] How To Use Shadows And Blur Effects In Modern UI Design, https://www.smashingmagazine.com/2017/02/shadows-blur-effects-user-interface-design/
[95] Typography in UI Design: An Ultimate Guide for Beginners, https://www.mockplus.com/blog/post/typography-design-guide
[96] Responsive Design, https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/topics/responsive-design